华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (8): 119-127.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210805
所属专题: 2022年材料科学与技术
PEO基固态聚合物电解质膜的免溶剂熔融制备及性能
张桂珍,刘洋,严明保
- 华南理工大学 聚合物新型成型装备国家工程研究中心/聚合物成型加工工程教育部重点实验室/ 广东省高分子先进制造技术及装备重点实验室,广东 广州 510640
Preparation of PEO-Based Solid Polymer Electrolyte Membranes via Solvent-Free Melting and Properties of the Product
ZHANG Guizhen,LIU Yang,YAN Mingbao
- National Engineering Research Center for New Polymer Molding Equipment / Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Technique and Equipment for Macromolecular Advanced Manufacturing / Key Laboratory of Polymer Processing Engineering of the Ministry of Education,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
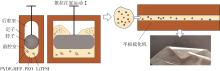
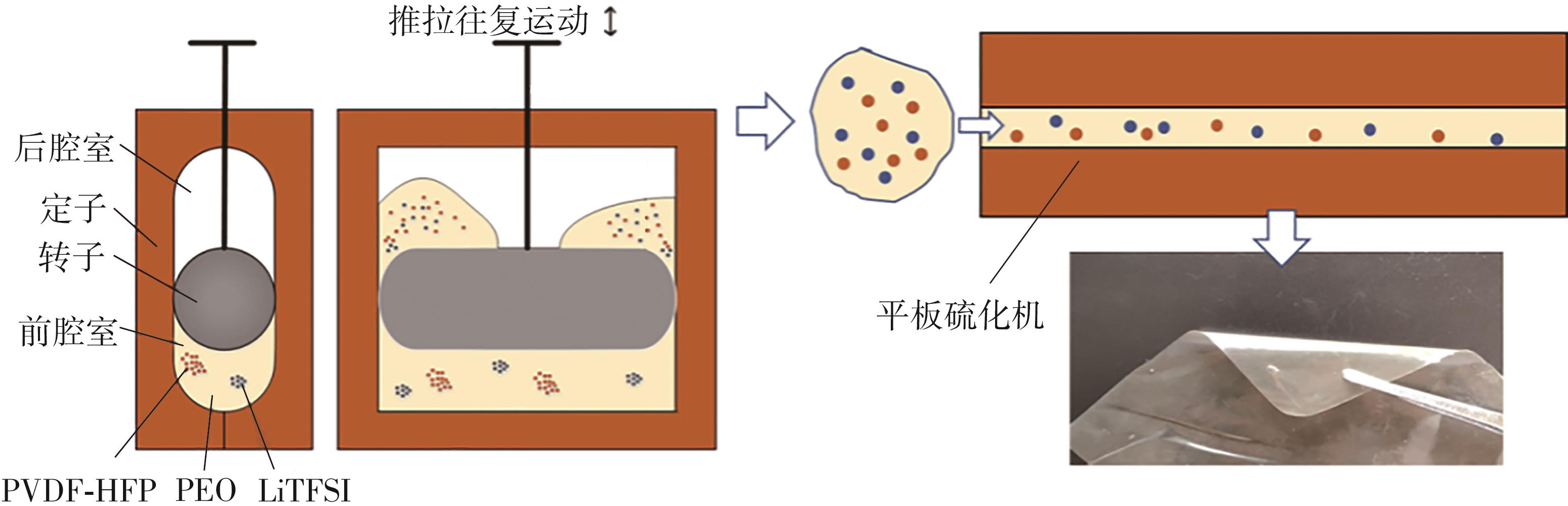
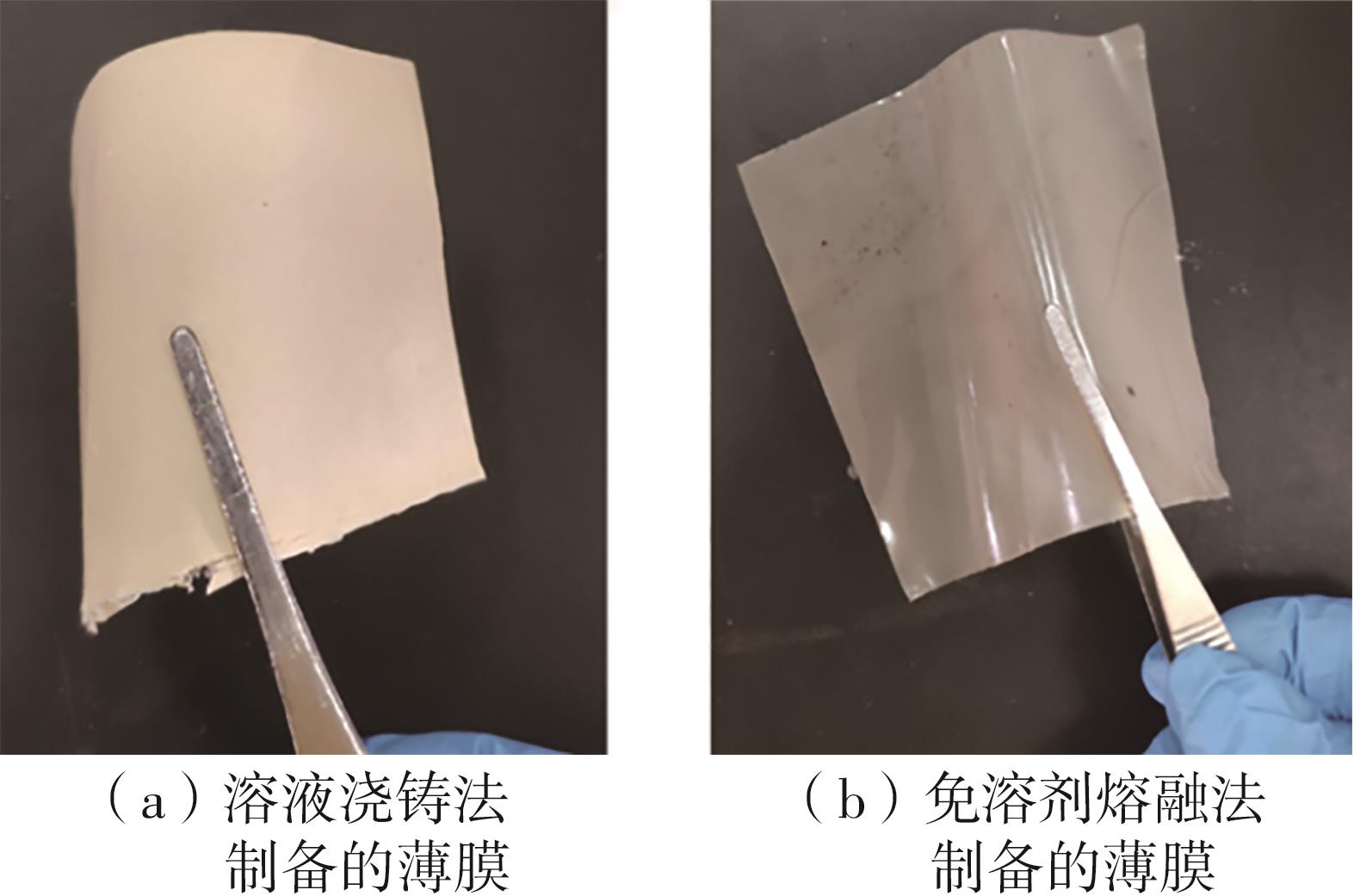
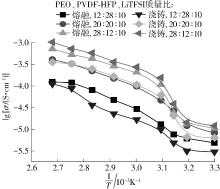
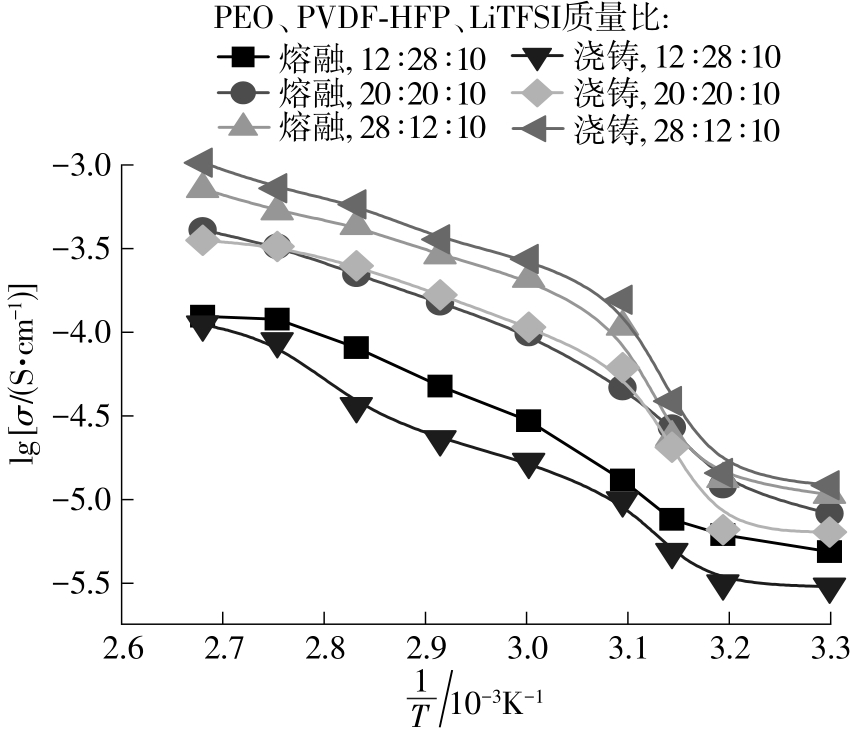
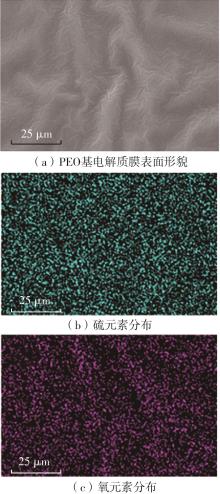
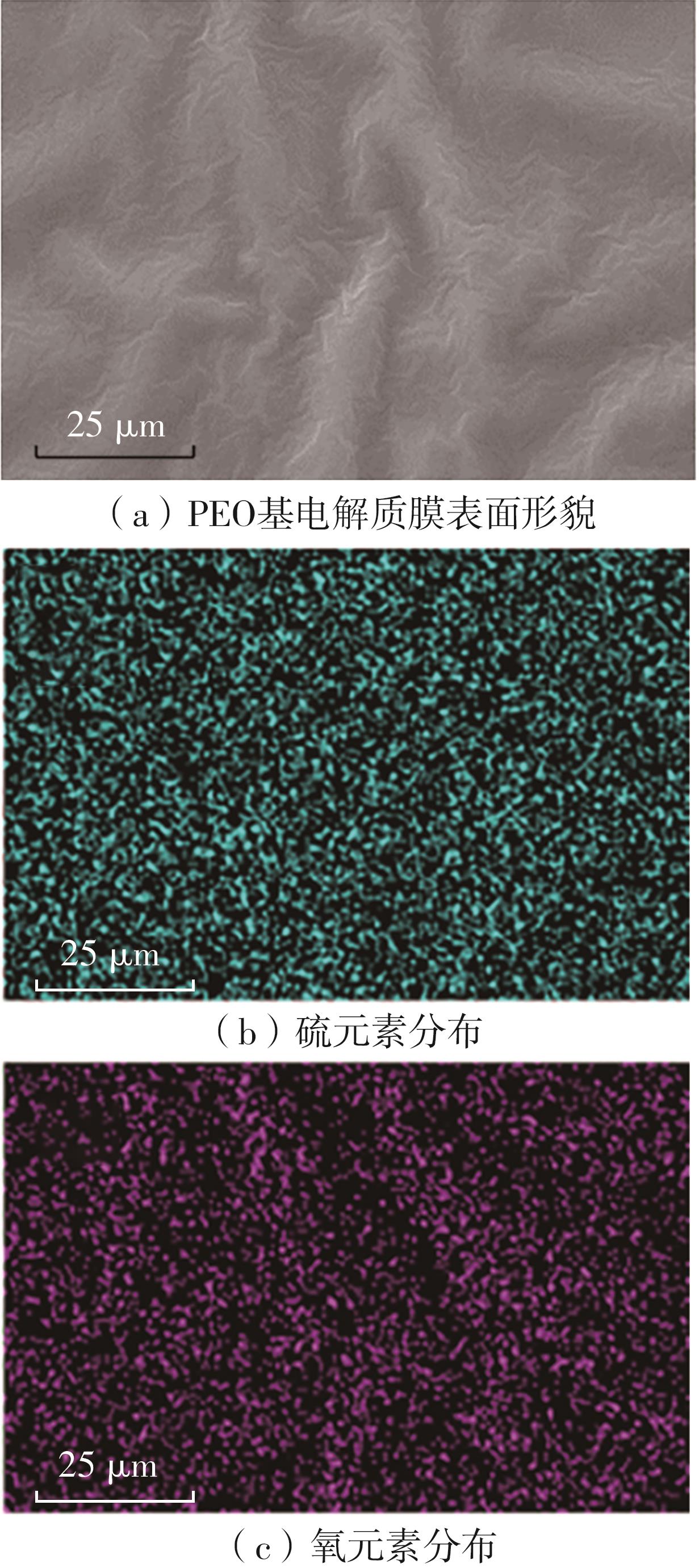
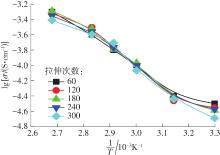
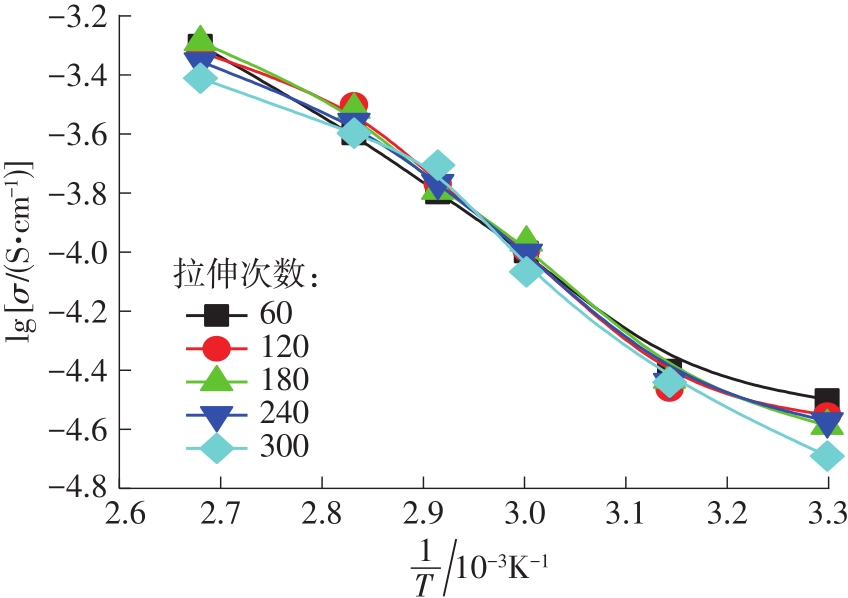
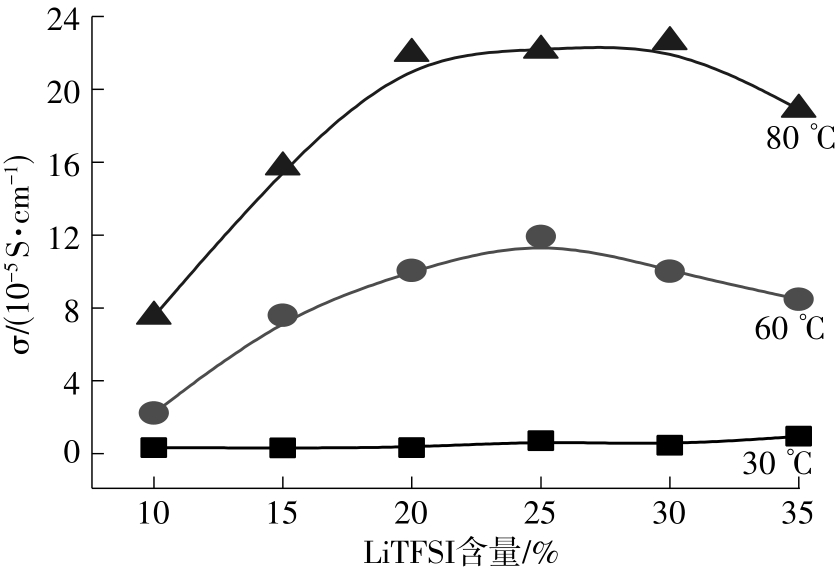
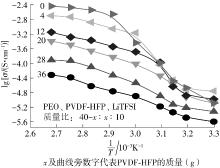
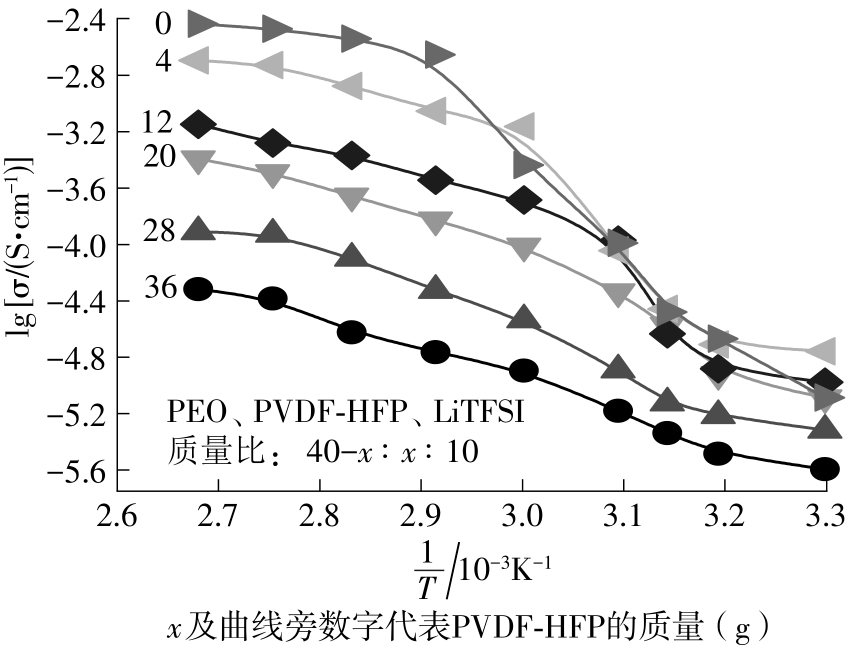
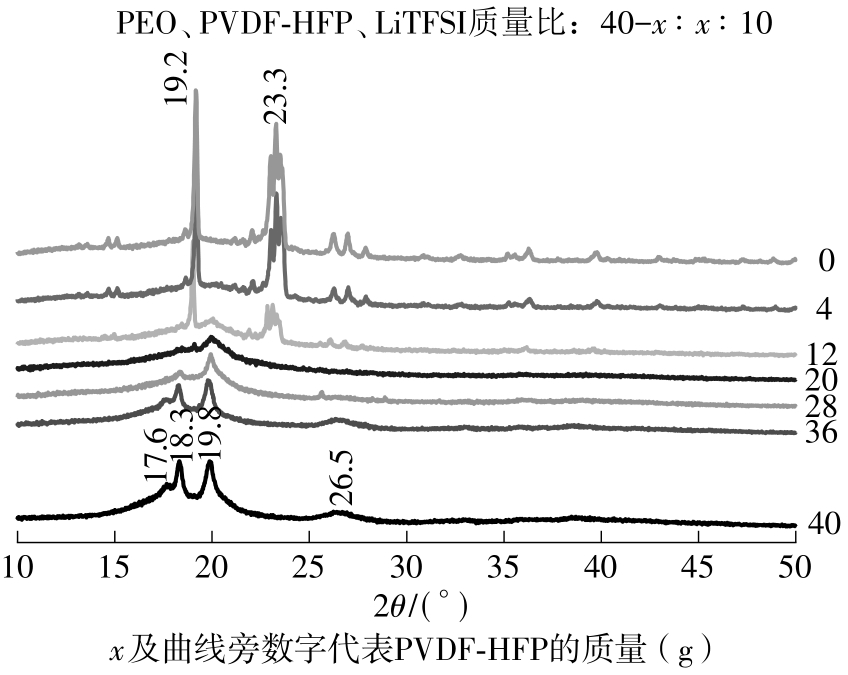
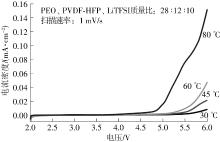
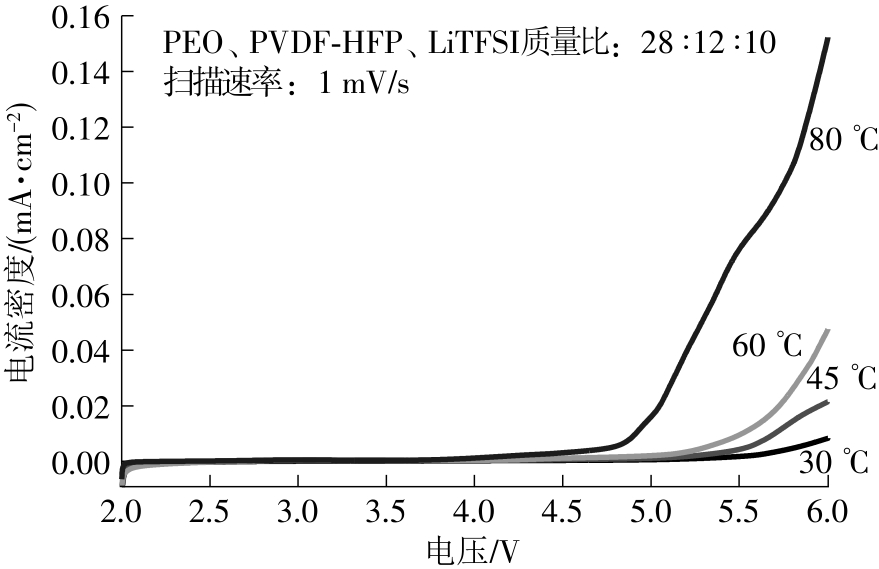
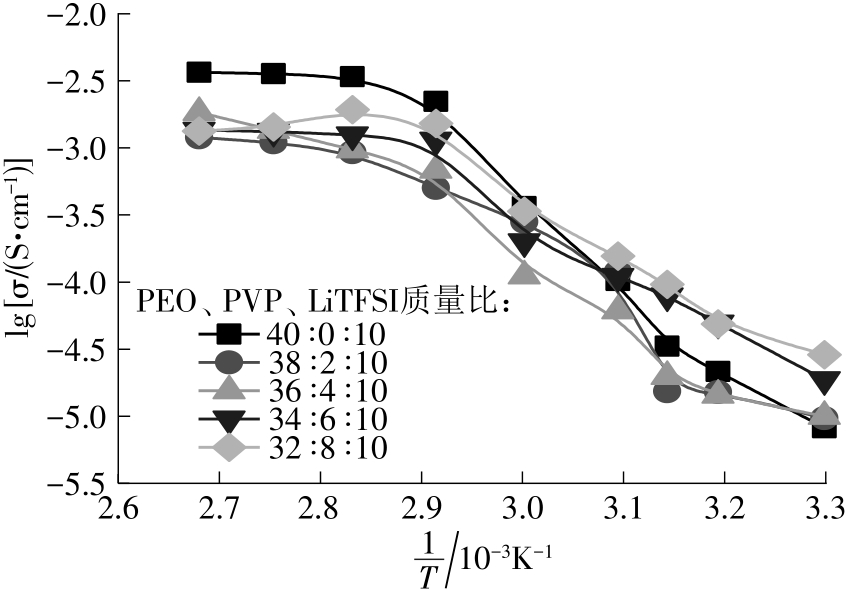
随着科学技术的进步,各种智能电子设备和电动车、电网体系迅速成长,人们对高能量密度和可充电电池系统的需求越来越大,锂离子电池也得到了长足的发展。目前市场上常用的锂离子电池由正负极、电解液和隔膜组成。由于电解液易挥发、泄露,因此电池容易发生短路甚至着火、爆炸等安全事故。固态电解质的出现很大程度上消除了这一安全隐患。固态电解质在电池中既能分隔正负极、防止内部短路,又能充当离子导体实现正负极活性物质之间的锂离子传递,已成为新能源领域的研究热点之一。目前固态电解质膜的制备方法主要包括有机溶剂浇铸、涂布和热模压等,这些方法普遍存在有机溶剂污染环境、制造周期长、成本高等问题。有鉴于此,文中提出了一种聚环氧乙烷(PEO)基复合固态电解质膜的拉伸应力诱导免溶剂熔融制备新方法,并采用SEM、XRD表征电解质膜的结晶形态和微观形貌,采用DSC表征膜的热性能,通过线性扫描伏安法、电导率测试来表征膜的电化学性能。结果表明,与简单的机械混合相比,采用文中提出的新方法制备的聚环氧乙烷/聚偏氟乙烯-六氟丙烯/双三氟甲磺酰亚胺锂(PEO/PVDF-HFP/LiTFSI)复合固态聚合物电解质膜的锂盐分散性更好。离子电导率测试结果表明:即便不使用有机溶剂,采用文中方法制备的复合固态聚合物电解质膜仍与采用溶液浇铸法制备的电解质膜的离子电导率相当;所加入的PVDF-HFP含量为30%时,PEO基固态聚合物电解质膜在60 ℃下的离子电导率达2.07×10-4 S/cm,电化学稳定窗口超过5.0 V。
中图分类号: