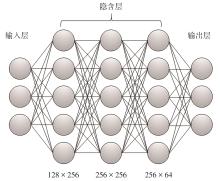
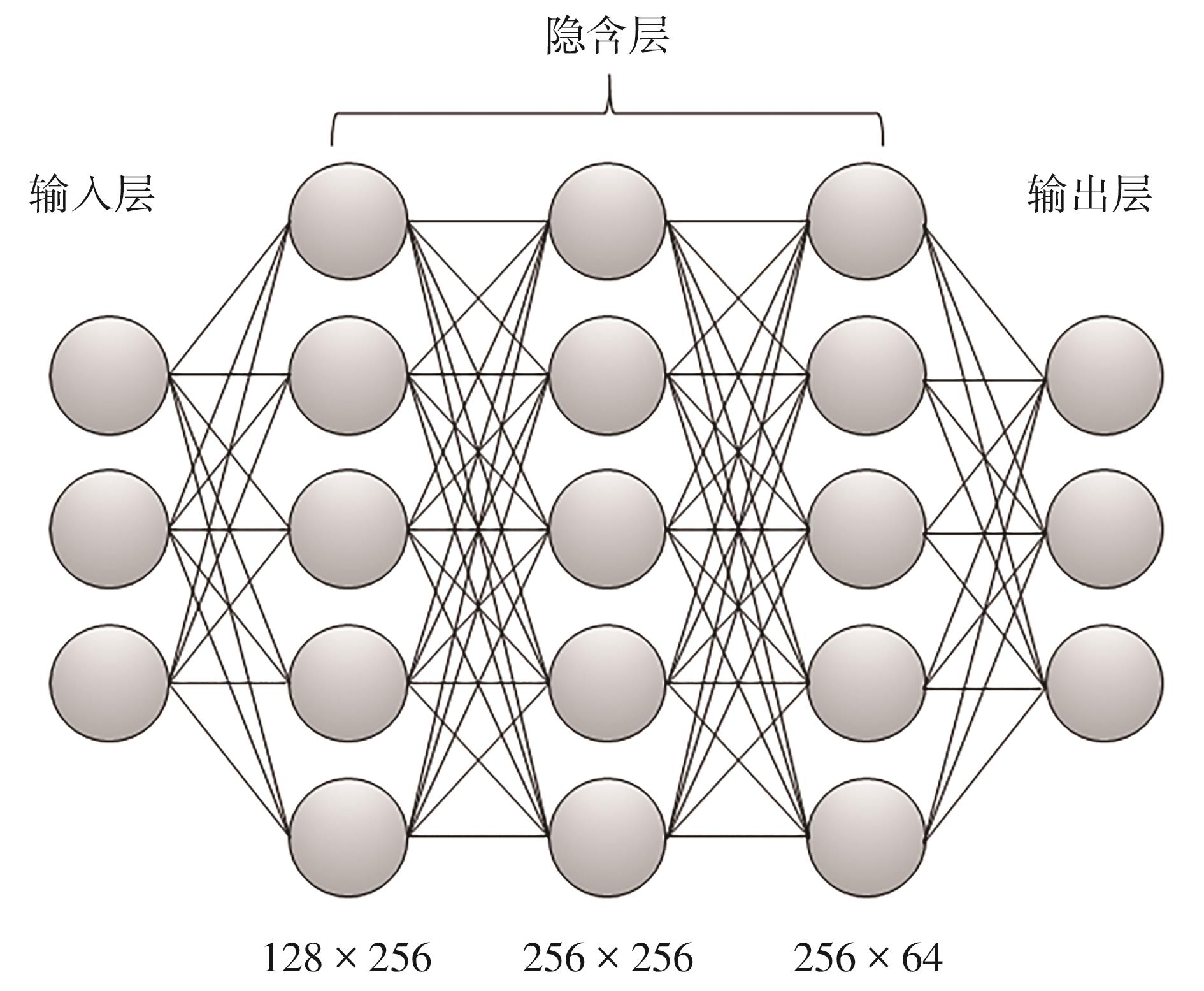
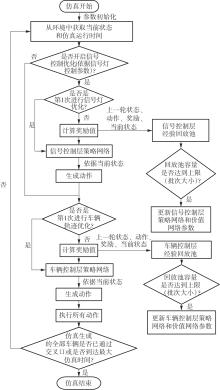
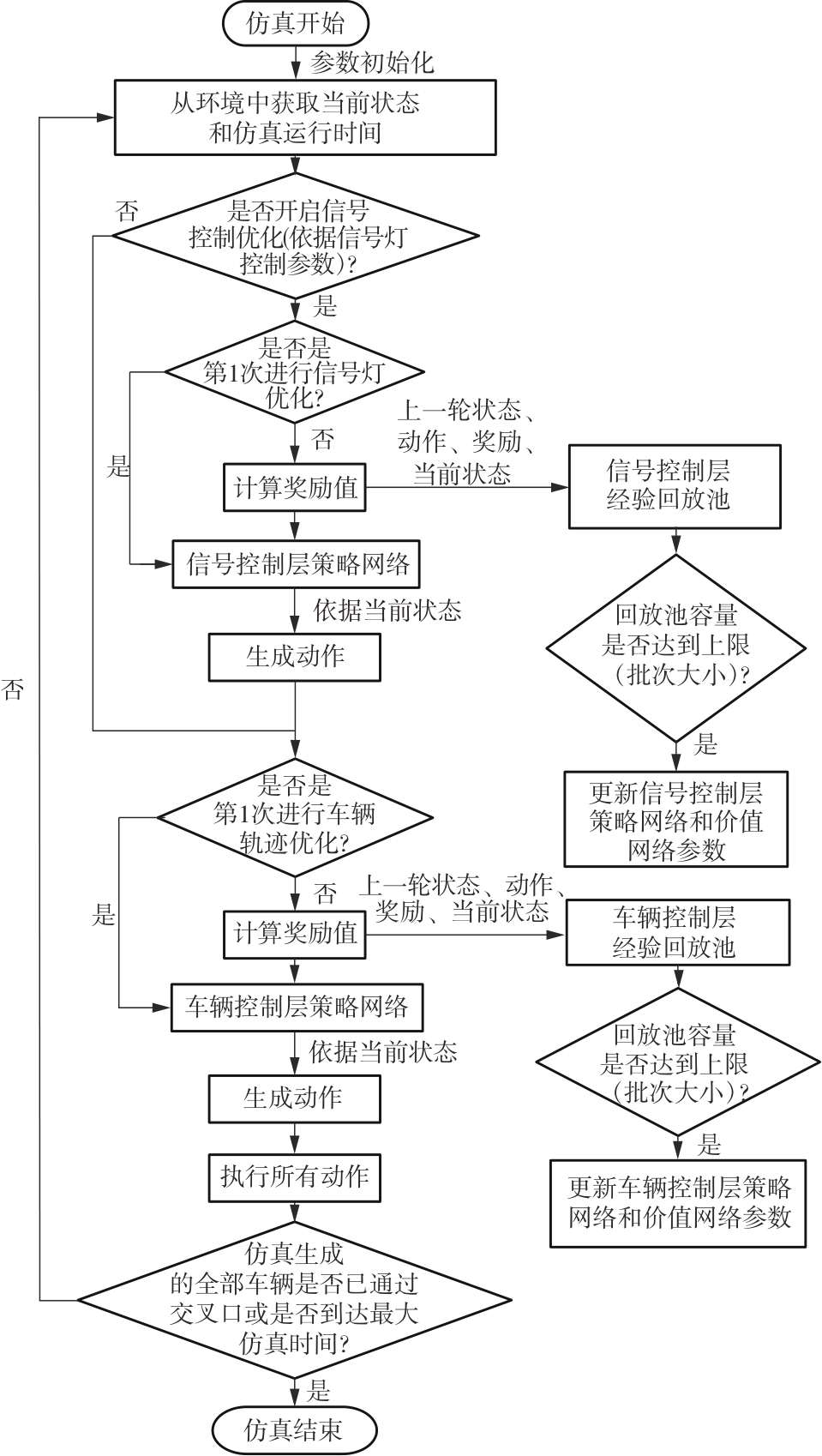
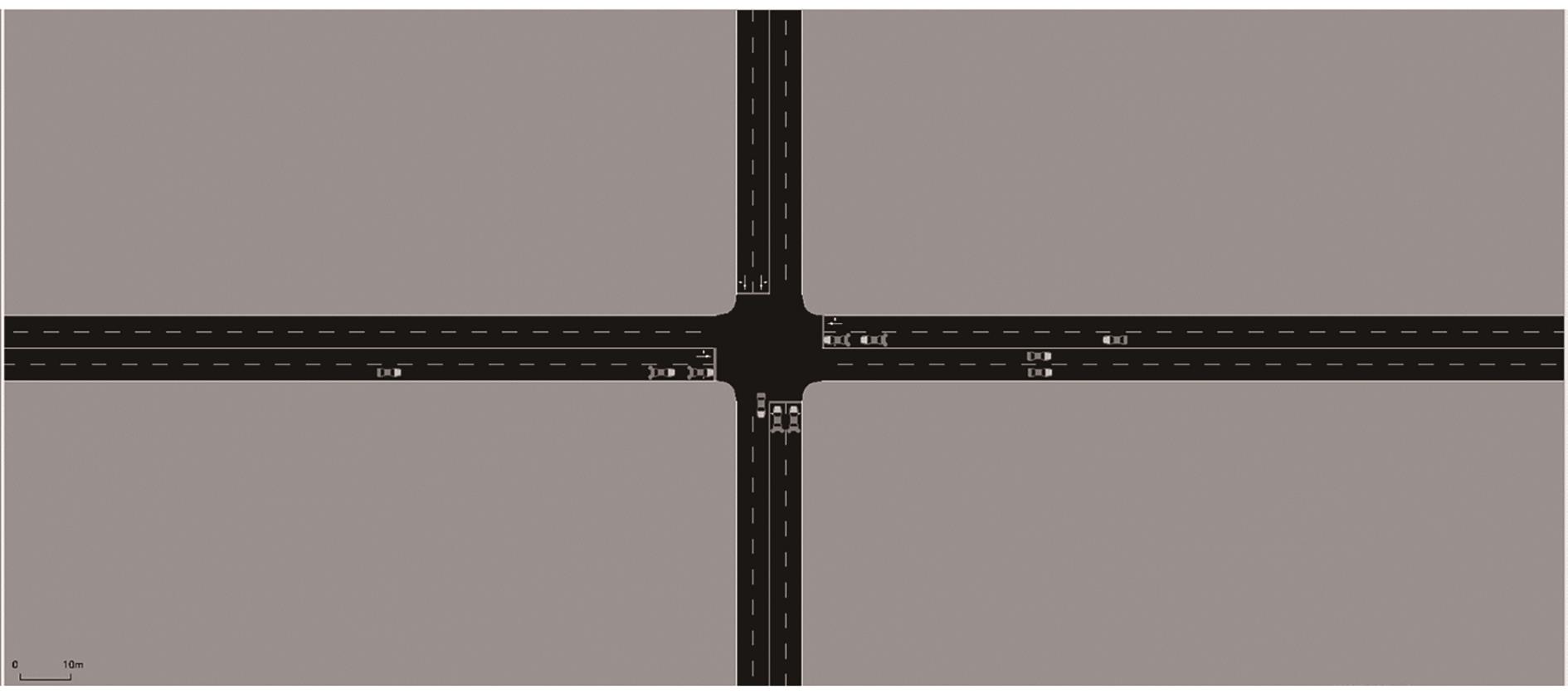
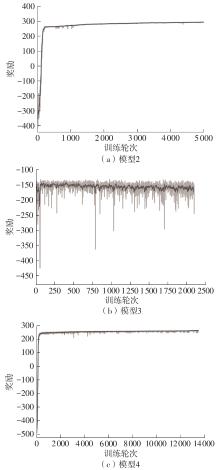
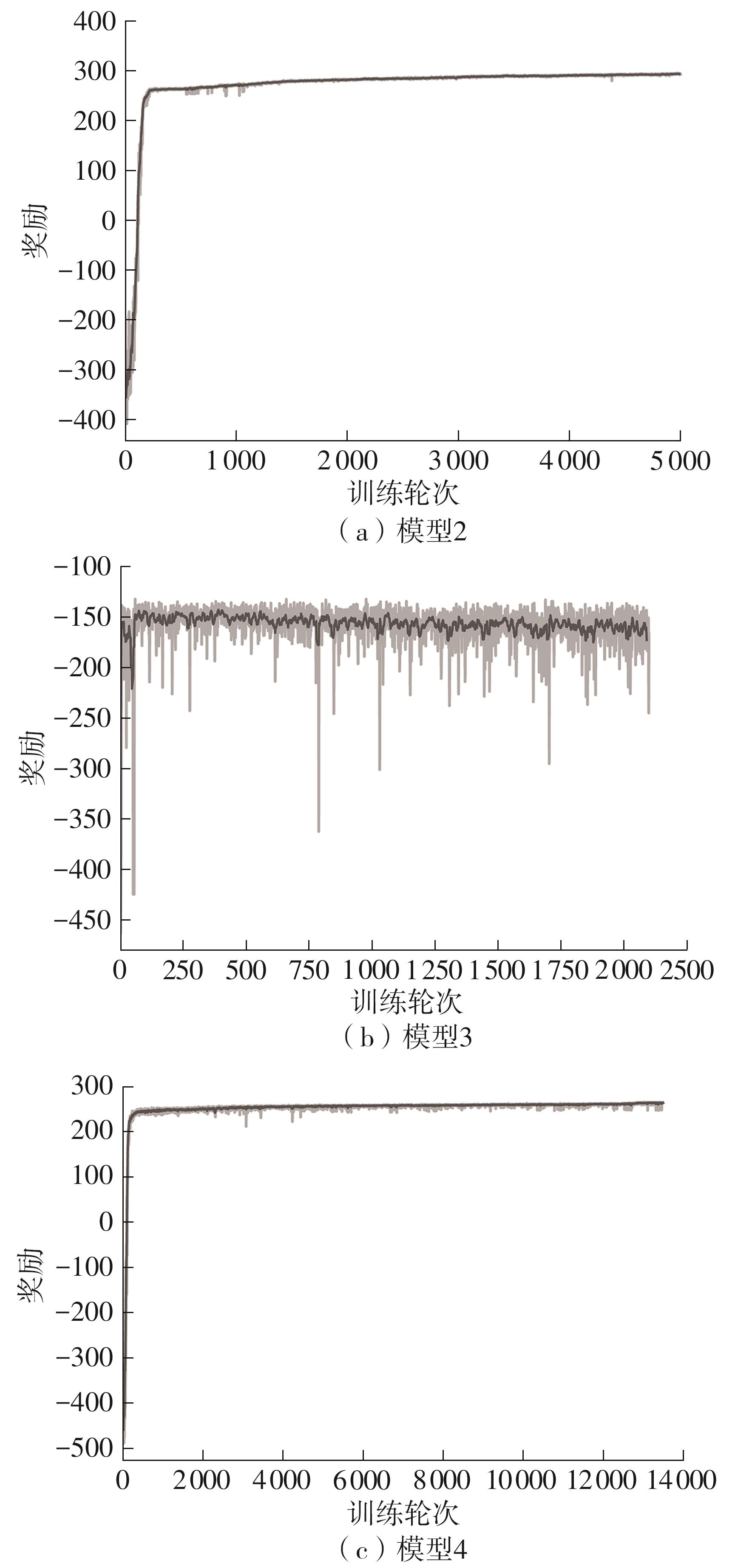
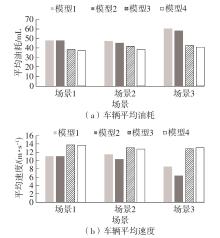
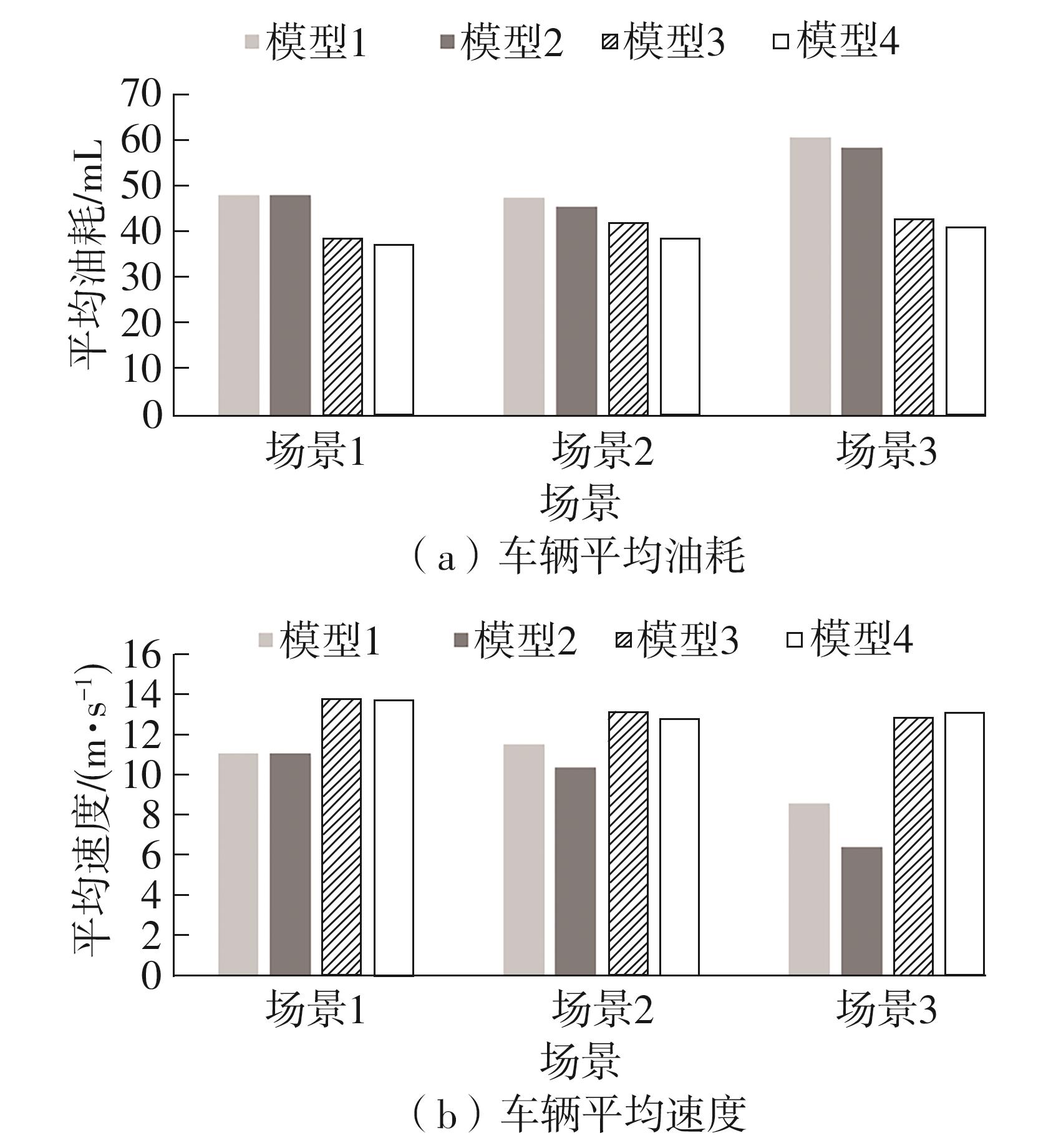
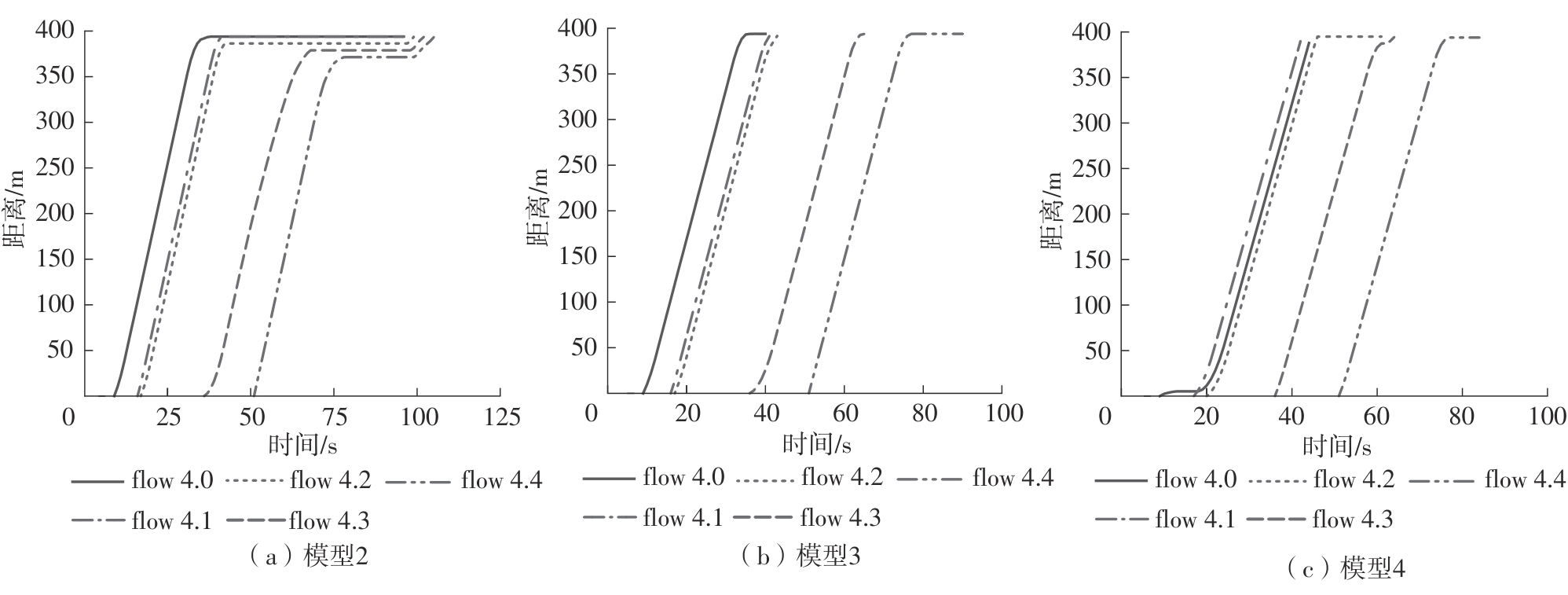
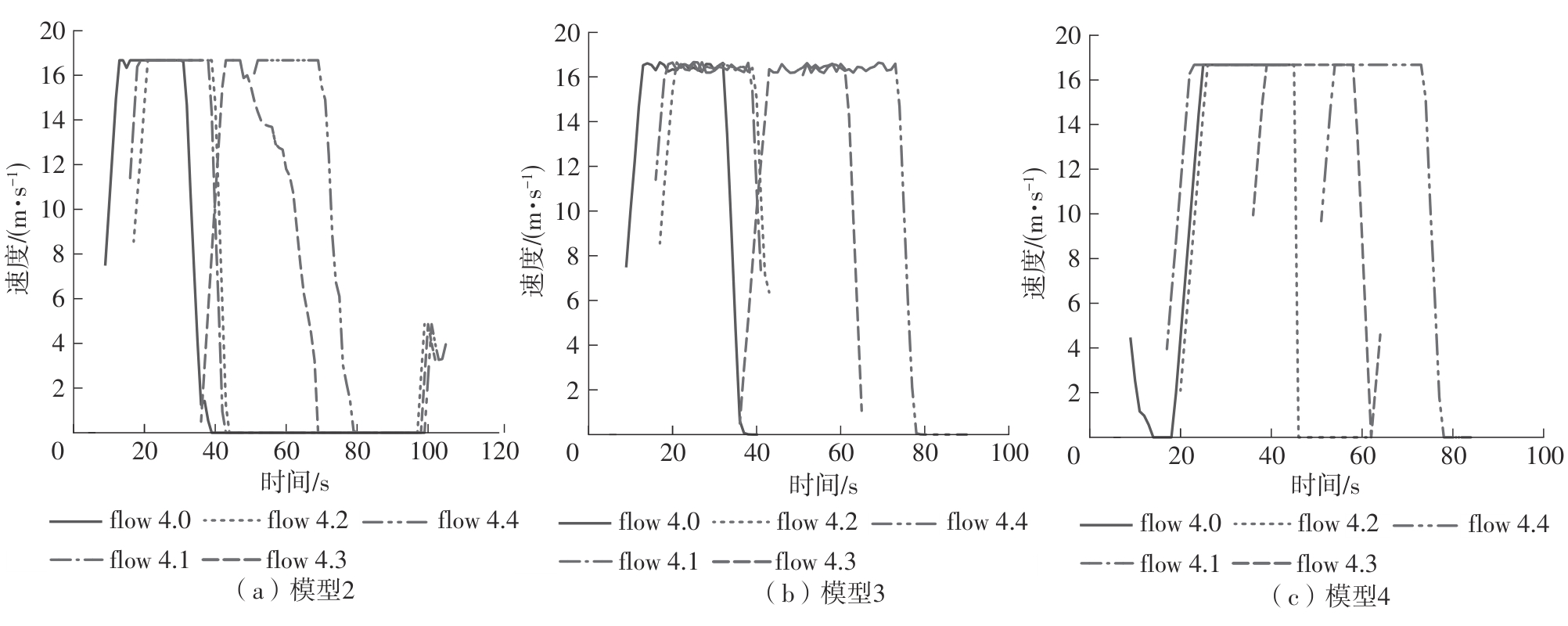
| [1] |
MA W J, WAN L, YU C,et al .Multi-objective optimization of traffic signals based on vehicle trajectory data at isolated intersections[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2020,120:102821/1-27.
|
| [2] |
LIANG X J, GULER S I, GAYAH V V .An equitable traffic signal control scheme at isolated signalized intersections using connected vehicle technology[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2020,110:81-97.
|
| [3] |
ZHANG Y, HAO R, ZHANG T,et al .A trajectory optimization-based intersection coordination framework for cooperative autonomous vehicles[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2021,23(9):14674-14688.
|
| [4] |
HAN X, MA R, ZHANG H M .Energy-aware trajectory optimization of CAV platoons through a signalized intersection[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emer-ging Technologies,2020,118:102652/1-16.
|
| [5] |
YAO H, CUI J, LI X,et al .A trajectory smoothing method at signalized intersection based on individualized variable speed limits with location optimization[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2018,62:456-473.
|
| [6] |
YAO H, LI X .Lane-change-aware connected automated vehicle trajectory optimization at a signalized intersection with multi-lane roads[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2021,129:103182/1-43.
|
| [7] |
MA M, LI Z .A time-independent trajectory optimization approach for connected and autonomous vehicles under reservation-based intersection control[J].Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives,2021,9:100312/1-11.
|
| [8] |
YU C, FENG Y, LIU H X,et al .Integrated optimization of traffic signals and vehicle trajectories at isolated urban intersections[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2018,112:89-112.
|
| [9] |
GUO Y, MA J, XIONG C,et al .Joint optimization of vehicle trajectories and intersection controllers with connected automated vehicles:combined dynamic programming and shooting heuristic approach[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2019,98:54-72.
|
| [10] |
JIANG X, SHANG Q .A dynamic CAV-dedicated lane allocation method with the joint optimization of signal timing parameters and smooth trajectory in a mixed traffic environment[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2022,24(6):6436-6449.
|
| [11] |
TAJALLI M, HAJBABAIE A .Traffic signal timing and trajectory optimization in a mixed autonomy traffic stream[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2021,23(7):6525-6538.
|
| [12] |
GUAN Y, REN Y, MA H,et al .Learn collision-free self-driving skills at urban intersections with model-based reinforcement learning[C]∥ Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC).Indianapolis,IN:IEEE,2021:3462-3469.
|
| [13] |
GUTIÉRREZ-MORENO R, BAREA R, LÓPEZ-GUILLÉN E,et al .Reinforcement learning-based autonomous driving at intersections in CARLA simulator[J].Sensors,2022,22(21):8373/1-16.
|
| [14] |
SILVA V A S, GRASSI V .Addressing lane keeping and intersections using deep conditional reinforcement learning[C]∥ Proceedings of the 2021 Latin American Robotics Symposium (LARS),2021 Brazilian Symposium on Robotics (SBR),and 2021 Workshop on Robotics in Education (WRE).Natal:IEEE,2021:330-335.
|
| [15] |
REN Y, JIANG J, ZHAN G,et al .Self-learned intelligence for integrated decision and control of automated vehicles at signalized intersections[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2022,23(12):24145-24156.
|
| [16] |
BERNHARD J, POLLOK S, KNOLL A .Addressing inherent uncertainty:risk-sensitive behavior generation for automated driving using distributional reinforcement learning[C]∥ Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ).Paris:IEEE,2019:2148-2155.
|
| [17] |
BORGES D F, LEITE J P R R, MOREIRA E M,et al .Traffic light control using hierarchical reinforcement learning and options framework[J].IEEE Access,2021,9:99155-99165.
|
| [18] |
LIANG X, DU X, WANG G,et al .A deep reinforcement learning network for traffic light cycle control [J].IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,2019,68(2):1243-1253.
|
| [19] |
MO Z, LI W, FU Y,et al .CVLight:decentralized learning for adaptive traffic signal control with connected vehicles[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2022,141:103728/1-9.
|
| [20] |
YANG S, YANG B, KANG Z,et al .IHG-MA:inductive heterogeneous graph multi-agent reinforcement learning for multi-intersection traffic signal control [J].Neural Networks,2021,139:265-277.
|
| [21] |
ZHANG Y, ZHOU Y, LU H,et al .Cooperative multi-agent actor-critic control of traffic network flow based on edge computing[J].Future Generation Computer Systems,2021,123:128-141.
|
| [22] |
ABDOOS M, BAZZAN A L C .Hierarchical traffic signal optimization using reinforcement learning and traffic prediction with long-short term memory[J].Expert Systems with Applications,2021,171:114580/1-9.
|
| [23] |
LEE J, CHUNG J, SOHN K .Reinforcement learning for joint control of traffic signals in a transportation network[J].IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Techno-logy,2020,69(2):1375-1387.
|
| [24] |
GUO Y, MA J .DRL-TP3:a learning and control framework for signalized intersections with mixed connected automated traffic[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2021,132:103416/1-54.
|
| [25] |
DUAN J, EBEN LI S, GUAN Y,et al .Hierarchical reinforcement learning for self‐driving decision‐making without reliance on labelled driving data[J].IET Intelligent Transport Systems,2020,14(5):297-305.
|
| [26] |
LIAO J, LIU T, TANG X,et al .Decision-making strategy on highway for autonomous vehicles using deep reinforcement learning[J].IEEE Access,2020,8:177804-177814.
|
| [27] |
de JESUS J C, KICH V A, KOLLING A H,et al .Soft actor-critic for navigation of mobile robots[J].Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems,2021,102(2):1-31.
|
| [28] |
HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, HARTIKAINEN K,et al .Soft actor-critic algorithms and applications[EB/OL].(2019-01-29)[2024-11-18]..
|
| [29] |
WONG C C, CHIEN S Y, FENG H M,et al .Motion planning for dual-arm robot based on soft actor-critic[J].IEEE Access,2021,9:26871-26885.
|
| [30] |
HE Z, DONG L, SONG C,et al .Multiagent soft actor-critic based hybrid motion planner for mobile robots[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2022,34(12):10980-10992.
|
| [31] |
TANG H, WANG A, XUE F,et al .A novel hierarchical soft actor-critic algorithm for multi-logistics robots task allocation[J].IEEE Access,2021,9:42568-42582.
|
| [32] |
KRAUSS S .Microscopic modeling of traffic flow:investigation of collision-free vehicle dynamics[D].Köln:DLR,1998.
|
| [33] |
KRAUSS S, WAGNER P, GAWRON C .Metastable states in a microscopic model of traffic flow[J].Physical Review E,1997,55(5):5597/1-6.
|
| [34] |
VINITSKY E, KREIDIEH A, LE FLEM L,et al .Benchmarks for reinforcement learning in mixed-autonomy traffic[C]∥ Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning.Zürich:PMLR,2018:399-409.
|