华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 91-97.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220295
所属专题: 2023年电子、通信与自动控制
基于直扩超声波宽带人体通信多点接入的自适应速率调整
刘娇蛟 陈阿粤 马碧云
- 华南理工大学 电子与信息学院,广东 广州 510640
Rate Adaptation in Multiple Access Based on DS-UsWB Body Communication
LIU Jiaojiao CHEN Ayue MA Biyun
- School of Electronic and Information Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
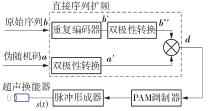
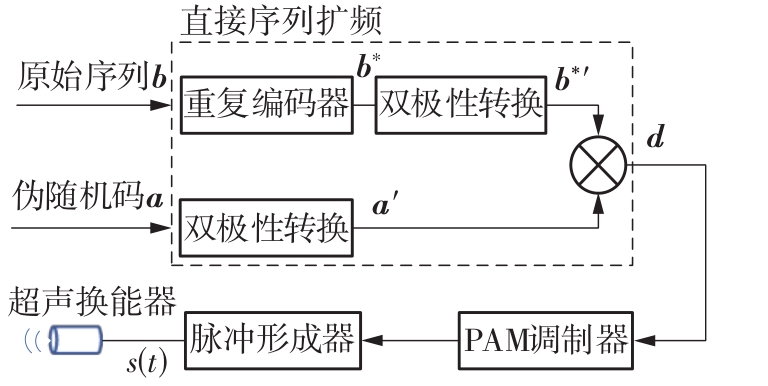
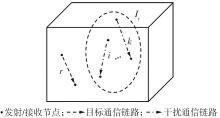
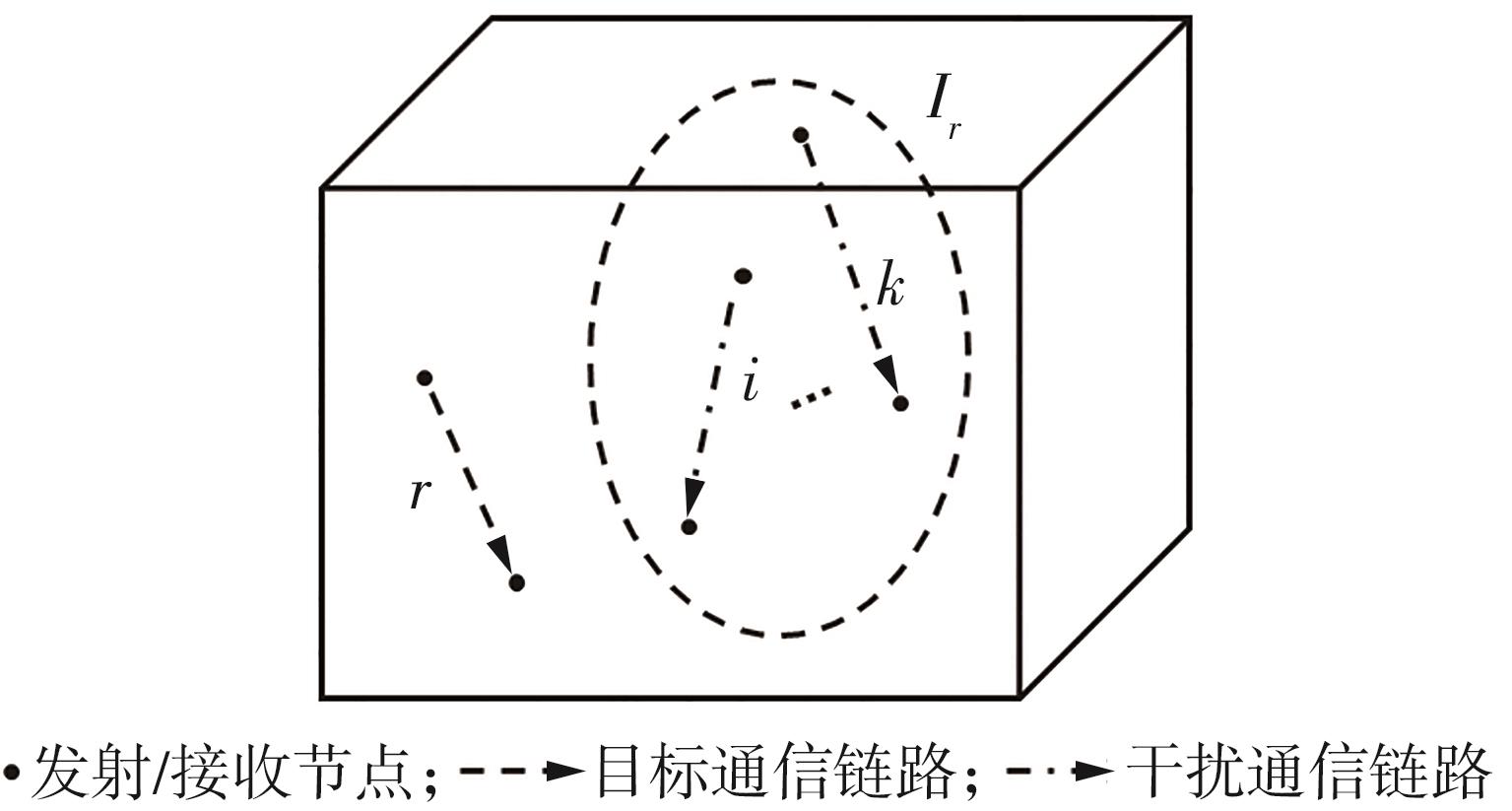
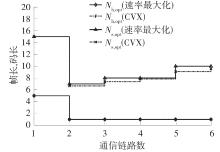
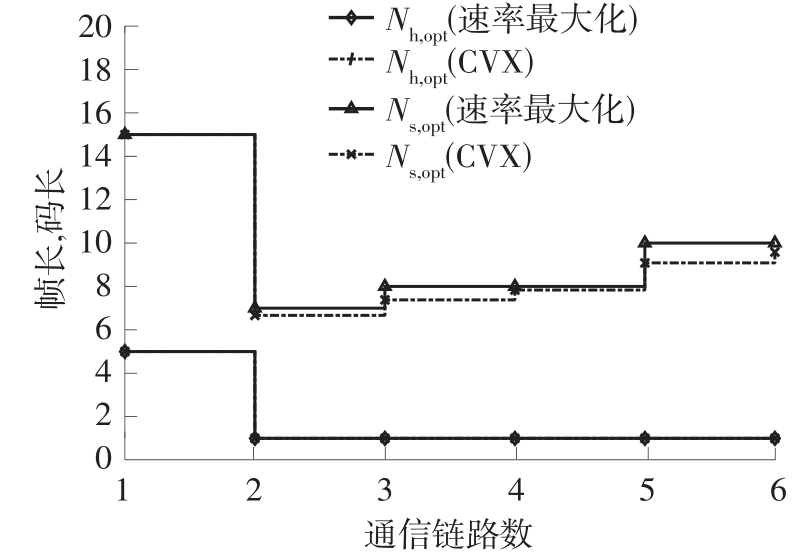
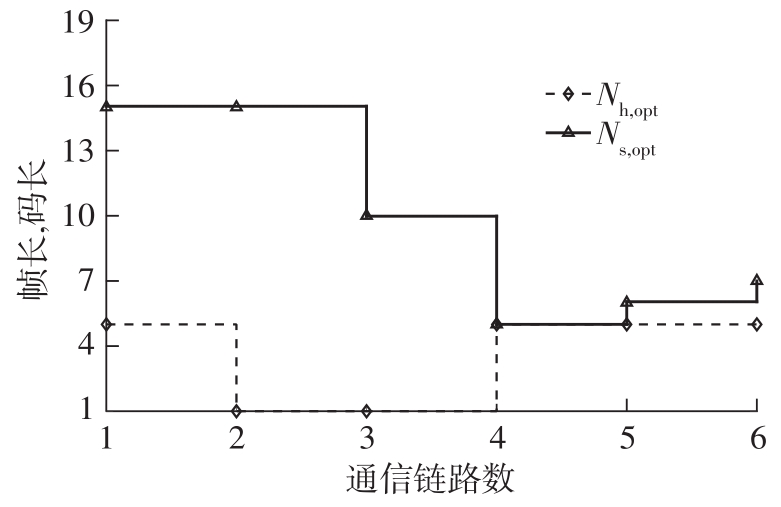
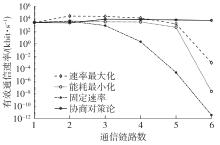
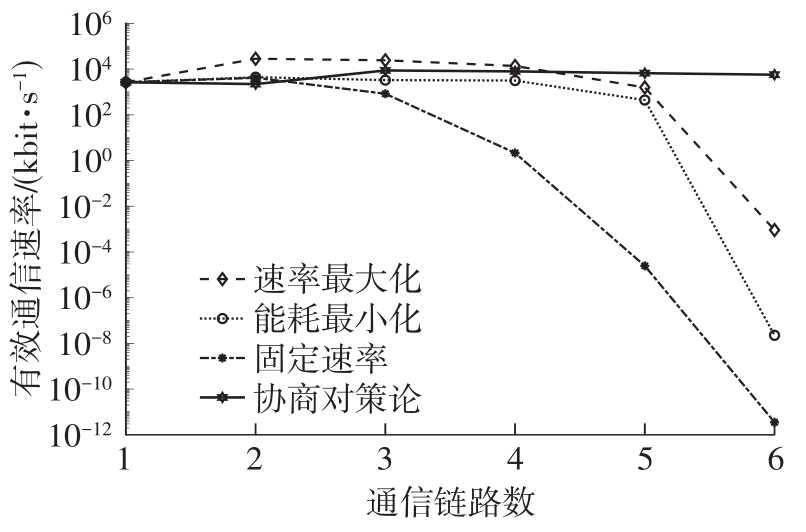
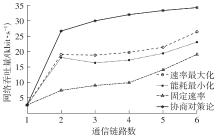
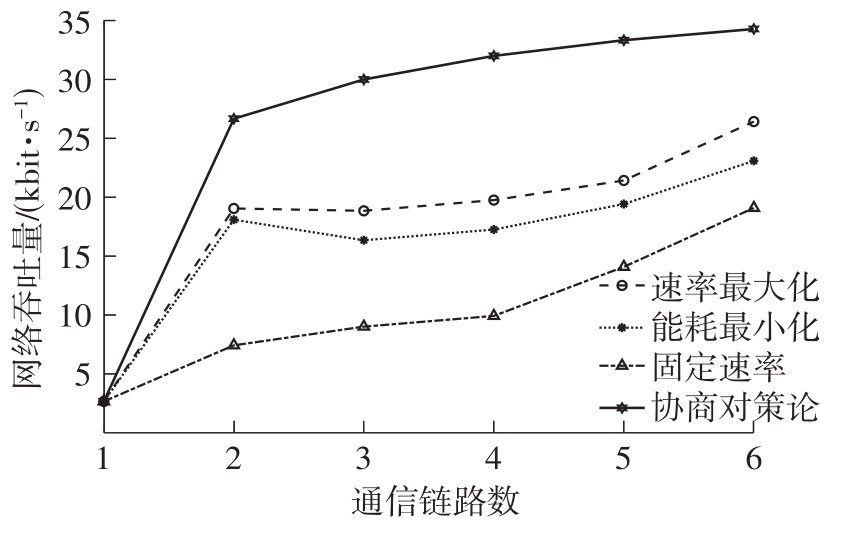
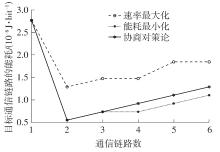
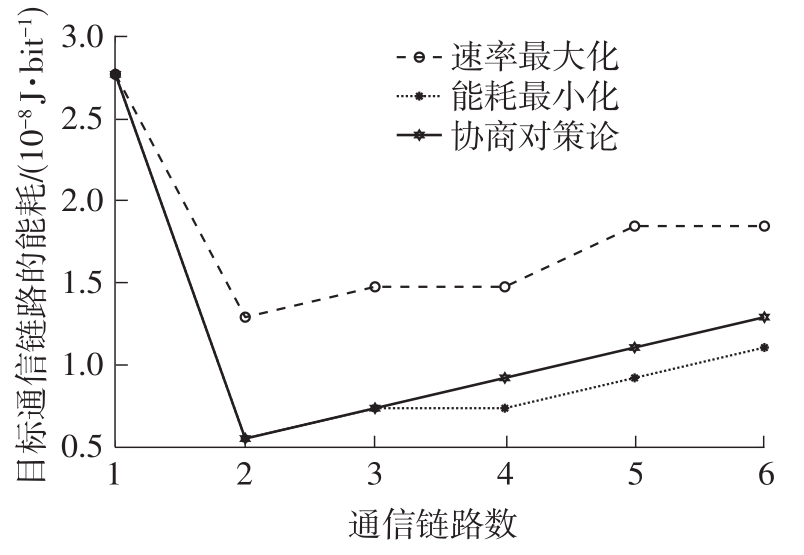
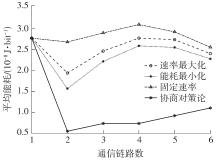
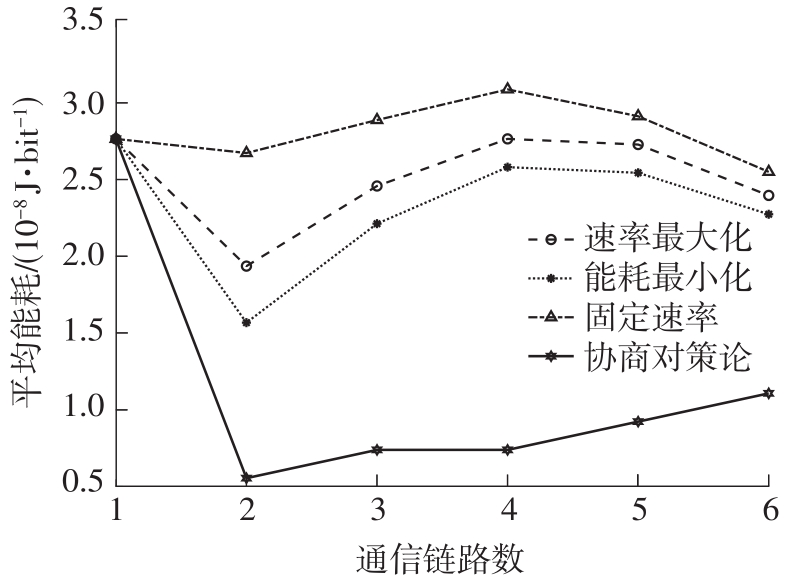
体域网是远程医疗和健康监护的重要环节,现有研究多采用电磁波传输。相比之下,人体软组织中超声波传播衰减小,产生的热量少,比电磁波传输距离远且致病风险低,利用超声波实现人体范围的通信和组网具有一定优势。现有的超声波宽带通信多采用超短脉冲减少多径交叠及其带来的干扰,结合直接序列扩频技术可以共享信道实现多点接入。但是,增加通信数量带来的干扰使目标通信链路接收节点的信噪比降低,采用固定帧长与码长无法保证通信可靠性。文中针对多点接入的场景,对节点的通信速率进行数学建模,研究竞争与合作两种场景下的自适应速率调整方法,利用凸优化理论的拉格朗日乘数法推导了帧长和码长的闭式解,在多点通信中动态改变帧长和码长实现速率调整。仿真结果表明,文中方法随着通信链路数及其干扰变化可实现自适应速率调整,其中,基于协商对策论的合作方案可以平衡不同节点的通信速率,获得更好的网络性能,基于速率最大的竞争方案有助于提高目标通信链路的有效通信速率,实际应用中需根据应用场景进行选择。
中图分类号: