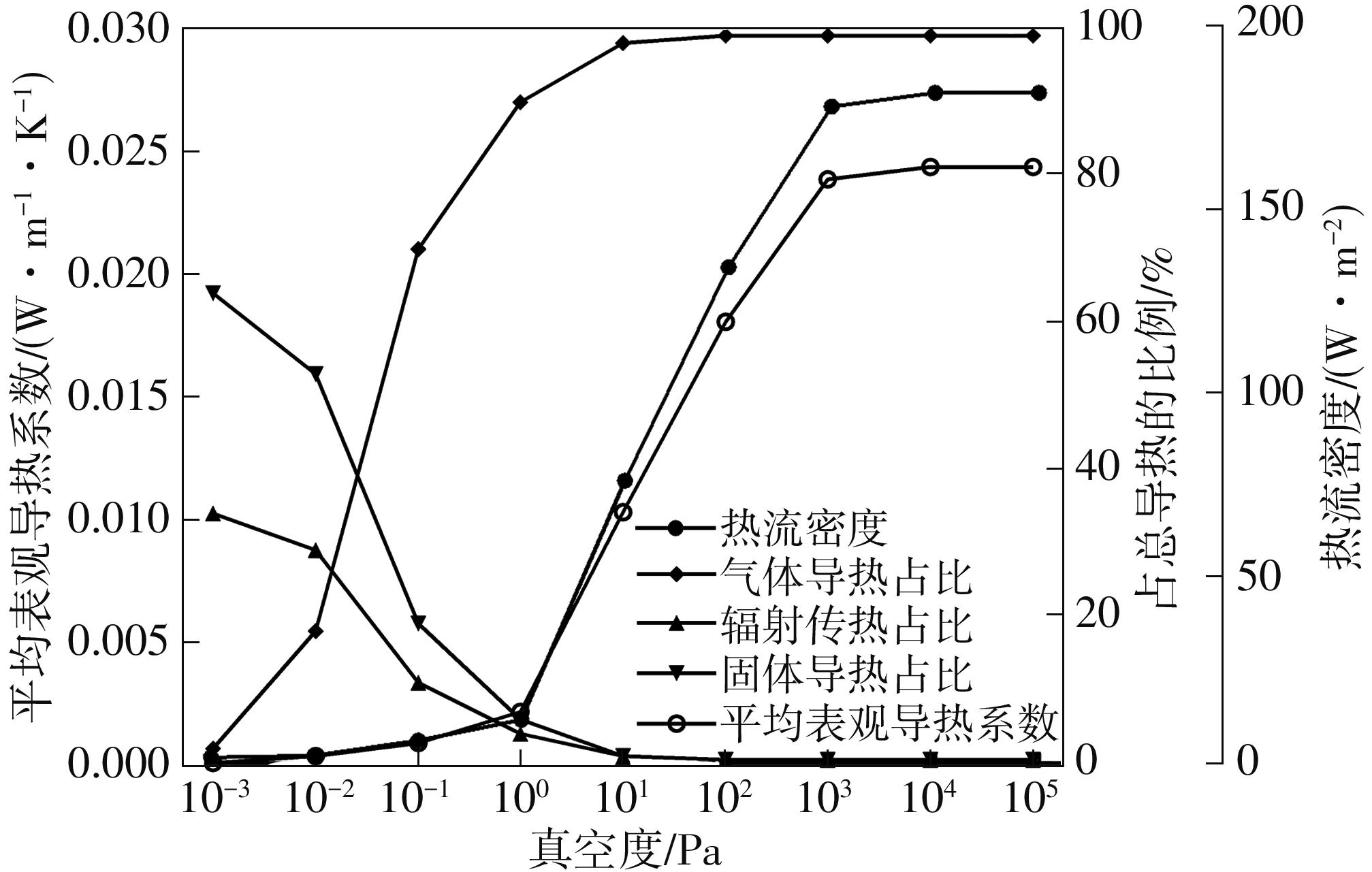
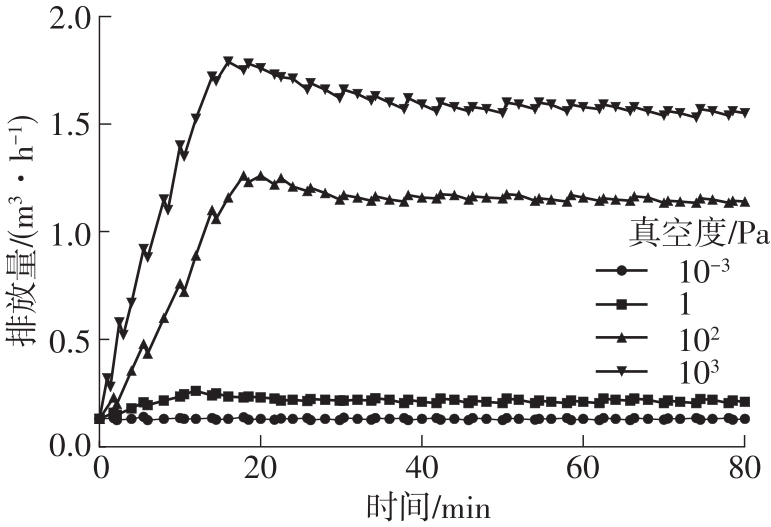
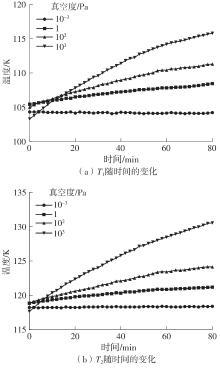
| 1 |
周伟明,陈朝晖,魏蔚 .深冷真空绝热容器标准技术发展与展望[J].压力容器,2013,30(2):1-14.
|
|
ZHOU Weiming, CHEN Zhaohui, WEI Wei .Standard technical development and prospect of cryogenic vacuum adiabatic vessel[J].Pressure Vessel Technology,2013,30(2):1-14.
|
| 2 |
周伟明 .低温液体运输装备行业现状与发展对策[J].专用汽车,2004,21(2):41-44.
|
|
ZHOU Weiming .State of the art of transportable equipment for cryogen and relative countermeasures[J].Special Purpose Vehicle,2004,21(2):41-44.
|
| 3 |
王武昌,李玉星,孙法峰,等 .大型LNG储罐内压力及蒸发率的影响因素分析[J].天然气工业,2010,30(7):87-92,137-138.
|
|
WANG Wuchang, LI Yuxing, SUN Fafeng,et al .Controlling factors of internal pressure and evaporation rate in a huge LNG storage tank[J].Natural Gas Industry,2010,30(7):87-92,137-138.
|
| 4 |
KANDA M, MATSUMOTO K, YAMAGUCHI S .Heat transfer through multi-layer insulation (MLI)[J].Physica C:Superconductivity and Its Applications,2020,583:1353799/1-7.
|
| 5 |
LUDWIG C, DREYER M E, HOPFINGER E J .Pressure variations in a cryogenic liquid storage tank subjected to periodic excitations[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2013,66:223-234.
|
| 6 |
罗若尹,王博,甘智华,等 .真空完全丧失下LNG罐式集装箱的储存规律研究[J].工程热物理学报,2021,42(8):1930-1935.
|
|
LUO Ruoyin, WANG Bo, GAN Zhihua,et al .Study on performance of LNG tank containers after insulating vacuum loss[J].Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2021,42(8):1930-1935.
|
| 7 |
SANGEUN R, GIHUN S .Numerical study of natural convection in a liquefied natural gas tank[J].Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology,2012,26(10):3133-3140.
|
| 8 |
陈亮,梁国柱,邓新宇,等 .贮箱内低温推进剂汽化过程的CFD数值仿真[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2013,39(2):264-268.
|
|
CHEN Liang, LIANG Guozhu, DENG Xinyu,et al .CFD numerical simulation of cryogenic propellant vaporization in tank[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2013,39(2):264-268.
|
| 9 |
MANSU S, SANGKWON J .Analysis of self-pressurization phenomenon of cryogenic fluid storage tank with thermal diffusion model[J].Cryogenics,2010,50(9):549-555.
|
| 10 |
秦天怡,石玉美 .低温液体无损储存数学模型的修正和验证[J].化工学报,2018,69(S2):89-94.
|
|
QIN Tianyi, SHI Yumei .Revision and validation of ventless storage model of cryogenic fluid[J].Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering,2018,69(S2):89-94.
|
| 11 |
WEBER C, HENRIQUES A, GROHMANN S .Study on the heat transfer of helium cryostats following loss of insulating vacuum[J].IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering,2019,502: 012170/1-5.
|
| 12 |
YANG Changhai, QU Shoujiang, MENG Songhe,et al.Steady heat transfer analysis and parameter optimization for multilayer thermal insulations[J].Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2006,23(4):257-263.
|
|
闫长海,曲寿江,孟松鹤,等 .金属热防护系统多层隔热材料的传热分析及参数优化[J].南京航空航天大学学报(英文版),2006,23(4):257-263.
|
| 13 |
WANG B, HUANG Y H, LI P,et al .Optimization of variable density multilayer insulation for cryogenic application and experimental validation[J].Cryogenics,2016,80:154-163.
|
| 14 |
ZONG Z, OHUCHI N, TSUCHIYA K,et al .Experimental study on heat transfer through a few layers of multilayer insulation from 300 K to 4.2 K[J].IOP Conference:Materials Science and Engineering,2017,171(1):012089/1-7.
|
| 15 |
赵一力,陈叔平,金树峰,等 .基于两相流的无损储存系统仿真与实验研究[J].低温工程,2018(6):65-71.
|
|
ZHAO Yili, CHEN Shuping, JIN Shufeng,et al .Simulation and experimental study of ZBO storage system based on two-phase flow[J].Cryogenics,2018(6):65-71.
|
| 16 |
陈国邦,张鹏 .低温绝热与传热技术[M].北京:科学出版社,2004.
|
| 17 |
陈杰,张家骐,欧吉辉 .气体稀薄效应对热流计算的影响[J].空气动力学学报,2019,37(5):691-697.
|
|
CHEN Jie, ZHANG Jiaqi, Jihui OU .Influence of rarefied gas effect on the computation of heat flux[J].Acta Aerodynamica Sinica,2019,37(5):691-697.
|
| 18 |
PRASANTH P S, KAKKASSERY J K .Molecular models for simulation of rarefied gas flows using direct simulation monte carlo method[J].Fluid Dynamics Research,2008,40(4):233-252.
|
| 19 |
朱传勇,李增耀,赵新朋,等 .纳米尺度下气体导热的DSMC模拟[J].工程热物理学报,2016,37(5):1027-1031.
|
|
ZHU Chuanyong, LI Zengyao, ZHAO Xinpeng,et al .The DSMC study on gas heat conduction in nanoscale[J].Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2016,37(5):1027-1031.
|
| 20 |
ABHIMANYU G, AMIT A, UPENDRA B .Study of rarefied gas flows in backward facing micro-step using direct simulation monte carlo[J].Vacuum,2018,155:249-259.
|
| 21 |
真空绝热深冷设备性能试验方法第6部分:漏热量测量: [S].
|