华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (11): 14-24.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220004
所属专题: 2022年交通运输工程
考虑出行焦虑的异质小汽车通勤者早高峰出发时刻选择研究
胡郁葱1,2 骆明明1,2 潘雷3 凌美宁4 卢晓珊5
- 1.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广东 广州 510640
2.现代城市交通技术江苏高校协同创新中心,江苏 南京,211189
3.广州市交通运输研究院有限公司,广东 广州 510627
4.广州市城市规划勘测设计研究院,广东 广州 510060
5.合肥工业大学 汽车与交通工程学院,安徽 合肥 230009
Study on the Choice of Morning Peak Departure Time of Heterogeneous Car Commuters Considering Travel Anxiety
HU Yucong1,2 LUO Mingming1,2 PAN Lei3 LING Meining4 LU Xiaoshan5
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Collaborative Innovation Center of Modern Urban Traffic Technologies,Nanjing 211189,Jiangsu,China
3.Guangzhou Transports Research Institute,Guangzhou 510627,Guangdong,China
4.Guangzhou Urban Planning and Design Survey Research Institute,Guangzhou 510060,Guangdong,China
5.School of Automobile and Transportation Engineering,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,Anhui,China
摘要:
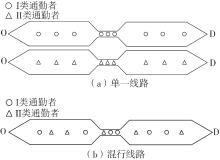
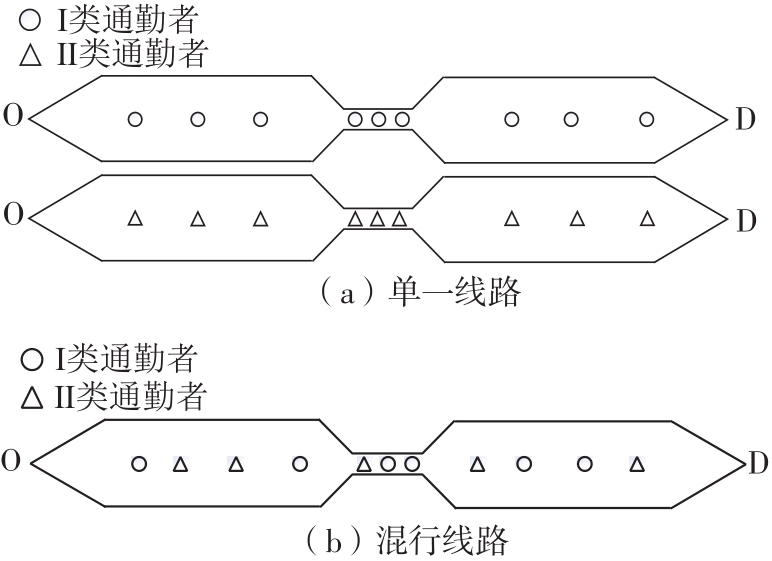
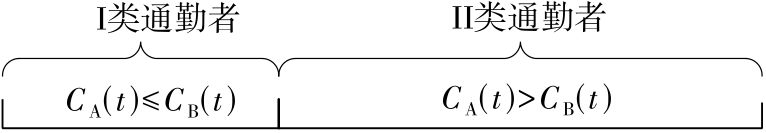
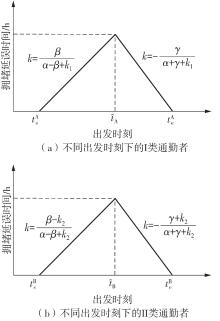
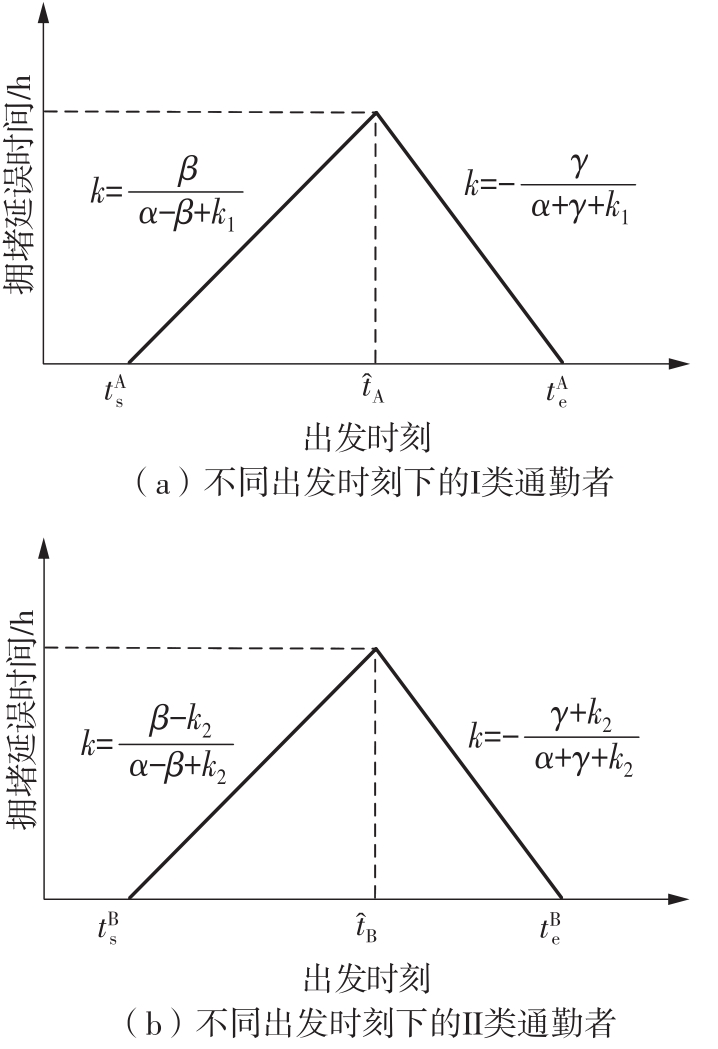
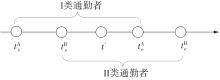
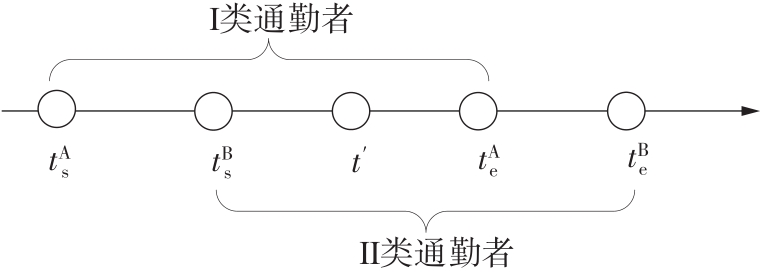
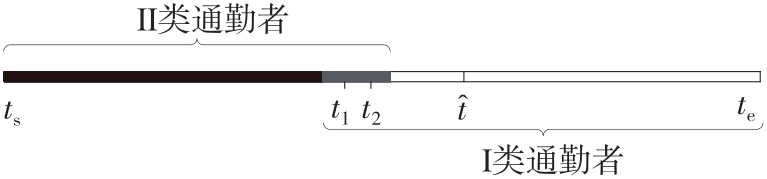
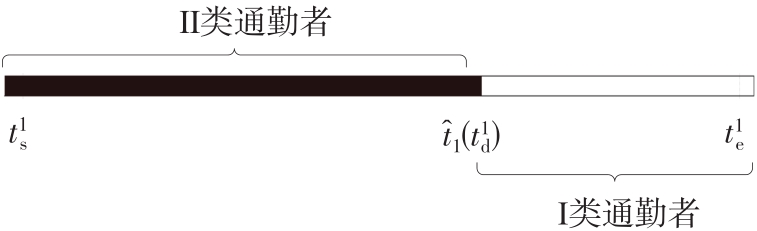
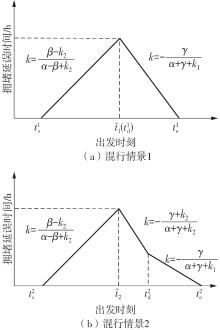
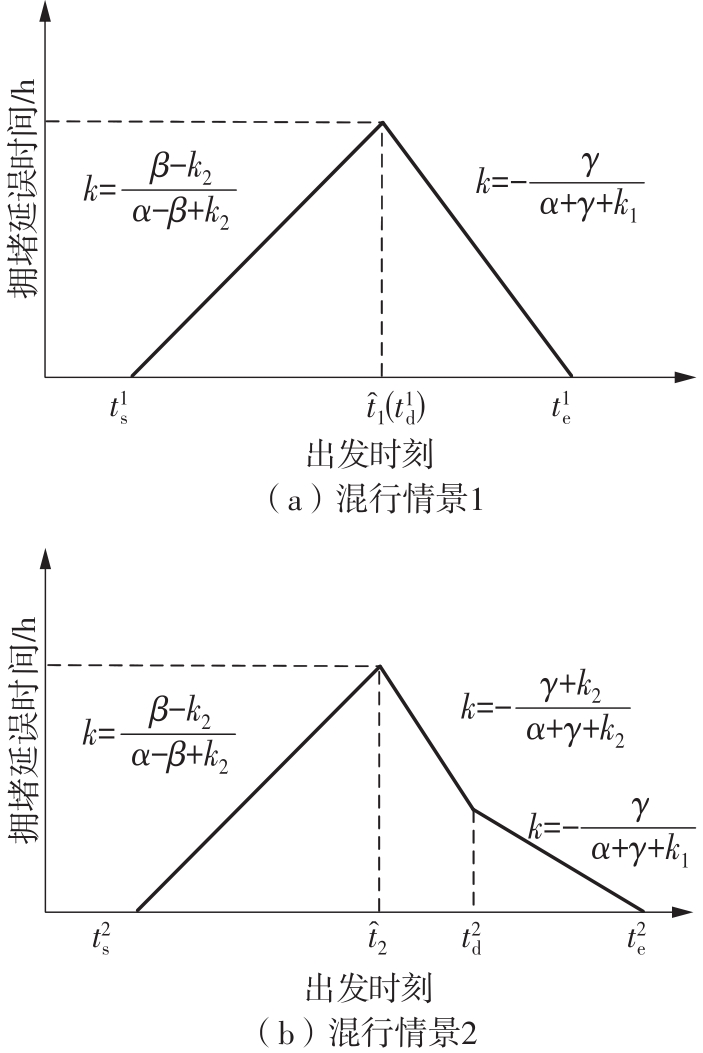
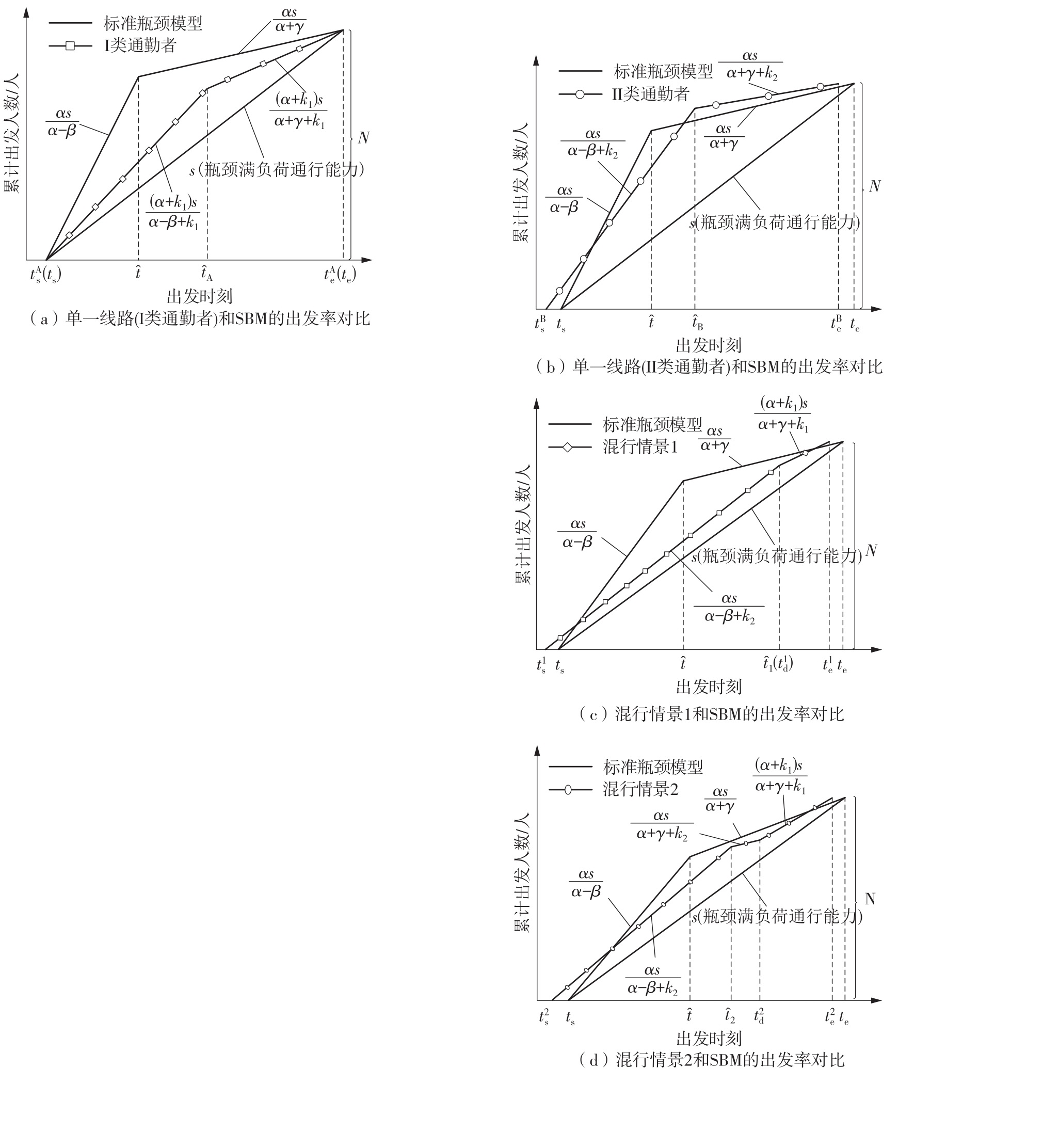
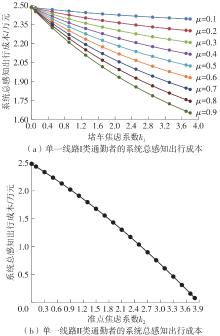
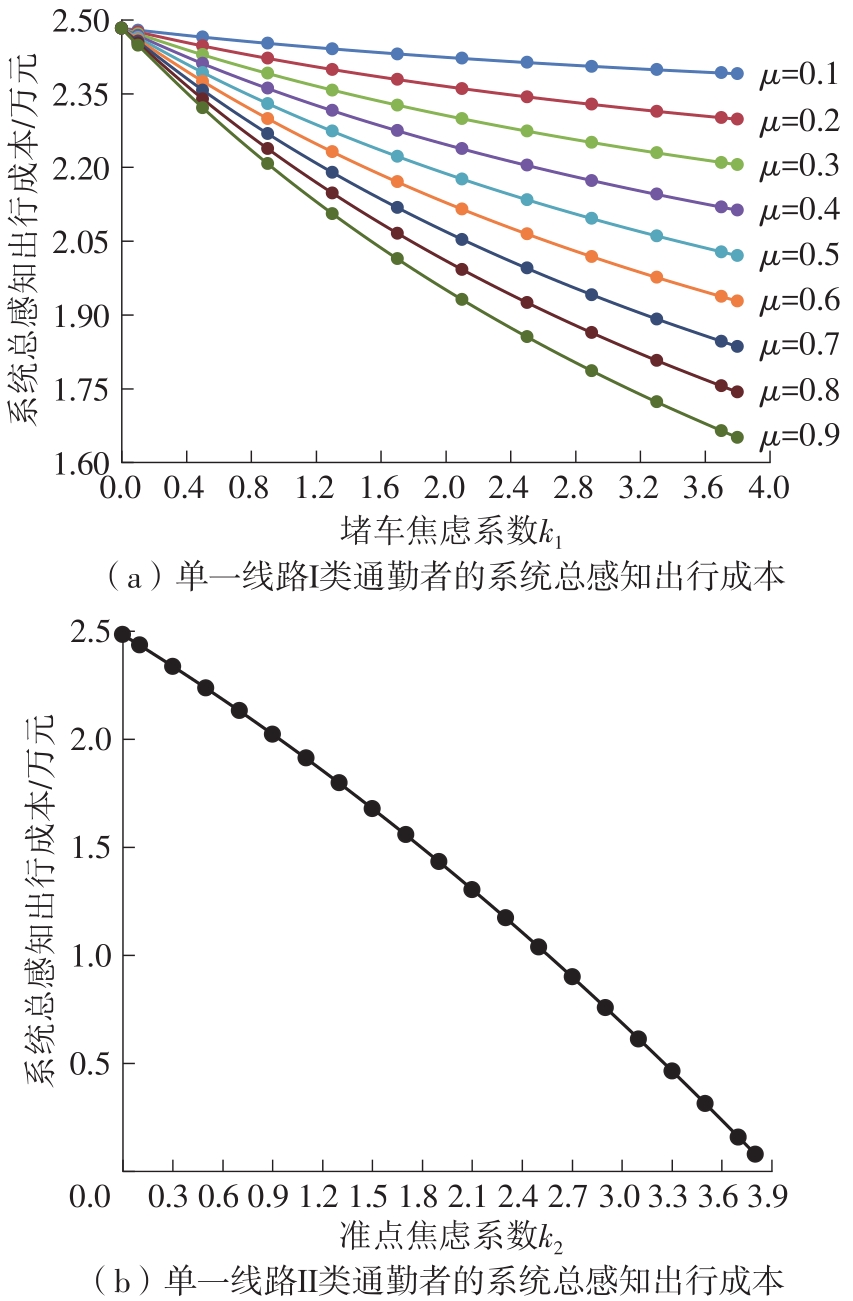
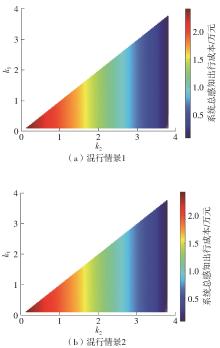
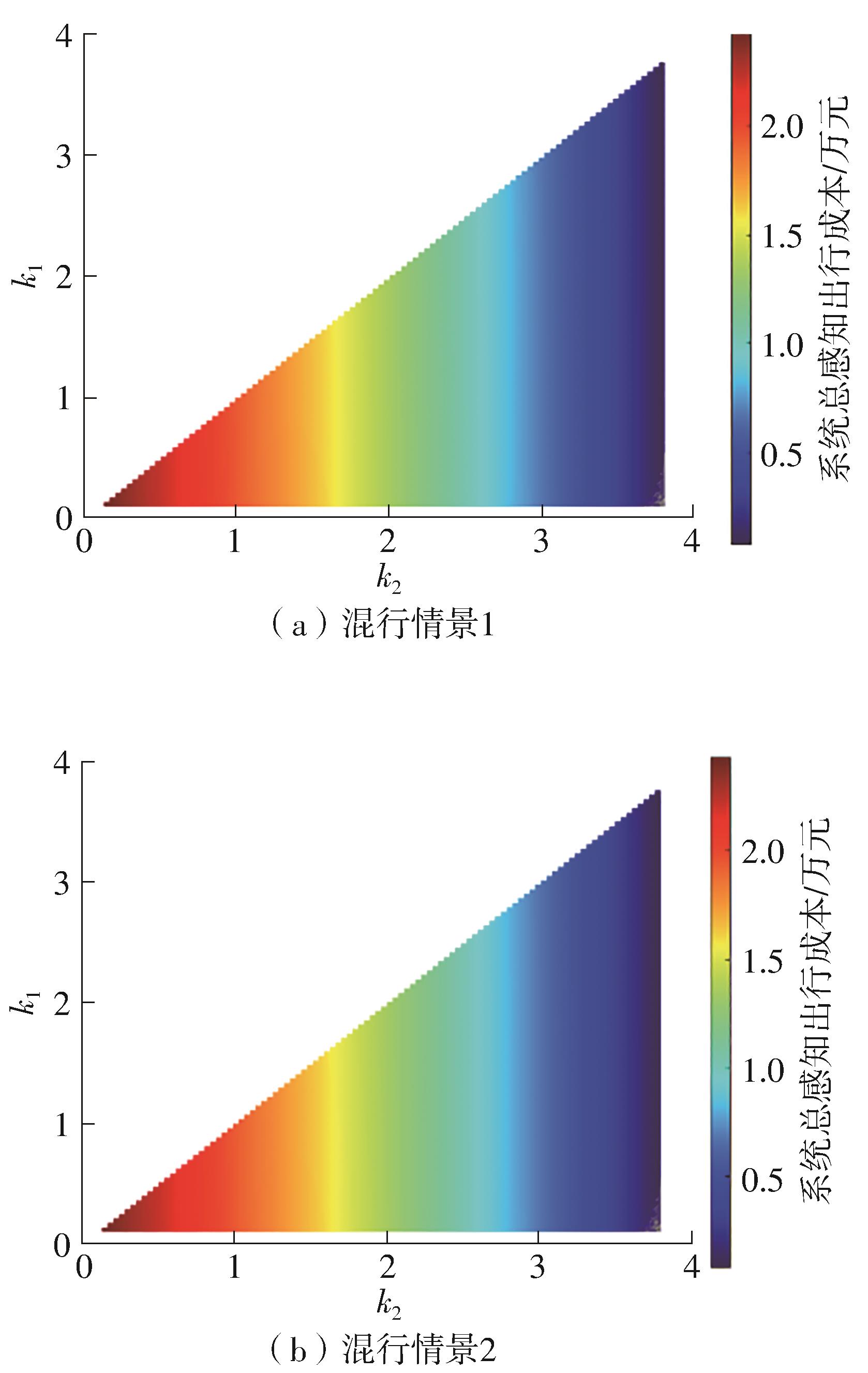
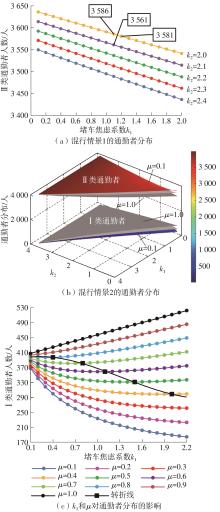
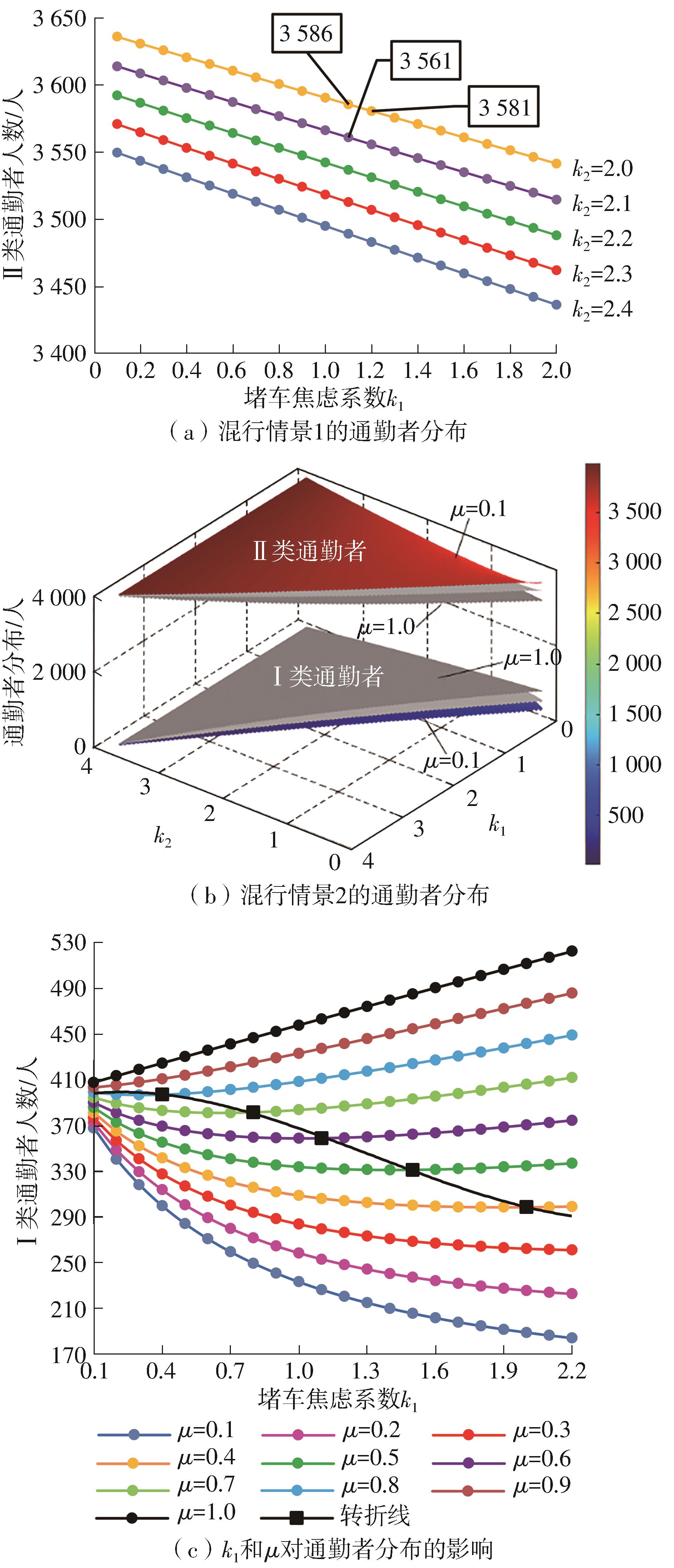
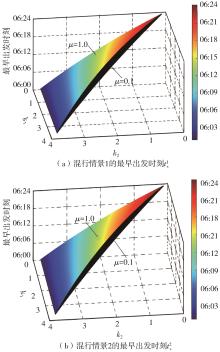
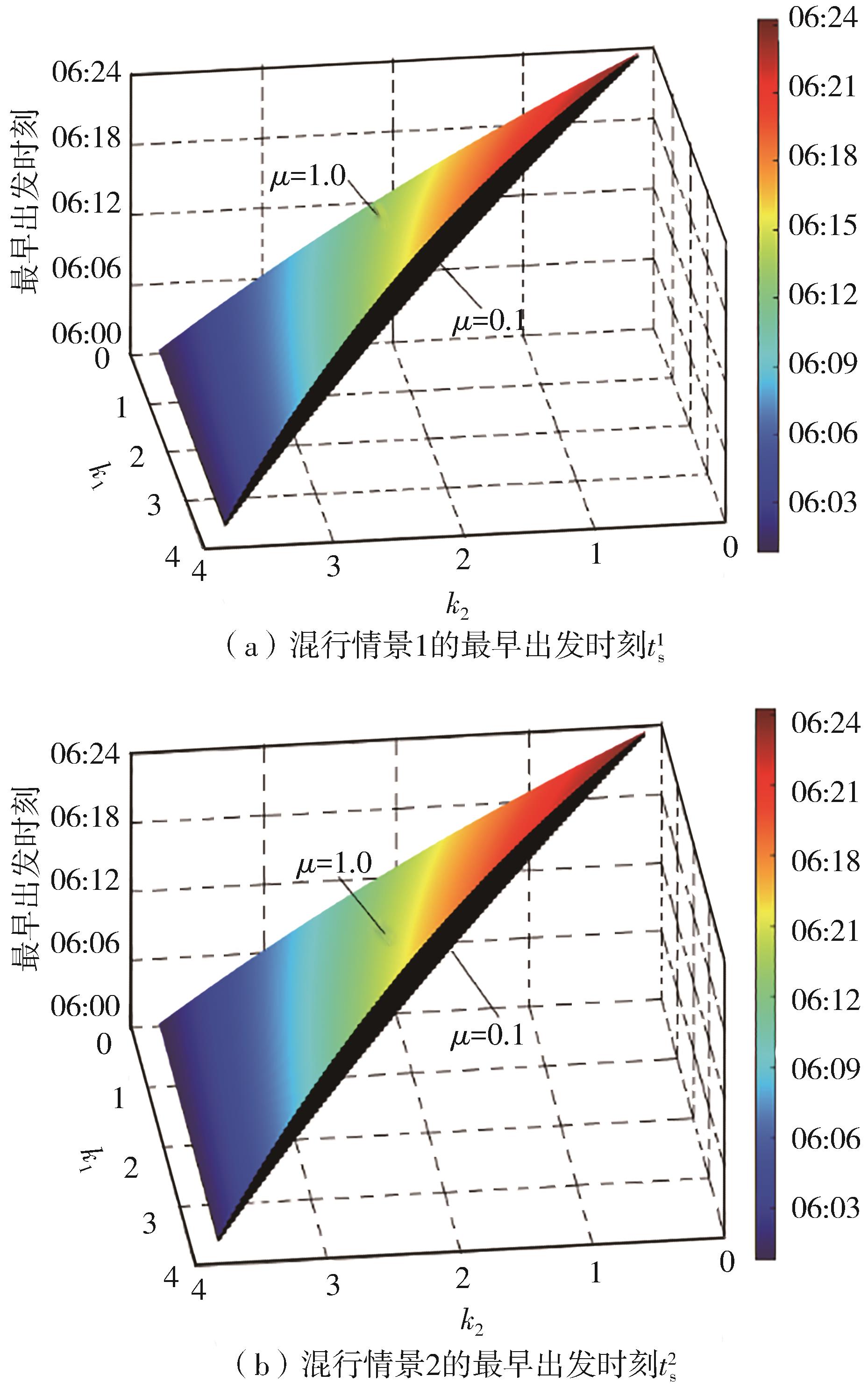
将私人小汽车通勤者划分为Ⅰ类堵车焦虑型和Ⅱ类准点焦虑型两种类型,引入出行敏感系数(堵车焦虑系数、准点焦虑系数)和瓶颈忍耐系数来刻画两类通勤者的出行焦虑程度,在标准瓶颈模型的基础上构建新的出行成本函数,并将其应用于分析单一线路和混行线路下的出发率、高峰期起止时刻和通勤者构成等指标。研究结果表明:当道路上仅有某一类通勤者存在时,堵车焦虑系数、瓶颈忍耐系数以及准点焦虑系数的增加均会使单一线路通勤者的系统总感知出行成本降低;混行情形1中Ⅱ类通勤者的准点焦虑系数增大时,该类通勤者数量增加,系统总感知出行成本减小,高峰期前移,瓶颈忍耐系数增大时,系统总感知出行成本减少,高峰期后移;混行情形2中Ⅰ类通勤者的堵车焦虑系数与瓶颈忍耐系数对该类群体数量的影响具有两面性,不同瓶颈忍耐系数与堵车焦虑系数的组合下,该类群体的吸引力呈现单调减小、先减后增和单调增加三种不同的趋势。
中图分类号: