华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 22-30.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230628
所属专题: 2024年电子、通信与自动控制技术
基于多频脉冲采样的血流速度估计方法
- 华南理工大学 电子与信息学院,广东 广州 510640
Blood Flow Velocity Estimation Method Based on Multi-Frequency Pulse Sampling
MA Biyun( ), FAN Yihua, LIU Jiaojiao(
), FAN Yihua, LIU Jiaojiao( )
)
- School of Electronic and Information Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
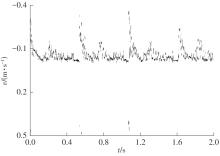
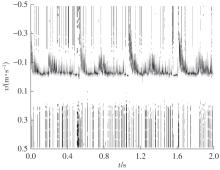
传统双模超声技术相较于新兴技术更具实现可穿戴化的潜力。在进行脉冲多普勒血流速度估计时,双模超声需同时发射B模式脉冲进行成像定位,这要求B模式脉冲和多普勒脉冲共享采样时间。采用基于单频多普勒脉冲的稀疏间隔发射方式可以解决这一问题,但常见的稀疏发射排布方式(如嵌套发射、互质发射等)存在采样时间窗较长的缺点,特别是在血流速度变化明显的情况下存在时间分辨率不足的问题。此外,长时间窗包含了较多的血流速度分量,容易由于稀疏采样引起伪影,从而影响血流速度估计的准确性。因此,文中提出了一种基于多频脉冲采样的新型血流速度估计方法。首先,构建了多频脉冲采样的回波模型,并对该模型进行推导,证明了在频率衰减平稳假设下,该数学模型等价于单频多普勒脉冲稀疏发射方式,即多频脉冲采样可以通过较短的时间窗实现类似于基于单频脉冲采样模式的长时间窗的性能,从而提高血流速度谱的时间分辨率和估计精度;然后,提出了两种可用于多频脉冲采样模式的血流速度谱的构建方法,分别为复杂度较低的BMUSIC算法和伪影抑制效果较佳的VMUSIC算法。基于Field Ⅱ仿真数据和人体实测数据的实验结果表明:相较于单频多普勒脉冲稀疏发射方式,文中方法不仅可以采用较短的时间窗提升血流速度谱的时间分辨率,还可以获得连续、清晰、精度较高且伪影抑制效果较佳的血流速度估计结果;在人体实测数据实验中,由于实验条件所限,文中方法无法实现非整数倍频,未能充分展现VMUSIC算法的性能优势。
中图分类号: