华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 1-9.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230433
壳聚糖对氧化淀粉凝胶热挤压3D打印成型性的影响
陈玲 吕嘉宇 邱志鹏†
- 华南理工大学 食品科学与工程学院/广东省天然产物绿色加工与产品安全重点实验室/淀粉与植物蛋白 深加工教育部工程研究中心,广东 广州 510640
Effect of Chitosan on the Hot-Extrusion 3D Printing Formability of Oxidized Starch Gel
CHEN Ling LÜ Jiayu QIU Zhipeng
- School of Food Science and Engineering/Guangdong Province Key Laboratory for Green Processing of Natural Products and Product Safety/Engineering Research Center of Starch and Vegetable Protein Processing of the Ministry of Education,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
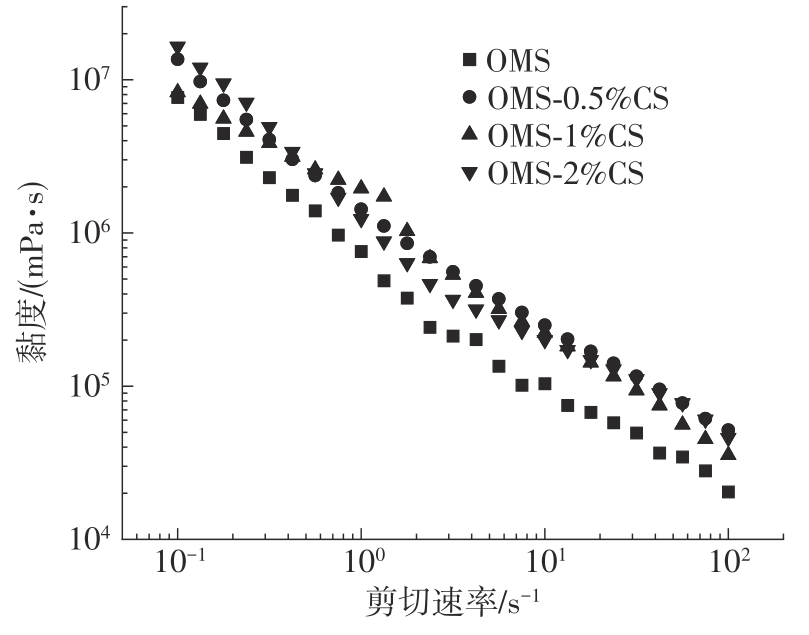
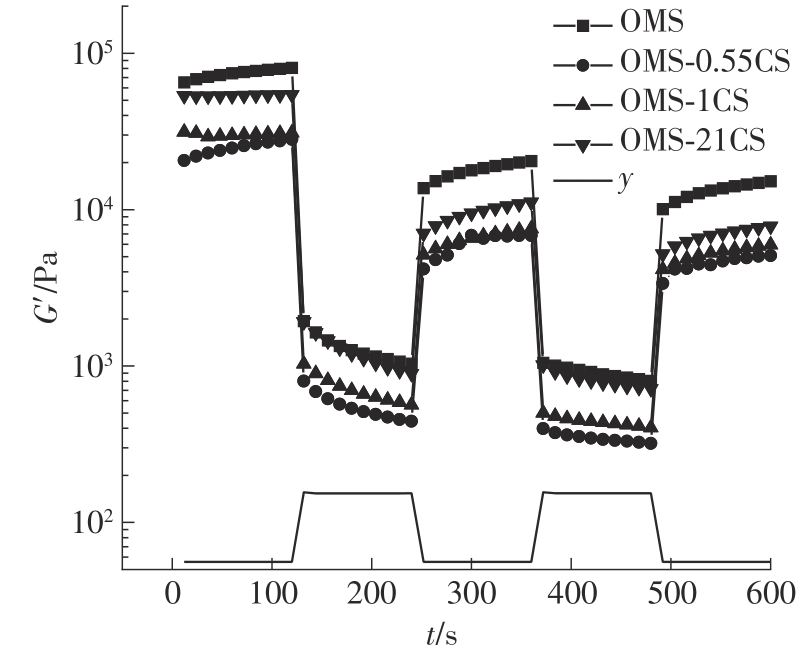
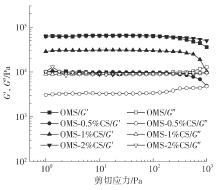
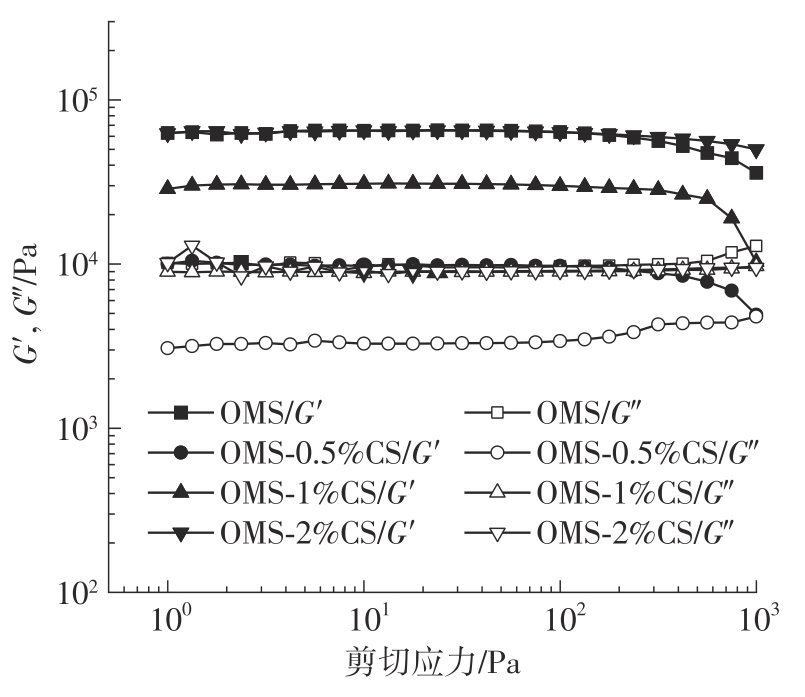
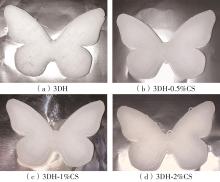
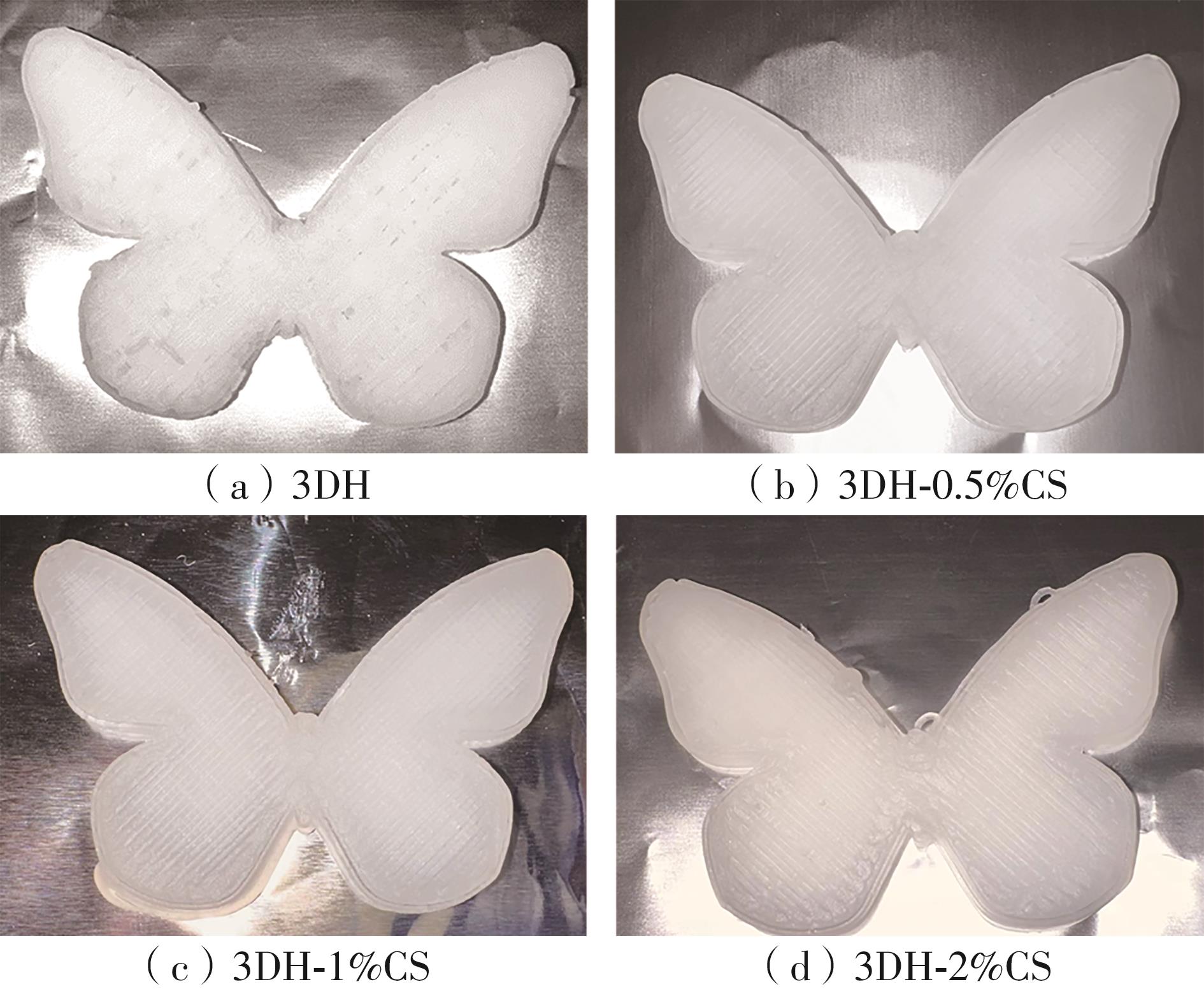
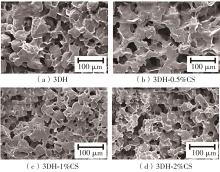
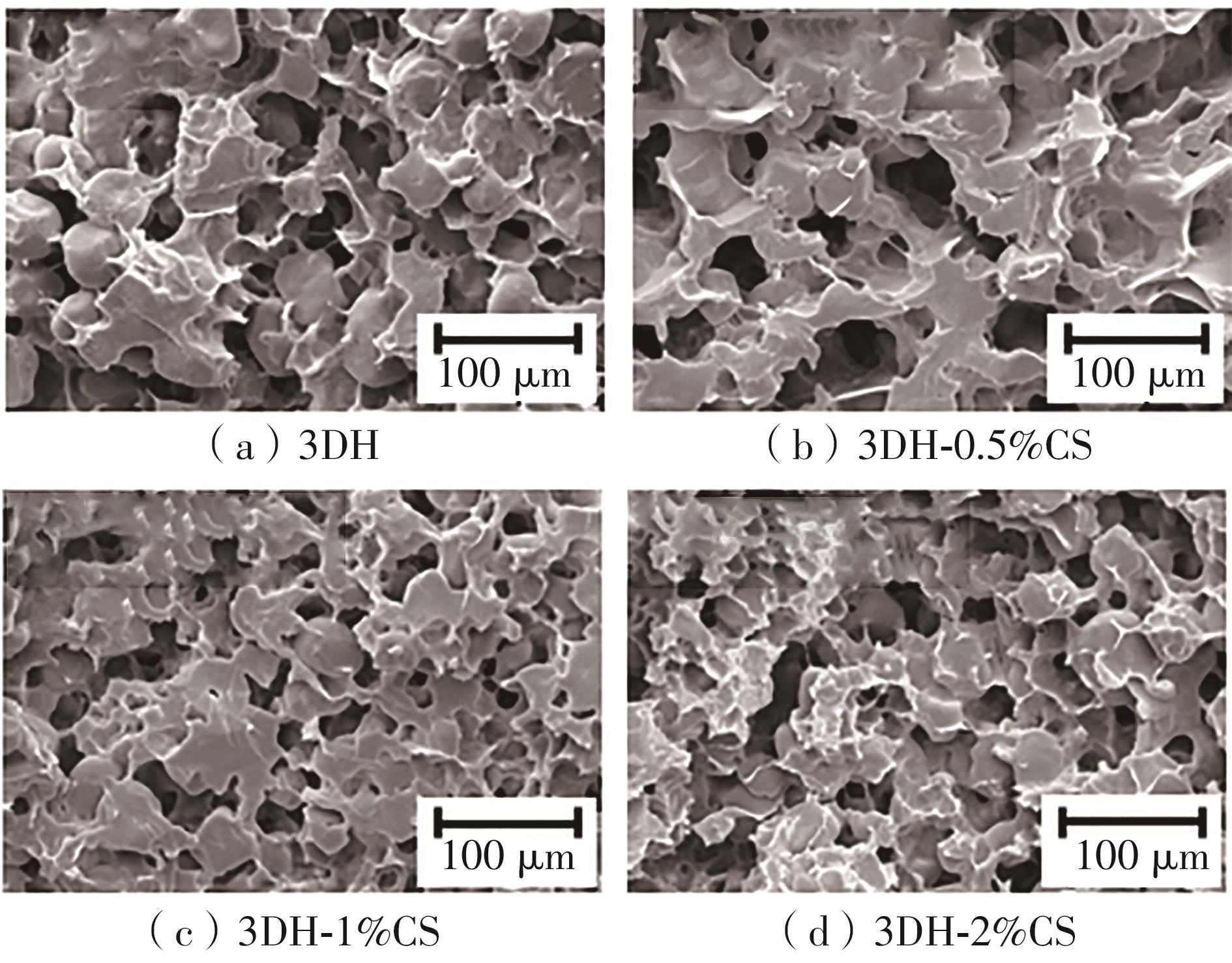
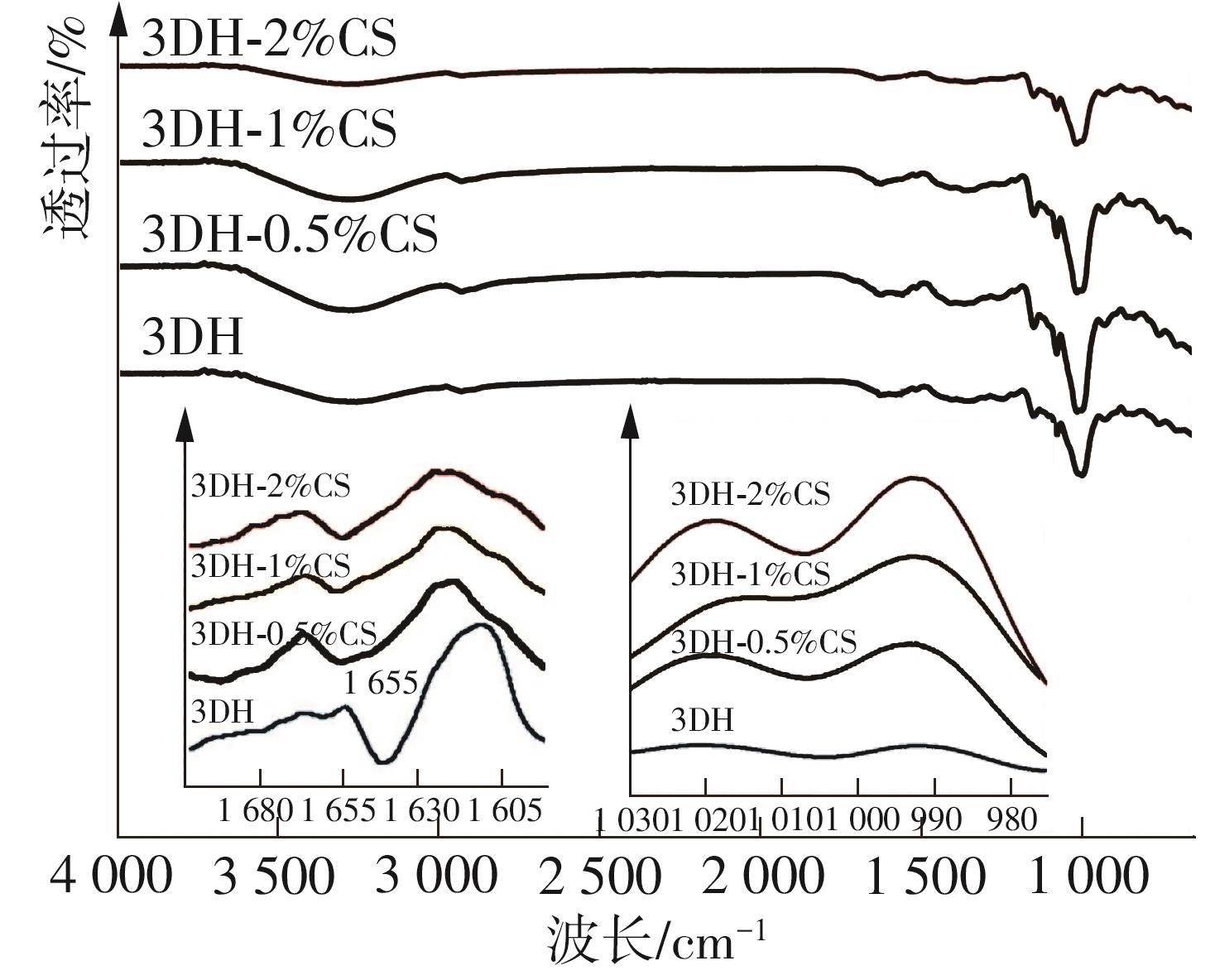
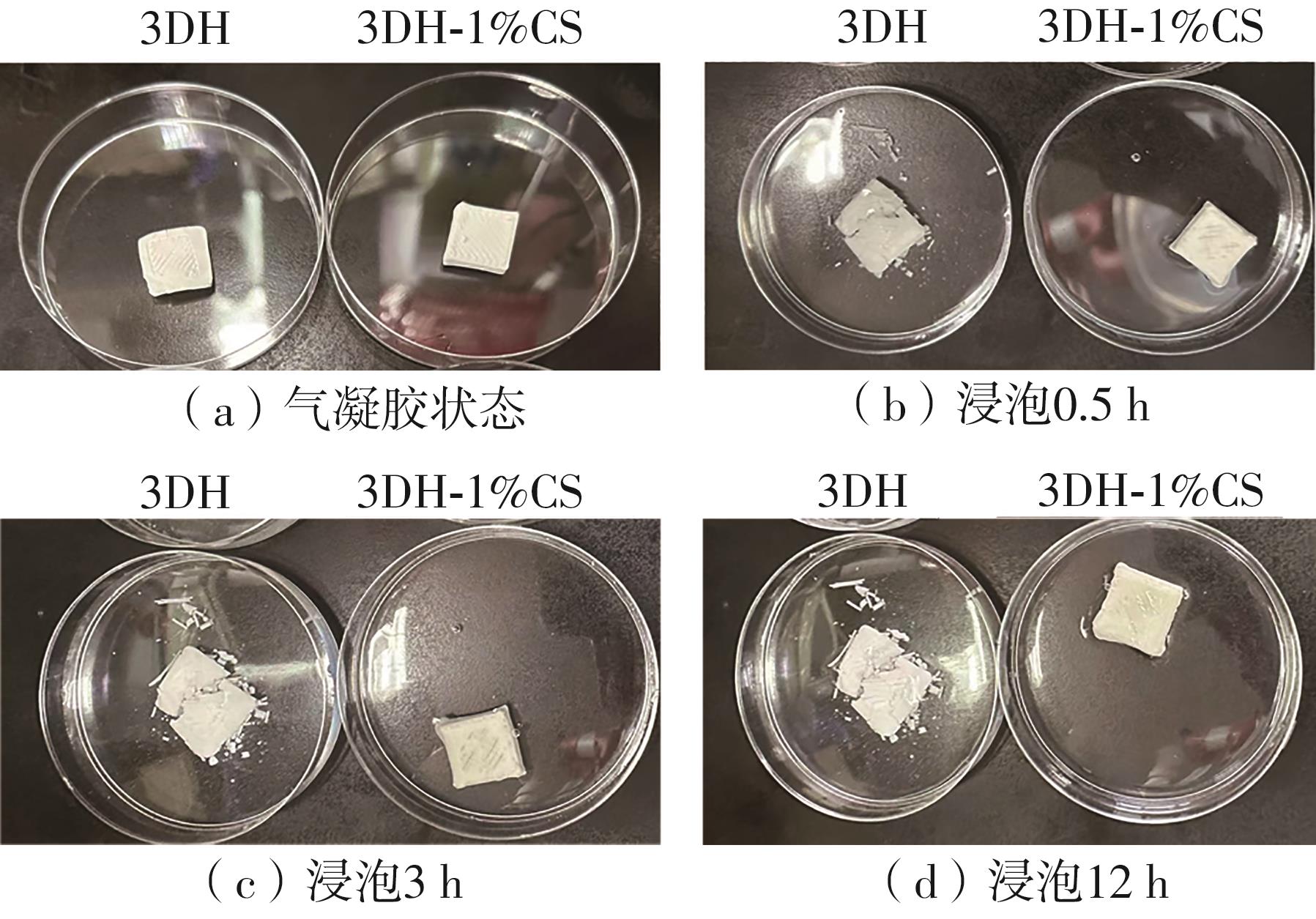
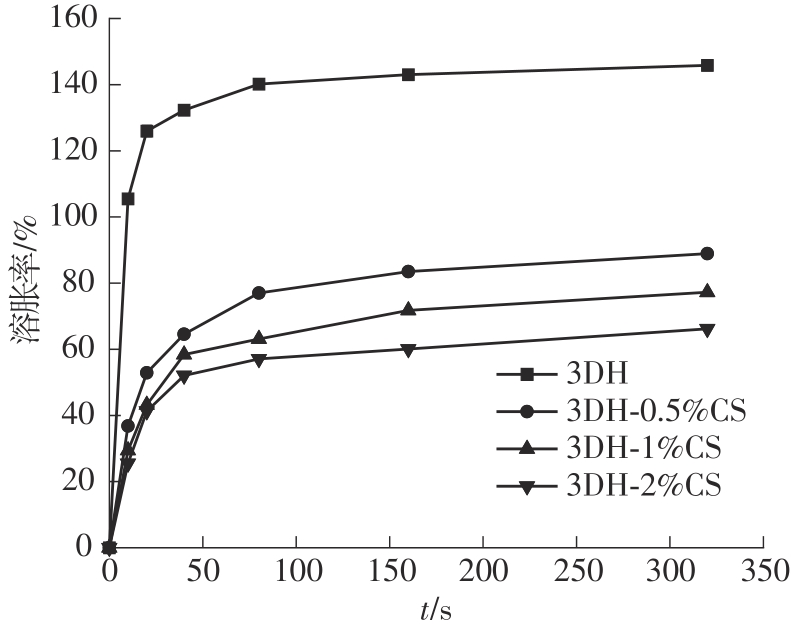
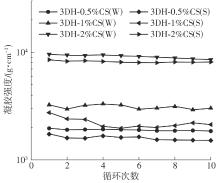
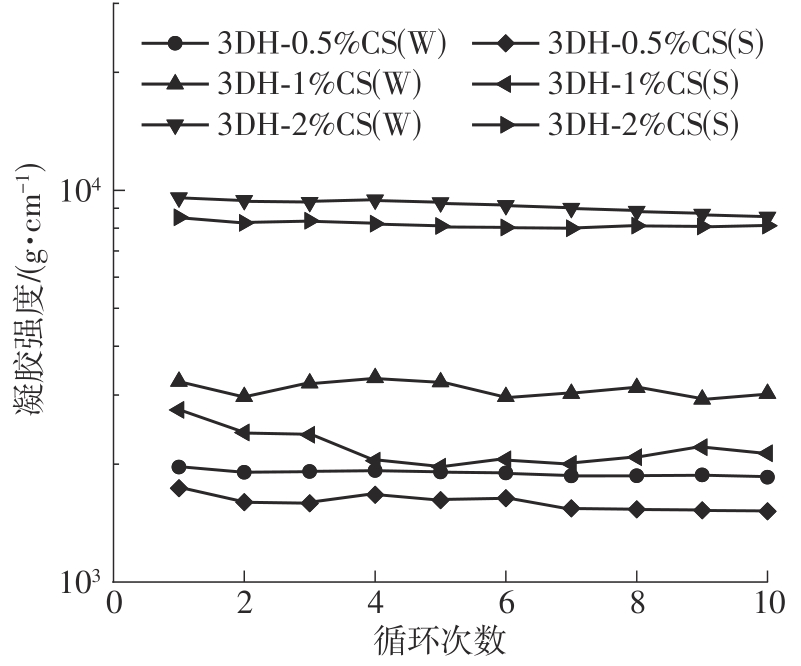
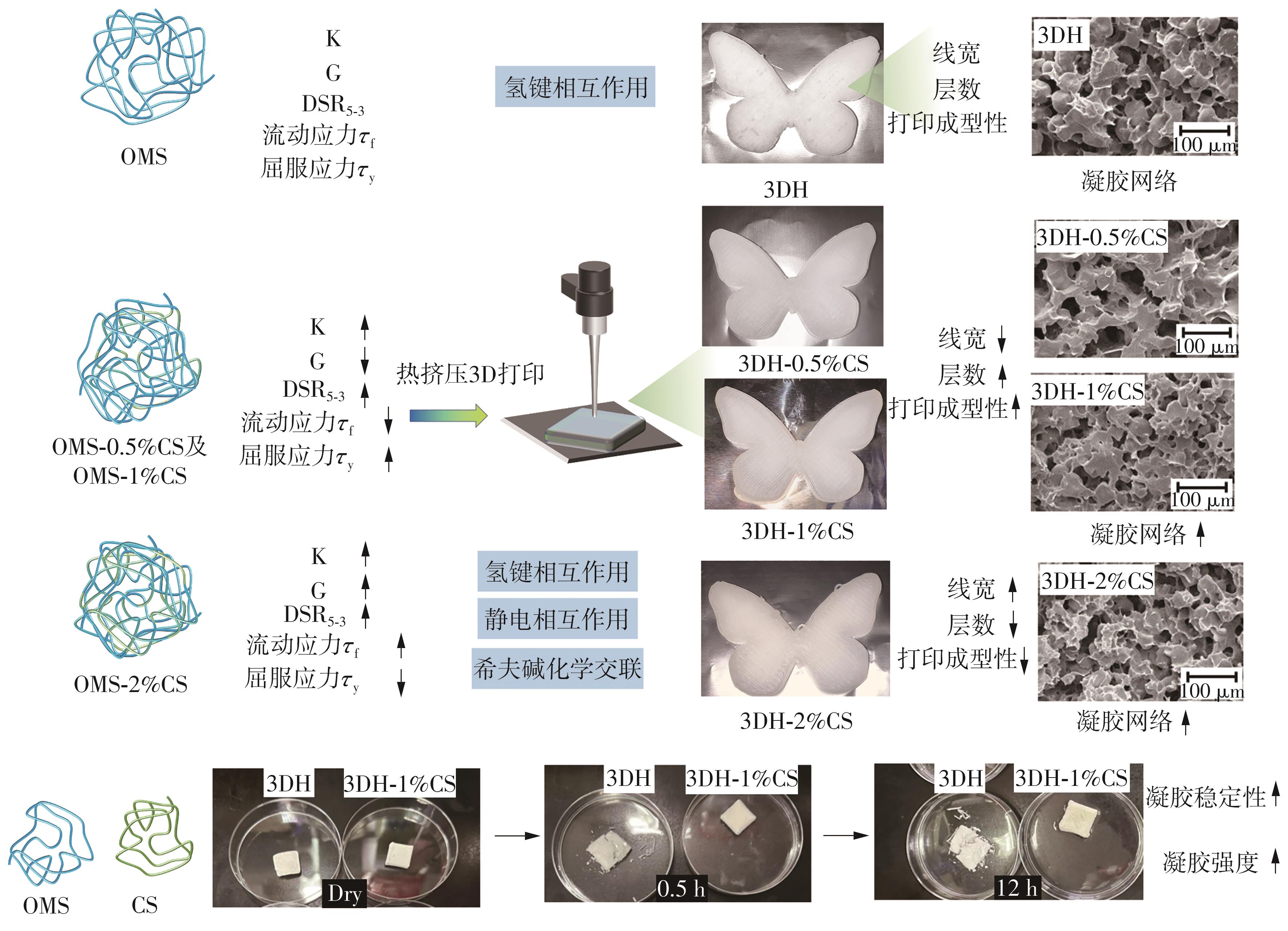
氧化淀粉凝胶材料因其具有亲水性和电荷性、易反应与组装等优势,成为近年来食品及生物医药等领域研究和应用的热点材料,但其作为热挤压3D打印凝胶材料时却存在打印成型性较差及凝胶强度较低等缺陷。本研究提出利用壳聚糖与氧化淀粉分子间的非共价及化学交联作用对其进行调控,探究不同壳聚糖添加量对氧化淀粉凝胶材料的流变性能、打印成型性和凝胶强度的影响。结果表明:壳聚糖与氧化淀粉糊特性依然呈现典型的剪切稀化特征,随着壳聚糖添加量增加(0.5%~2%),氧化淀粉-壳聚糖凝胶体系中存在氢键及静电吸引等非共价相互作用导致黏度增大,触变性先提升后下降,流动应力(τf)先减小后增大、屈服应力(τy)先增大后减小。相比于氧化淀粉凝胶,氧化淀粉-壳聚糖凝胶均具有良好的打印成型性,尤其是当壳聚糖添加量为1%时,复合凝胶触变性最好,流动应力(τf)最小、屈服应力(τy)最大,因此打印成型性与打印精度最佳。此外,由于壳聚糖与氧化淀粉的非共价相互作用以及希夫碱化学交联作用,使得氧化淀粉凝胶网络结构更加致密,稳定性提升,凝胶强度显著增大,且随壳聚糖添加量增加变化趋势愈加明显。本研究结果可为氧化淀粉凝胶材料的性能改善及适合热挤压3D打印加工需求的氧化淀粉-壳聚糖凝胶材料设计与应用提供理论依据和技术支撑。
中图分类号: