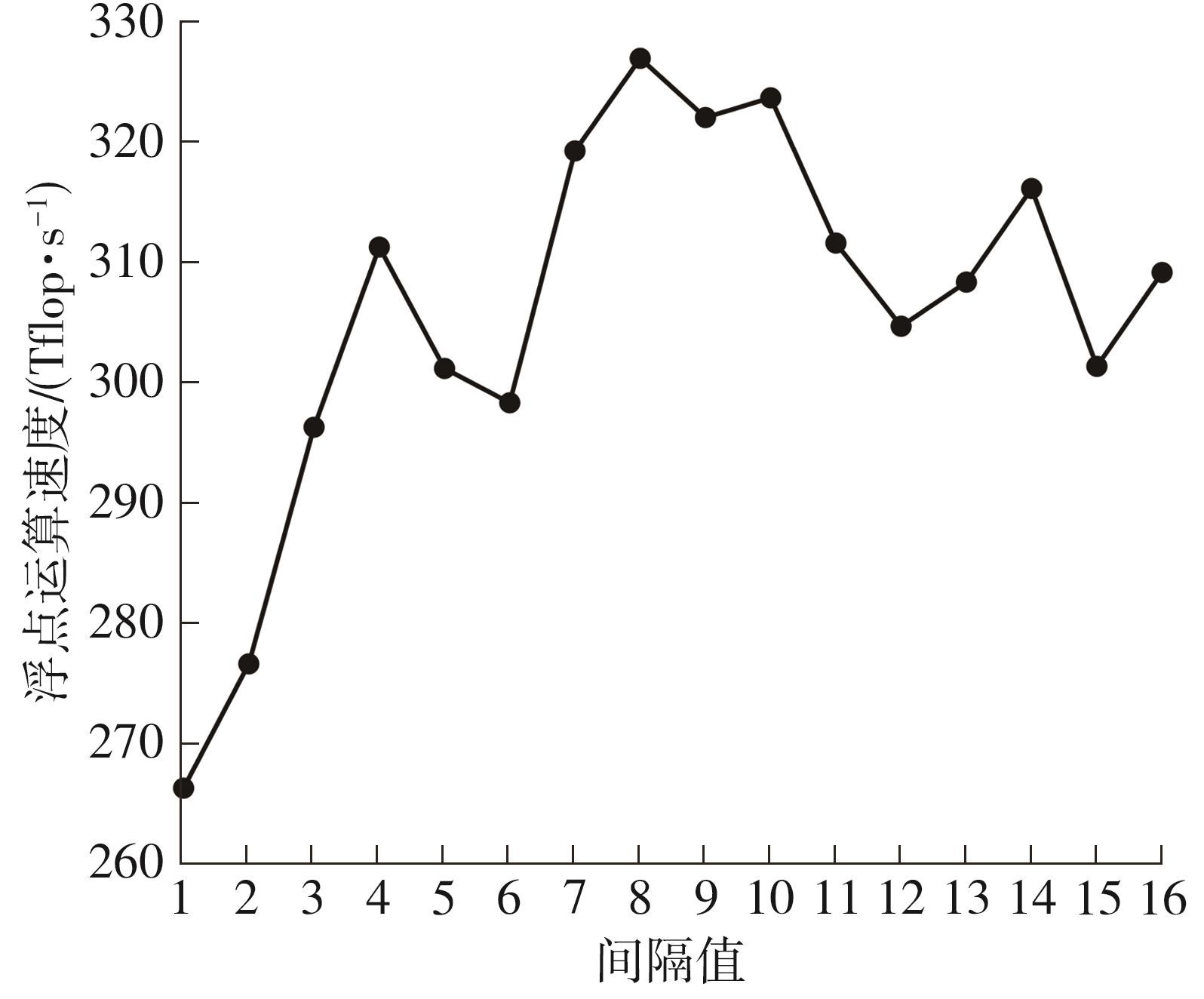
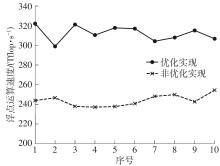
| 1 |
DAVICES T, KARLSSON C, LIU H,et al .High performance LINPACK benchmark:a fault tolerant implementation without checkpointing[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Supercomputing.Tucson:ACM,2011:162-171.
|
| 2 |
STROHMAIER E, DONGARRA J, SIMON H,et al .TOP500 list[EB/OL].(2022-11-14) [2023-03-05]..
|
| 3 |
HU Y, LU L .Design of a simulation model for high performance LINPACK in hybrid CPU-GPU systems[J].The Journal of Supercomputing,2021,77(12):13739-13756.
|
| 4 |
OpenAI. GPT-4 technical report[EB/OL].(2023-03-27)[2023-05-14]..
|
| 5 |
DONGARRA J, LUSZCZEK P, TSAI Y M .HPL-AI mixed-precision benchmark[EB/OL].(2022-10-31)[2023-03-05]..
|
| 6 |
ABDELFATTAH A, ANZT H, BOMAN E G,et al .A survey of numerical linear algebra methods utilizing mixed-precision arithmetic[J].The International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications,2021,35(4):344-369.
|
| 7 |
MOLER, CLEVE B .Iterative refinement in floating point[J].Journal of the ACM,1967,14(2):316-321.
|
| 8 |
KURZAK J, DONGARRA J .Implementation of mixed precision in solving systems of linear equations on the CELL processor[J].Concurrency and Computation:Practice and Experience,2007,19(10):1371-1385.
|
| 9 |
LEI W, YUNQUAN Z, XIANYI Z,et al .Accelerating LINPACK performance with mixed precision algorithm on CPU+GPGPU heterogeneous cluster[C]∥Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology.Bradford:IEEE,2010:1169-1174.
|
| 10 |
BABOULIN M, BUTTARI A, DONGARRA J,et al .Accelerating scientific computations with mixed precision algorithms[J].Computer Physics Communications,2009,180(12):2526-2533.
|
| 11 |
HAIDAR A, TOMOV S, DONGARRA J,et al .Harnessing GPU tensor cores for fast FP16 arithmetic to speed up mixed-precision iterative refinement solvers[C]∥Proceedings of the SC18:International Conference for High Performance Computing,Networking,Storage and Analysis. Dallas:IEEE,2018:603-613.
|
| 12 |
HAIDAR A, WU P, TOMOV S,et al .Investigating half precision arithmetic to accelerate dense linear system solvers[C]∥Proceedings of the 8th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems. Denver:ACM,2017:1-8.
|
| 13 |
DEMMEL J, HIDA Y, KAHAN W,et al .Error bounds from extra-precise iterative refinement[J].ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software,2006,32(2):325-351.
|
| 14 |
OKTAY E, CARSON E .Multistage mixed precision iterative refinement[J].Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications,2022,29(4):e2434/1-24.
|
| 15 |
AMESTOY P, BUTTARI A, HIGHAM N J,et al .Combining sparse approximate factorizations with mixed-precision iterative refinement[J].ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software,2023,49(1):1-29.
|
| 16 |
RAKKA M, FOUDA M E, KHARGONEKAR P,et al .Mixed-precision neural networks:a survey[EB/OL].(2022-08-11)[2023-03-05]..
|
| 17 |
MICIKEVICIUS P, NARANG S, ALBEN J,et al .Mixed precision training[EB/OL].(2018-02-15)[2023-03-05]..
|
| 18 |
LATOTZKE C, CIESIELSKI T, GEMMEKE T .Design of high-throughput mixed-precision CNN accelerators on FPGA[C]∥Proceedings of the 2022 32nd International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL).Belfast:IEEE,2022:358-365.
|
| 19 |
DAS D, MELLEMPUDI N, MUDIGERE D,et al .Mixed precision training of convolutional neural networks using integer operations FPGA[EB/OL].(2018-02-23)[2023-03-05]..
|
| 20 |
LUSZCZEK P, TSAI Y M .Reference implementationof the HPL-AI benchmark[CP/OL].(2019-12-20) [2023-03-05]..
|
| 21 |
KUDO S, NITADORI K, INA T,et al .Implementation and numerical techniques for one EFlop/s HPL-AI benchmark on Fugaku[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACM 11th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA).GA:IEEE,2020:69-76.
|
| 22 |
KUDO S, NITADORI K, INA T,et al .Prompt report on exa-scale HPL-AI benchmark[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing(CLUSTER).Kobe:IEEE,2020:418-419.
|
| 23 |
SATO M, KODAMA Y, TSUJI M,et al .Co-design and system for the supercomputer “Fugaku”[J].IEEE Micro,2021,42(2):26-34.
|
| 24 |
MATSUOKA S .Fugaku and A64FX:the first exascale supercomputer and its innovative arm CPU[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 Symposium on VLSI Circuits.Kyoto:IEEE,2021:1-3.
|
| 25 |
DEMMEL J W, HIGHAM N J, SCHREIBER R S .Stability of block LU factorization[J].Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications,1995,2(2):173-190.
|
| 26 |
WILKINSON J H .Error analysis of direct methods of matrix inversion[J].Journal of the ACM,1961,8(3):281-330.
|
| 27 |
FASI M, HIGHAM N J .Matrices with tunable infinity-norm condition number and no need for pivoting in LU factorization[J].SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications,2021,42(1):417-435.
|