

收稿日期: 2023-08-01
网络出版日期: 2024-01-31
基金资助
工信部制造业高质量发展专项资金资助项目(R-ZH-023-QT-001-20221009-001);广州市科技计划项目(2023B01J0016)
Multi-Task Assisted Driving Policy Learning Method for Autonomous Driving
Received date: 2023-08-01
Online published: 2024-01-31
Supported by
the Special Fund for High-Quality Development of the Manufacturing Industry of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology(R-ZH-023-QT-001-20221009-001)
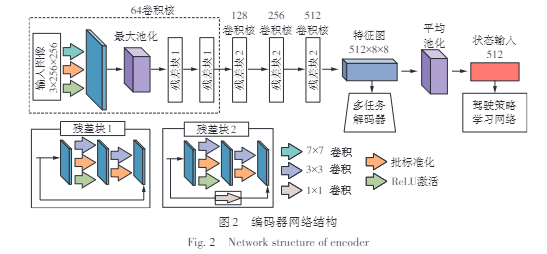
随着自动驾驶技术的发展,深度强化学习成为实现高效驾驶策略学习的重要手段。然而,实施自动驾驶面临着复杂多变的交通场景带来的挑战,并且现有的深度强化学习方法存在场景适应能力单一、收敛速度较慢的问题。针对此类问题,为提高自动驾驶车辆的场景适应能力和策略学习效率,文中提出了一种多任务辅助的驾驶策略学习方法。该方法首先基于深度残差网络构建了编码器-多任务解码器模块,将高维驾驶场景压缩为低维表征,并采用语义分割、深度估计和速度预测的多任务辅助学习,以提高低维表征的场景信息丰富程度;然后,以该低维表征作为状态输入,构建基于强化学习的决策网络,并设计多约束奖励函数来引导驾驶策略的学习;最后,在CARLA中进行仿真实验。结果表明:相较于DDPG、TD3等经典方法,文中方法通过多任务的辅助改善了训练进程,学习到更优的驾驶策略;在环岛、路口等多个典型城市驾驶场景中实现了更高的任务成功率和驾驶得分,具备优秀的决策能力和场景适应性。
罗玉涛 , 薛志成 . 面向自动驾驶的多任务辅助驾驶策略学习方法[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024 , 52(10) : 31 -40 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230503
With the development of autonomous driving technology, deep reinforcement learning has become an important means to realize the efficient driving policy learning. However, the implementation of autonomous driving is faced with the challenges brought by the complex and changeable traffic scenes, and the existing deep reinforcement learning methods have the problems of single scene adaptation ability and slow convergence speed. To address these issues and to improve the scene adaptability and policy learning efficiency of autonomous vehicles, this paper proposed a multi-task assisted driving policy learning method. Firstly, this method constructed the encoder-multi-task decoder module based on the deep residual network, squeezing high-dimensional driving scenes into low-dimensional representations, and adopted multi-task-assisted learning of semantic segmentation, depth estimation and speed prediction to improve the scene information richness of low-dimensional representations. Then, the low-dimensional representation was used as the state input to build a decision network based on reinforcement learning, and the multi-constraint reward function was designed to guide the learning of driving strategies. Finally, simulation experiments were conducted in CARLA. The experimental results show that, compared to classic methods such as DDPG and TD3, the proposed method improves the training process through multi-task assistance and learns better driving policies. It achieves higher task success rates and driving scores in several typical urban driving scenarios such as roundabouts and intersections, demonstrating excellent decision-making capabilities and scene adaptability.

| 1 | ELALLID B B, BENAMAR N, HAFID A S,et al .A comprehensive survey on the application of deep and reinforcement learning approaches in autonomous driving[J].Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences,2022,34(9):7366-7390. |
| 2 | 林泓熠,刘洋,李深,等 .车路协同系统关键技术研究进展[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(10):46-67. |
| LIN Hongyi, LIU Yang, LI Shen,et al .Research progress on key technologies in the cooperative vehicle infrastructure system[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,51(10):46-67. | |
| 3 | HEJASE B, YURTSEVER E, HAN T,et al .Dynamic and interpretable state representation for deep reinforcement learning in automated driving[J].IFAC-PapersOnLine,2022,55(24):129-134. |
| 4 | HUANG C, ZHANG R, OUYANG M,et al .Deductive reinforcement learning for visual autonomous urban driving navigation[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2021,32(12):5379-5391. |
| 5 | ZHU M, WANG X, WANG Y .Human-like autonomous car-following model with deep reinforcement learning[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2018,97:348-368. |
| 6 | KENDALL A, HAWKE J, JANZ D,et al .Learning to drive in a day[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Montreal:IEEE,2019:8248-8254. |
| 7 | DOSOVITSKIY A,ROS G, CODEVILLA F,et al .CARLA:an open urban driving simulator[C]∥ Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Robot Learning.New York:ML Research Press,2017:1-16. |
| 8 | SAXENA D M,BAE S, NAKHAEI A,et al .Driving in dense traffic with model-free reinforcement learning[C]∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Paris:IEEE,2020:5385-5392. |
| 9 | 邓小豪,侯进,谭光鸿,等 .基于强化学习的多目标车辆跟随决策算法[J].控制与决策,2021,36(10):2497-2503. |
| DEND Xiaohao, HOU Jin, TAN Guanghong,et al .Multi-objective vehicle following decision algorithm based on reinforcement learning[J].Control and Decision,2021,36(10):2497-2503. | |
| 10 | TOROMANOFF M, WIRBEL E, MOUTARDE F .End-to-end model-free reinforcement learning for urban driving using implicit affordances[C]∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Seattle:IEEE,2020:7153-7162. |
| 11 | CAI P, WANG H, SUN Y,et al .DiGNet:learning scalable self-driving policies for generic traffic scenarios with graph neural networks[C]∥ Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.Prague:IEEE,2021:8979-8984. |
| 12 | CHEN J, YUAN B, TOMIZUKA M .Model-free deep reinforcement learning for urban autonomous driving[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference.Auckland:IEEE,2019:2765-2771. |
| 13 | AGARWAL T, ARORA H, SCHNEIDER J .Learning urban driving policies using deep reinforcement learning[C]∥ Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference.Indianapolis:IEEE,2021:607-614. |
| 14 | KARGAR E, KYRKI V .Increasing the efficiency of policy learning for autonomous vehicles by multi-task representation learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles,2022,7(3):701-710. |
| 15 | ZHANG Z, LINIGER A, DAI D,et al .End-to-end urban driving by imitating a reinforcement learning coach[C]∥ Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:15222-15232. |
| 16 | HAN Y, YILMAZ A .Learning to drive using sparse imitation reinforcement learning[C]∥ Proceedings of 2022 the 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition.Montreal:IEEE,2022:3736-3742. |
| 17 | CODEVILLA F, SANTANA E, LóPEZ A M,et al .Exploring the limitations of behavior cloning for autonomous driving[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Seoul:IEEE,2019:9328-9337. |
| 18 | CHITTA K, PRAKASH A, JAEGER B,et al .Transfuser:imitation with transformer-based sensor fusion for autonomous driving[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2023,45(11):12878-12895. |
| 19 | CHITTA K, PRAKASH A, GEIGER A .NEAT:neural attention fields for end-to-end autonomous driving[C]∥ Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:15793-15803. |
| 20 | LILLICRAP T P, HUNT J J, PRITZEL A,et al .Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning [EB/OL].(2019-07-05)[2023-07-28].. |
| 21 | FUJIMOTO S, VAN HOOF H, MEGER D .Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods[C]∥ Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning.New York:ML Research Press,2018:1587-1596. |
| 22 | SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P,et al .Proximal policy optimization algorithms[EB/OL].(2017-08-28)[2023-07-28].. |
| 23 | HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, ABBEEL P,et al .Soft actor-critic:off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor[C]∥ Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning.New York:ML Research Press,2018:1861-1870. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |