

收稿日期: 2023-05-15
网络出版日期: 2023-07-12
基金资助
广东省自然科学基金面上项目(2021A1515010638)
Effect of Tea Polyphenols on Soy Protein Isolate-Stabilized Emulsions and Interfacial Protein Displacement by Bile Salts
Received date: 2023-05-15
Online published: 2023-07-12
Supported by
the General Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021A1515010638)
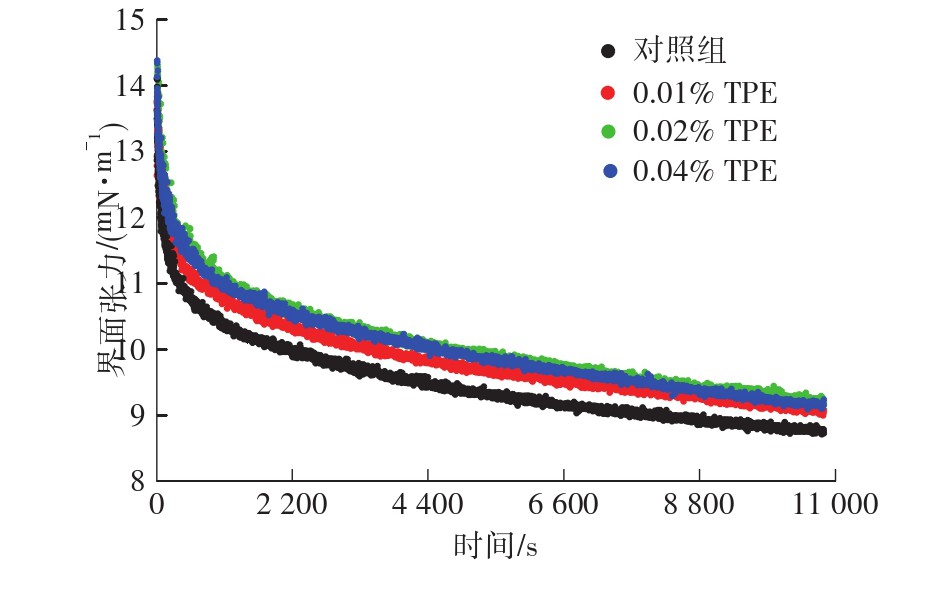
通过添加不同含量的茶多酚提取物修饰大豆分离蛋白制备水包油乳液,考察大豆分离蛋白乳液的界面张力、蛋白吸附比例、乳液粒径以及Zeta电位等性质变化,探究茶多酚对大豆分离蛋白乳液性质和界面蛋白置换的影响。实验结果表明:添加茶多酚后,大豆分离蛋白的界面张力升高;大豆分离蛋白溶液(1%,质量分数)按照9∶1(质量比)与大豆油混合后,经过高速剪切和超声制备成水包油乳液,添加茶多酚制备的乳液稳定性提高,与空白对照组相比,当茶多酚添加量为0.04%时,乳液平均粒径从1.702 μm显著下降至1.203 μm(P < 0.05),乳液的蛋白吸附比例从9.22%显著上升至20.68%(P < 0.05),Zeta电位绝对值从25.7 mV显著上升至27.1 mV(P < 0.05);大豆分离蛋白在油-水界面上具有抗胆盐置换的特性,由茶多酚修饰的大豆分离蛋白更加难以被胆盐置换,这可能是添加茶多酚后大豆分离蛋白具有较强的静电相互作用以及较厚的界面层导致的。肠道中的脂质消化是界面过程,探究脂滴界面上蛋白与胆盐的置换反应对研究脂质代谢和食品精准设计具有指导作用。
葛鸽, 林立, 郑家宝, 等 . 茶多酚对大豆分离蛋白乳液性质及界面蛋白胆盐置换的影响[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024 , 52(4) : 26 -32 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230325
The soy protein isolate was modified by adding different concentrations of tea polyphenols extract to prepare the oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion. The interfacial tension, interfacial protein adsorption fraction, emulsion particle size and zeta potential were investigated to explore the effect of tea polyphenols on the properties of soy protein isolate emulsion and interfacial protein displacement. The results show that the interfacial tension of soy protein isolate is increased after the addition of tea polyphenols. When soy protein isolate (1%, mass concentration) and soy oil are prepared into O/W emulsion with 9∶1 mass ratio by high-speed shear and ultrasound, tea polyphenols addition can improve the emulsion stability. Compared to the blank control group, when the amount of tea polyphenols added is 0.04%, the particle size of emulsion decreases significantly from 1.702 μm to 1.203 μm (P < 0.05), the protein adsorption fraction increases significantly from 9.22% to 20.68% (P < 0.05), and the zeta potential increases significantly from 25.7 mV to 27.1 mV (P < 0.05), respectively. Soy protein isolate shows resistance to bile salts displacement at the oil-water interface. In addition, the soy protein isolate modified by tea polyphenols is more difficult to be displaced by bile salts because of the strong electrostatic interaction and the thicker interface layer. Lipid digestion in intestine is an interfacial process. Exploring the interfacial displacement between protein and bile salts is beneficial to the study of lipid metabolism and food precise design.

| 1 | NISHINARI K, FANG Y, GUO S,et al .Soy proteins:a review on composition,aggregation and emulsification[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2014,39:301-318. |
| 2 | TANG C-H .Nanostructured soy proteins:fabrication and applications as delivery systems for bioactives (a review)[J].Food Hydrocolloids, 2019,91:92-116. |
| 3 | JAMBRAK A R, LELAS V, MASON T J,et al .Physical properties of ultrasound treated soy proteins[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2009,93(4):386-393. |
| 4 | CHEN N, ZHAO Q, SUN W,et al .Effects of malondialdehyde modification on the in vitro digestibility of soy protein isolate[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(49):12139-12145. |
| 5 | DELFANIAN M, RAZAVI S M A, HADDAD-KHODAPARAST M H,et al .Influence of main emulsion components on the physicochemical and functional properties of W/O/W nano-emulsion:effect of polyphenols,Hi-Cap,basil seed gum,soy and whey protein isolates[J].Food Research International,2018,108:136-143. |
| 6 | LIU F, MA C, ZHANG R,et al .Controlling the potential gastrointestinal fate of beta-carotene emulsions using interfacial engineering:impact of coating lipid droplets with polyphenol-protein-carbohydrate conjugate[J].Food Chemistry,2017,221:395-403. |
| 7 | GOLDING M, WOOSTER T J .The influence of emulsion structure and stability on lipid digestion[J].Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science,2010,15(1/2):90-101. |
| 8 | MALDONADO-VALDERRAMA J, WILDE P,MACIER- ZANKA A,et al .The role of bile salts in digestion[J].Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2011,165(1):36-46. |
| 9 | SARKAR A, ZHANG S, HOLMES M,et al .Colloidal aspects of digestion of Pickering emulsions:experiments and theoretical models of lipid digestion kinetics[J].Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2019,263:195-211. |
| 10 | SARKAR A, HORNE D S, SINGH H .Interactions of milk protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions with bile salts in a simulated upper intestinal model[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2010,24(2/3):142-151. |
| 11 | CAO Y, AI N, TRUE A D,et al .Effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate incorporation on the physicochemical and oxidative stability of myofibrillar protein-soybean oil emulsions[J].Food Chemistry,2018,245:439-445. |
| 12 | TIAN L, KEJING Y, ZHANG S,et al .Impact of tea polyphenols on the stability of oil-in-water emulsions coated by whey proteins[J].Food Chemistry,2021,343:128448/1-9. |
| 13 | ZHAO M, JIAO M, ZHOU F,et al .Interaction of beta-conglycinin with catechin-impact on physical and oxidative stability of safflower oil-in-water emulsion[J].Food Chemistry,2018,268:315-323. |
| 14 | TAO F, JIANG H, CHEN W,et al .Covalent modification of soy protein isolate by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate:effects on structural and emulsifying properties[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2018,98(15):5683-5689. |
| 15 | JU M, ZHU G, HUANG G,et al .A novel pickering emulsion produced using soy protein-anthocyanin complex nanoparticles[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2020,99:105329/1-8. |
| 16 | 沈鹏辉 .基于可控酶解制备大豆蛋白纳米颗粒及其乳液脂质消化的调控研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2020. |
| 17 | 沈鹏辉,樊诗堃,赵谋明,等 .氧化对大豆蛋白结构、乳液稳定性及消化特性的影响[J].食品科学,2019,40(14):7-14 |
| SHEN Penghui, FAN Shikun, ZHAO Mouming,et al .Influence of oxidation on soy protein structure,emulsion stability and lipid digestion[J].Food Science,2019,40(14):7-14. | |
| 18 | LESMES U, BAUDOT P, MCCLEMENTS D J .Impact of interfacial composition on physical stability and in vitro lipase digestibility of triacylglycerol oil droplets coated with lactoferrin and/or caseinate[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2010,58(13):7962-7969. |
| 19 | CHEN Y, HU J, YI X,et al .Interactions and emulsifying properties of ovalbumin with tannic acid[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,95:282-288. |
| 20 | ZHAN F, LI J, WANG Y,et al .Bulk,foam,and interfacial properties of tannic acid/sodium caseinate nanocomplexes[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(26):6832-6839. |
| 21 | SUN W, ZHOU F, SUN D-W,et al .Effect of oxidation on the emulsifying properties of myofibrillar proteins[J].Food and Bioprocess Technology,2012,6(7):1703-1712. |
| 22 | REN C, XIONG W, PENG D,et al .Effects of thermal sterilization on soy protein isolate/polyphenol complexes:aspects of structure,in vitro digestibility and antioxidant activity[J].Food Research International,2018,112:284-290. |
| 23 | LI Q, HE Q, XU M,et al .Food-grade emulsions and emulsion gels prepared by soy protein-pectin complex nanoparticles and glycyrrhizic acid nanofibrils[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(4):1051-1063. |
| 24 | DONG Y, LAN T, HUANG G,et al .Development and characterization of nanoparticles formed by soy peptide aggregate and epigallocatechin-3-gallate as an emulsion stabilizer[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,152:112385/1-9. |
| 25 | WALSTRA P .Dispersed systems:basic considerations[M]∥ FENNEMA O R.Food chemistry.3rd ed .New York:Marcel Dekker Inc.,1996:95-155. |
| 26 | SHAO Y, TANG C-H .Characteristics and oxidative stability of soy protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions:influence of ionic strength and heat pretreatment[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2014,37:149-158. |
| 27 | CHEN W, LIANG G, LI X,et al .Impact of soy proteins,hydrolysates and monoglycerides at the oil/water interface in emulsions on interfacial properties and emulsion stability[J].Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces,2019,177:550-558. |
| 28 | MUN S, DECKER E A, McCLEMENTS D J .Influence of emulsifier type on in vitro digestibility of lipid droplets by pancreatic lipase[J].Food Research International,2007,40(6):770-781. |
| 29 | BELLESI F A, PIZONES RUIZ-HENESTROSA V M, PILOSOF A M R .Behavior of protein interfacial films upon bile salts addition[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2014,36:115-122. |
| 30 | SINGH H, SARKAR A .Behaviour of protein-stabilised emulsions under various physiological conditions[J].Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2011,165(1):47-57. |
| 31 | YANG N, YE J, LI J,et al .Interfacial behaviour of beta-lactoglobulin aggregates at the oil-water interface studied using particle tracking and dilatational rheology[J].Soft Matter,2021,17(10):2973-2984. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |