

收稿日期: 2022-09-27
网络出版日期: 2022-12-05
基金资助
广东省重点领域研发计划项目(2018B030338001);广州市基础研究计划基础与应用基础研究项目(202201010595);广东省教育厅创新人才项目;广东工业大学“青年百人计划”项目(220413548)
Design and Implementation of Hardware Structure for Online Learning of Spiking Neural Networks Based on FPGA Parallel Acceleration
Received date: 2022-09-27
Online published: 2022-12-05
Supported by
the Key-Area R&D Program of Guangdong Province(2018B030338001)
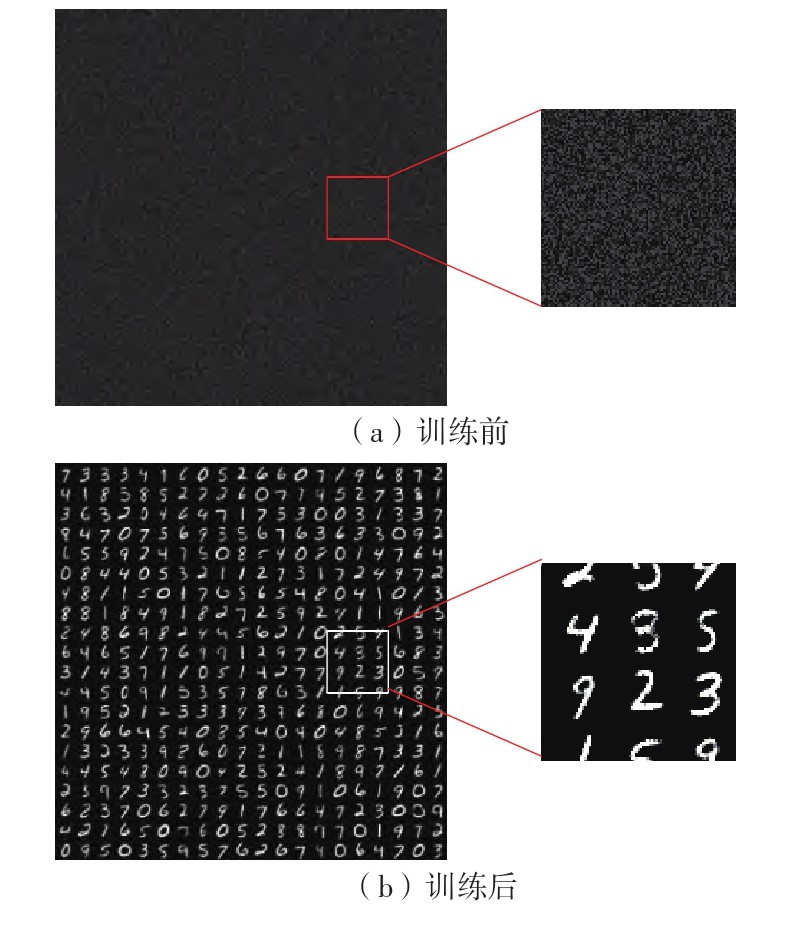
当前,基于数字电路的脉冲神经网络硬件设计,在学习功能方面的突触并行性不高,导致硬件整体延时较大,在一定程度上限制了脉冲神经网络模型在线学习的速度。针对上述问题,文中提出了一种基于FPGA并行加速的高效脉冲神经网络在线学习硬件结构,通过神经元和突触的双并行设计对模型的训练与推理过程进行加速。首先,设计具有并行脉冲传递功能和并行脉冲时间依赖可塑性学习功能的突触结构;然后,搭建输入编码层和赢家通吃结构的学习层,并优化赢家通吃网络的侧向抑制的实现,形成规模为784~400的脉冲神经网络模型。实验结果表明:在MNIST数据集上,使用该硬件结构的脉冲神经网络模型训练一幅图像需要的时间为1.61 ms、能耗约为3.18 mJ,推理一幅图像需要的时间为1.19 ms、能耗约为2.37 mJ,识别MNIST测试集样本的准确率可达87.51%;在文中设计的硬件框架下,突触并行结构能使训练速度提升38%以上,硬件能耗降低约24.1%,有助于促进边缘智能计算设备及技术的发展。
刘怡俊, 曹宇, 叶武剑, 等 . 基于FPGA并行加速的脉冲神经网络在线学习硬件结构的设计与实现[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023 , 51(5) : 104 -113 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220623
Currently, the hardware design of spiking neural networks based on digital circuits has a low synaptic parallel nature in terms of learning function, leading to a large overall hardware delay, which limits the speed of online learning of spiking neural network models to some extent. To address the above problems, this paper proposed an efficient spiking neural network online learning hardware architecture based on FPGA parallel acceleration, which accelerates the training and inference process of the model through the dual parallel design of neurons and synapses. Firstly, a synaptic structure with parallel spike delivery function and parallel spike time-dependent plasticity learning function was designed; then, the learning layers of input encoding layer and winner-take-all structure were built, and the implementation of lateral inhibition of the winner-take-all network was optimized, forming an impulsive neural network model with a scale of 784~400. The experiments show, the hardware has a training speed of 1.61 ms/image and an energy consumption of about 3.18 mJ/image for the SNN model and an inference speed of 1.19 ms/image and an energy consumption of about 2.37 mJ/image on the MNIST dataset, with an accuracy rate of 87.51%. Based on the hardware framework designed in this paper, the synaptic parallel structure can improve the training speed by more than 38%, and reduce the hardware energy consumption by about 24.1%, which can help to promote the development of edge intelligent computing devices and technologies.

Key words: neural network; learning algorithm; acceleration; parallel architecture
| 1 | STIMBERG M, BRETTE R, GOODMAN D F M .Brian 2,an intuitive and efficient neural simulator[J].Elife,2019,8:e47314/1-10. |
| 2 | CHOU T S, KASHYAP H J, XING J,et al .CARLsim 4:an open source library for large scale,biologically detailed spiking neural network simulation using heterogeneous clusters[C]∥ Proceedings of 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks.Rio de Janeiro:IEEE,2018:1158-1165. |
| 3 | LI S, ZHANG Z, MAO R,et al .A fast and energy-efficient SNN processor with adaptive clock/event-driven computation scheme and online learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers,2021,68(4):1543-1552. |
| 4 | SOLEIMANI H, AHMADI A, BAVANDPOUR M .Biologically inspired spiking neurons:piecewise linear models and digital implementation[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers,2012,59(12):2991-3004. |
| 5 | HEIDARPUR M, AHMADI A, AHMADI M,et al .CORDIC-SNN:on-FPGA STDP learning with Izhikevich neurons[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers,2019,66(7):2651-2661. |
| 6 | JOKAR E, SOLEIMANI H .Digital multiplierless realization of a calcium-based plasticity model[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ:Express Briefs,2017,64(7):832-836. |
| 7 | QUINTANA F M, PEREZ-PE?A F, GALINDO P L .Bio-plausible digital implementation of a reward modulated STDP synapse[J].Neural Computing and Applications,2022,34:15649-15660. |
| 8 | WU J, ZHAN Y, PENG Z,et al .Efficient design of spiking neural network with STDP learning based on fast CORDIC[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers,2021,68(6):2522-2534. |
| 9 | WAN L, LUO Y, SONG S,et al .Efficient neuron architecture for FPGA-based spiking neural networks[C]∥ Proceedings of 2016 the 27th Irish Signals and Systems Conference.Londonderry:IEEE,2016:1-6. |
| 10 | LIU Y, CHEN Y, YE W,et al .FPGA-NHAP:a general FPGA-based neuromorphic hardware acceleration platform with high speed and low power[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers,2022,69(6):2553-2566. |
| 11 | WANG Q, LI Y, SHAO B,et al .Energy efficient parallel neuromorphic architectures with approximate arithmetic on FPGA [J].Neurocomputing,2017,221:146-158. |
| 12 | HE Z, SHI C, WANG T,et al .A low-cost FPGA implementation of spiking extreme learning machine with on-chip reward-modulated STDP learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ:Express Briefs,2022,69(3):1657-1661. |
| 13 | DIEHL P U, COOK M .Unsupervised learning of digit recognition using spike-timing-dependent plasticity[J].Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience,2015,9:99/1-9. |
| 14 | VIGNERON A, MARTINET J .A critical survey of STDP in spiking neural networks for pattern recognition[C]∥ Proceedings of 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks.Glasgow:IEEE,2020:1-9. |
| 15 | GUO W, YANTIR H E, FOUDA M E,et al .Toward the optimal design and FPGA implementation of spiking neural networks[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2021,33(8):3988-4002. |
| 16 | MORRISON A, AERTSEN A, DIESMANN M .Spike-timing-dependent plasticity in balanced random networks[J].Neural Computation,2007,19(6):1437-1467. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |