

收稿日期: 2022-01-07
网络出版日期: 2022-04-22
基金资助
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61876010)
BiLSTM-BiDAF Named Entity Recognition Based on Machine Reading Comprehension
Received date: 2022-01-07
Online published: 2022-04-22
Supported by
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(61876010)
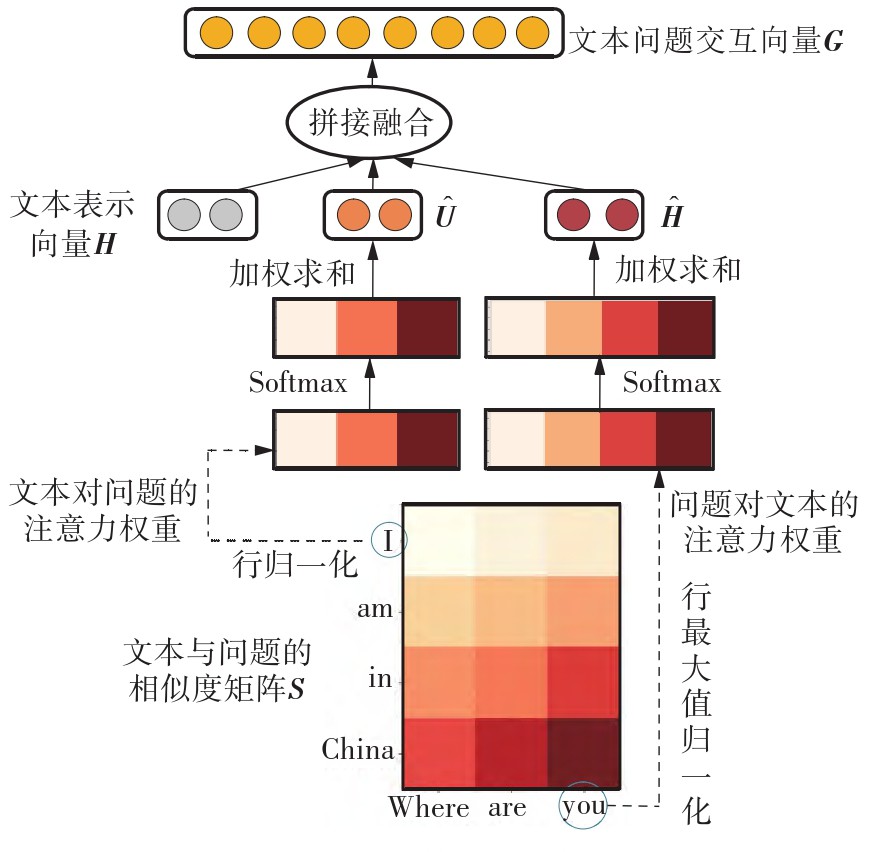
命名实体识别是自然语言处理的一项基本任务,对信息提取、机器翻译等具有重要的意义和价值。目前命名实体识别通常使用序列标注方法对文本中单个句子的实体进行抽取,忽略了句子间的语义信息。基于机器阅读理解的命名实体识别方法借助问题编码了实体类别的重要先验信息,更加容易区分出相似的分类标签,降低了模型学习难度,但仍然只在句子级别建模,忽略了句子间的语义信息,容易造成不同句子中实体标注不一致的问题。为此,文中将句子级别的命名实体识别扩展到文本级别的命名实体识别,提出了一种基于机器阅读理解的BiLSTM-BiDAF命名实体识别模型。首先,为了充分挖掘文本的上下文特征,使用NEZHA获取全文语境信息,并进一步通过BiLSTM提取局部特征,以加强模型对局部依赖信息的捕获能力;然后,引入双向注意力机制学习文本与实体类别之间的语义关联;最后,设计基于门控机制的边界检测器加强实体边界的相关关系,预测出实体在文本中的位置,同时通过建立答案数量检测器,将无答案问题识别出来。在CCKS2020中文电子病历数据集和CMeEE数据集上的实验结果表明,文中构建的模型能有效地识别文本中的命名实体,F1值可分别达到84.76%和57.35%。
王洁, 夏晓明 . 基于机器阅读理解的BiLSTM-BiDAF命名实体识别[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022 , 50(12) : 80 -88 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220013
Named entity recognition is a fundamental task of natural language processing (NLP) and plays an important role in many downstream NLP tasks, including information extraction and machine translation, etc. The existing named entity recognition methods are usually based on sequence labeling and extract entities within a sentence independently. These methods ignore the semantic information between sentences. Named entity recognition methods based on machine reading comprehension encode important prior information about the entity class. It is easier to distinguish similar classification labels, which reduces the difficulty of model learning, but it still only models at the sentence level, ignoring the semantic information between sentences, which is easy to cause the problem of inconsistent entity labeling in different sentences. To this end, this paper extended the sentence-level named entity recognition to the text-level named entity recognition, and then proposed a BiLSTM-BiDAF named entity recognition model based on machine reading comprehension. First, to utilize the context information within the whole text, NEZHA pre-training language model was used to obtain information of the full text and local features were further captured through BiLSTM, so as to strengthen the model’s ability to capture locally dependent information. Then, a bidirectional attention flow was introduce to learn the semantic association between the text and entity category. Finally, to predict the position of entities in the text, a boundary detector based on the gating mechanism was design to strengthen the correlation of the entity boundary. At the same time, an answer count detector was establish to identify the unanswerable questions. Experimental results on the CCKS2020 Chinese electronic medical records dataset and CMeEE dataset show that our model can effectively identify document-level and sentence-level named entities, and F1 can reach 84.76% and 57.35%, respectively.

| 1 | SHEN Y, MA X, TAN Z,et al .Locate and label:a two-stage identifier for nested named entity recognition [C]∥ Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing.Stroudsburg:Association for Computational Linguistics,2021:2782-2794. |
| 2 | LI J, SUN A, HAN J,et al .A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition [J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2022,34(1):50-70. |
| 3 | 刘奕洋,余正涛,高盛祥,等 .基于机器阅读理解的中文命名实体识别方法[J].模式识别与人工智能,2020,33(7):653-659. |
| 3 | LIU Yiyang, YU Zhengtao, GAO Shengxiang,et al .Chinese named entity recognition method based on machine reading comprehension [J].Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence,2020,33(7):653-659. |
| 4 | HUANG Z, XU W, YU K .Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging [EB/OL].(2015-08-09) [2022-01-07].. |
| 5 | HABIBI M, WEBER L, NEVES M,et al .Deep lear-ning with word embeddings improves biomedical named entity recognition [J].Bioinformatics,2017,33(14):i37-i48. |
| 6 | WANG X, ZHAMG Y, REN X,et al .Cross-type biomedical named entity recognition with deep multi-task lear-ning [J].Bioinformatics,2019,35(10):1745-1752. |
| 7 | YU H,KO Y .Expansion of word representation for named entity recognition based on bidirectional LSTM CRFs [J].Journal of KIISE,2017,44(3):306-313. |
| 8 | 郭知鑫,邓小龙 .基于BERT-BiLSTM-CRF的法律案件实体智能识别方法[J].北京邮电大学学报,2021,44(4):129-134. |
| 8 | GUO Zhi-xin, DENG Xiao-long .Intelligent identification method of legal case entity based on BERT-BiLSTM-CRF [J].Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,2021,44(4):129-134. |
| 9 | REI M, CRICHTON G, PYYSALO S .Attending to characters in neural sequence labeling models [C]∥ Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics.Stroudsburg:Association for Computational Linguistics,2016:309-318. |
| 10 | DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K,et al .BERT:pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2019 Confe-rence of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:Human Language Technologies.Minneapolis:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:4171-4186. |
| 11 | RADMARD P, FATHULLAH Y, LIPANI A . Subsequence based deep active learning for named entity recognition [C]∥ Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing.Stroudsburg:Association for Computational Linguistics,2021:4310-4321. |
| 12 | MA R, PENG M, ZHANG Q,et al .Simplify the usage of lexicon in Chinese NER [C]∥ Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.Stroudsburg:Association for Computational Linguistics,2020:5951-5960. |
| 13 | LU T, GUI Y, GAO Z .Document-level named entity recognition with Q-network [C]∥ Proceedings of the 16th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Cham:Springer,2019:164-178. |
| 14 | LEVY O, SEO M, CHOI E,et al .Zero-shot relation extraction via reading comprehension [C]∥ Proceedings of the 21st Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning.Stroudsburg:Association for Computational Linguistics,2017:333-342. |
| 15 | LI X, YIN F, SUN Z,et al .Entity-relation extraction as multi-turn question answering [C]∥ Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.Minneapolis:Association for Computational Linguistics,2019:1340-1350. |
| 16 | LI X, FENG J, MENG Y,et al .A unified MRC framework for named entity recognition [C]∥ Procee-dings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.Stroudsburg:Association for Computational Linguistics,2020:5849-5859. |
| 17 | XUE M, YU B, ZHANG Z,et al .Coarse-to-fine pre-training for named entity recognition [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing.Stroudsburg:Association for Computational Linguistics,2020:6345-6354. |
| 18 | HU A, DOU Z, NIE J Y,et al .Leveraging multi-token entities in document-level named entity recognition [C]∥ Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Menlo Park:AAAI,2020:7961-7968. |
| 19 | WEI J, REN X, LI X,et al .NEZHA:neural contextualized representation for Chinese language understanding [EB/OL].(2019-08-31) [2022-01-07].. |
| 20 | ZHANG W, JIANG S, ZHAO S,et al .A BERT-BiLSTM-CRF model for Chinese electronic medical records named entity recognition [C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 the 12th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation.Xiangtan:IEEE,2019:166-169. |
| 21 | STRUBELL E, VERGA P, BELANGER D,et al .Fast and accurate entity recognition with iterated dilated convolutions [C]∥ Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing.Copenhagen:Association for Computational Linguistics,2017:2670-2680. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |