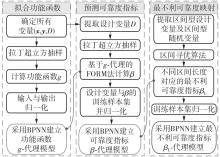
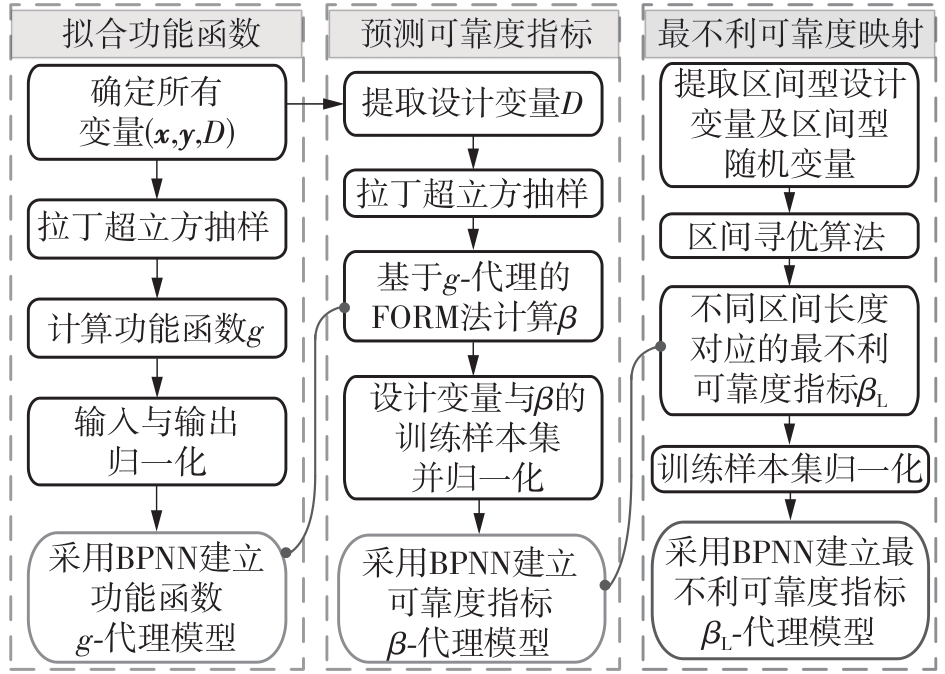
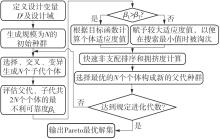
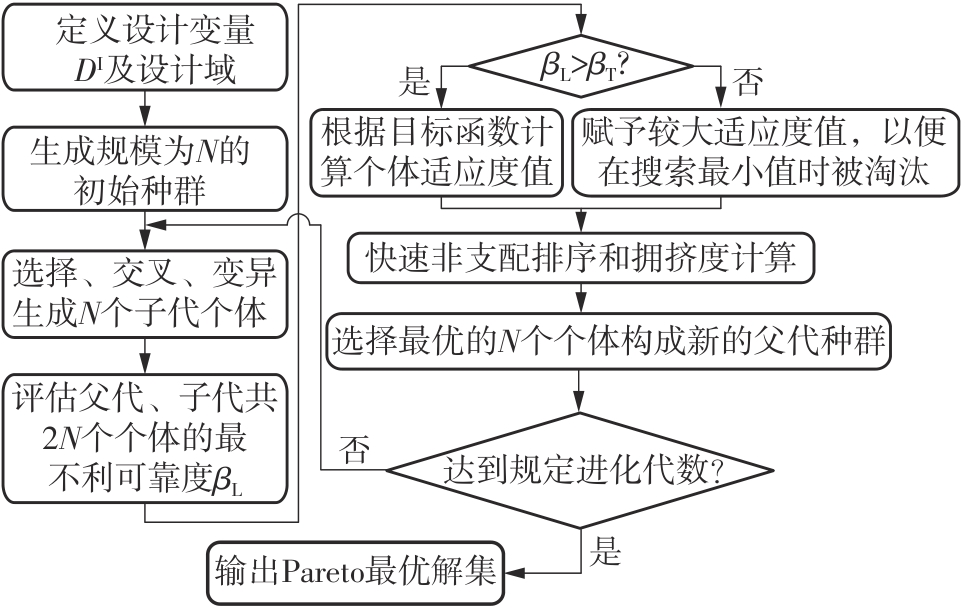
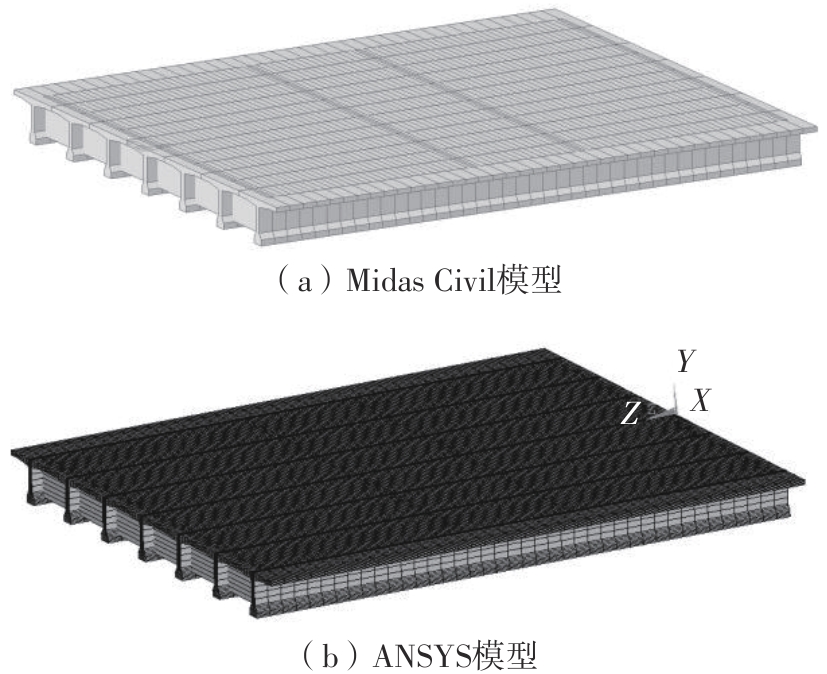
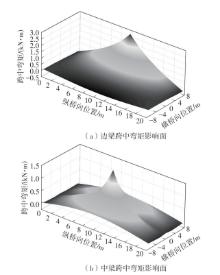
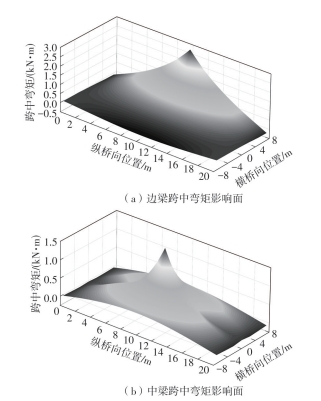
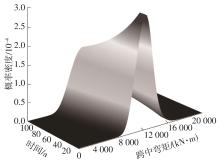
| 1 |
王凌波 .在役预应力梁桥残余承载力评估方法研究[D].西安:长安大学公路学院,2011.
|
| 2 |
吴海军,陈艾荣 .桥梁结构耐久性设计方法研究[J].中国公路学报,2004,17(3):60-64,70.
|
|
WU Hai-jun, CHEN Ai-rong .Sudy of durability design method for bridge structures[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2004,17(3):60-64,70.
|
| 3 |
彭卫兵,沈佳栋,唐翔,等 .近期典型桥梁事故回顾、分析与启示[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(12):132-144.
|
|
PENG Wei-bing, SHEN Jia-dong, TANG Xiang,et al .Review,analysis,and insights on recent typical bridge accidents[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2019,32(12):132-144.
|
| 4 |
王枫,吴华勇,赵荣欣 .国内外近三年桥梁坍塌事故原因与经验教训[J].城市道桥与防洪,2020(7):73-76,13.
|
|
WANG Feng, WU Huayong, ZHAO Rongxin .Causes and lessons of bridges collapse accidents in past three years at home and abroad[J].Urban Roads Bridges & Flood Control,2020(7):73-76,13.
|
| 5 |
吉伯海,傅中秋 .近年国内桥梁倒塌事故原因分析[J].土木工程学报,2010,43(S1):495-498.
|
|
JI Bohai, FU Zhongqiu .Analysis of Chinses bridge collapse accident causes in recent years[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2010,43(S1):495-498.
|
| 6 |
张劲泉,李鹏飞,董振华,等 .服役公路桥梁可靠性评估的若干问题探究[J].土木工程学报,2019,52(S1):159-173.
|
|
ZHANG Jinquan, LI Pengfei, DONG Zhenhua,et al .Study on some reliability evaluation problems of existing highway bridges[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2019,52(S1):159-173.
|
| 7 |
李宏男,董皓璐,李超 .基于全寿命周期抗震性能的桥梁结构维修决策方法研究进展[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(2):1-14.
|
|
LI Hong-nan, DONG Hao-lu, LI Chao .Research progress on life-cycle performance-based seismic maintenance decision method for bridge structures[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2020,33(2):1-14.
|
| 8 |
MORI Y, ELLINGWOOD B R .Reliability-based service-life assessment of aging concrete structures[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,1993,119(5):1600-1621.
|
| 9 |
OKASHA N, FRANGOPOL D .Computational platform for the integrated life-cycle management of highway bridges[J].Engineering Structures,2011,33(7):2145-2153.
|
| 10 |
GHODOOSI F, ABU-SAMRA S, ZEYNALIAN M,et al .Maintenance cost optimization for bridge structures using system reliability analysis and genetic algorithms[J].Journal of Construction Engineering and Management,2018,144(2):101-116.
|
| 11 |
庞博 .气候变化背景下PC桥梁生命周期维修加固综合策略优化[D].北京:北京交通大学,2018.
|
| 12 |
罗玮 .基于计划行为和多属性效用理论的PC桥梁可持续加固策略[D].北京:北京交通大学,2021.
|
| 13 |
李林春 .基于长期WIM数据的公路桥梁车辆荷载模型及效应研究[D].兰州:兰州理工大学,2022.
|
| 14 |
中国汽车工业总公司 .中国汽车车型手册[M].济南:山东科学技术出版社,1993.
|
| 15 |
安振源 .基于实桥车辆调查的在役桥梁可靠度研究[D].西安:长安大学,2010.
|
| 16 |
交通部专家委员会 .公路桥梁通用图[M].北京:人民交通出版社,2008.
|
| 17 |
陈水生,赵辉,李锦华,等 .实际车流荷载作用的混凝土梁桥可靠度评估[J].振动与冲击,2022,41(20):158-167.
|
|
CHEN Shuisheng, ZHAO Hui, LI Jinhua,et al .Reliability assessment of a concrete beam bridge under actual traffic load[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2022,41(20):158-167.
|
| 18 |
ENRIGHT M P, FRANGOPOL D M .Service-life prediction of deteriorating concrete bridges[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,1998,124(3):309-317.
|
| 19 |
赵国藩 .工程结构可靠性理论与应用[M].大连:大连理工大学出版社,1996.
|
| 20 |
王涛 .基于WIM数据的钢筋混凝土桥梁限载研究[D].长沙:湖南大学,2021.
|
| 21 |
孙晓燕,黄承逵,赵国藩,等 .基于动态可靠度和经济优化相结合的服役桥梁维修加固风险决策[J].工程力学,2004,21(5):5-10.
|
|
SUN Xiao-yan, HUANG Cheng-kui, ZHAO Guo-fan,et al .Risk-ranking decision of repair and strengthening of existing bridges based on time-dependent reliability and economical optimization[J].Engineering Mechanics,2004,21(5):5-10.
|
| 22 |
徐岳,武同乐 .桥梁加固工程生命周期成本横向对比分析[J].长安大学学报(自然科学版),2004,24(3):30-34.
|
|
XU Yue, WU Tong-le .Comparative analysis of life-cycle cost for bridges strengthening[J].Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition),2004,24(3):30-34.
|
 ), 李鹏飞2, 吴润涵1, 杨文杰1, 李晨曦1
), 李鹏飞2, 吴润涵1, 杨文杰1, 李晨曦1
 ), LI Pengfei2, WU Runhan1, YANG Wenjie1, LI Chenxi1
), LI Pengfei2, WU Runhan1, YANG Wenjie1, LI Chenxi1