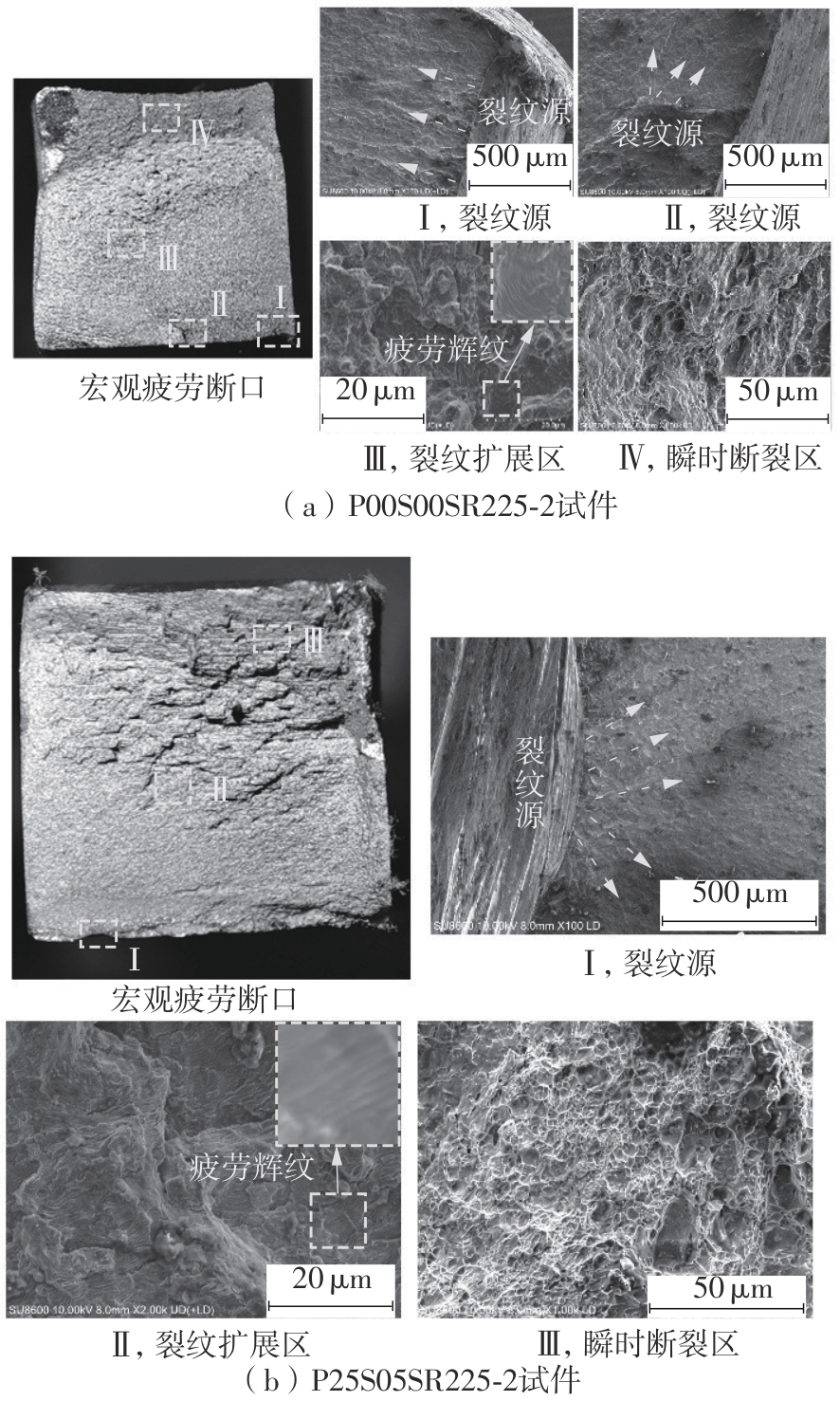
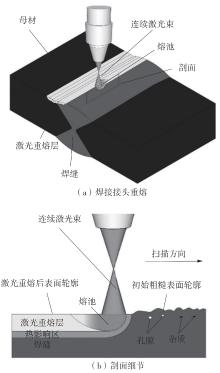
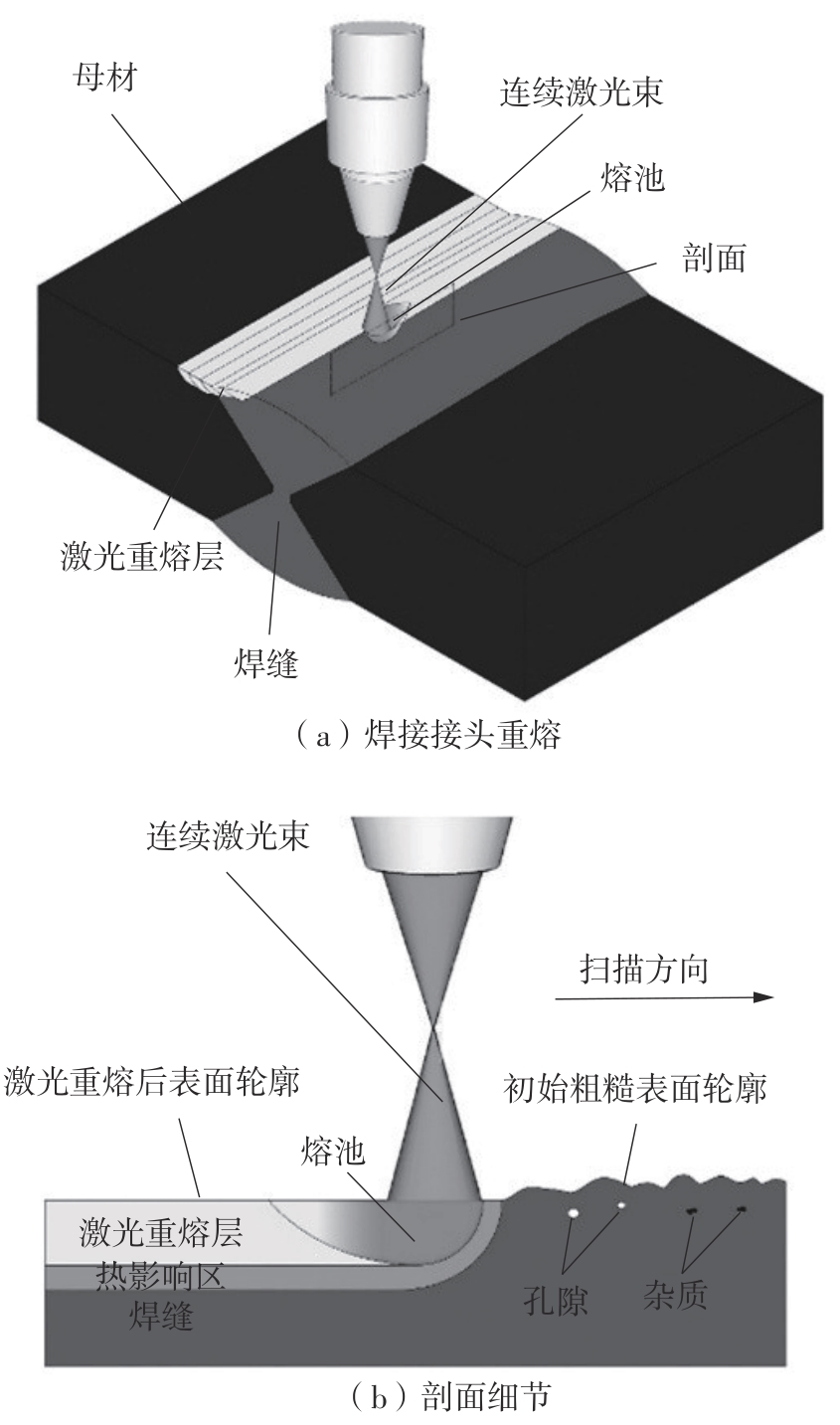
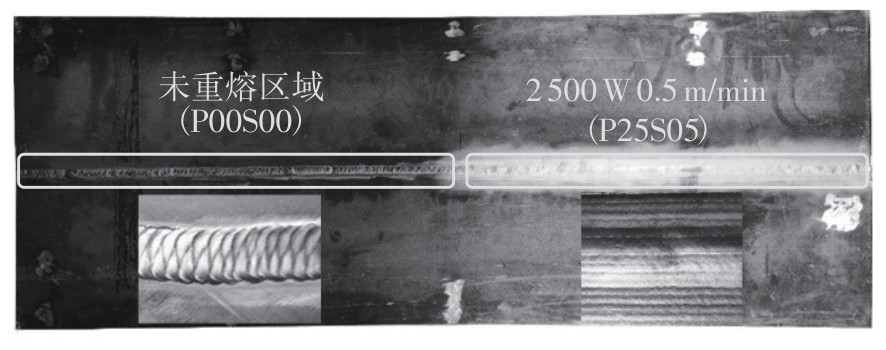
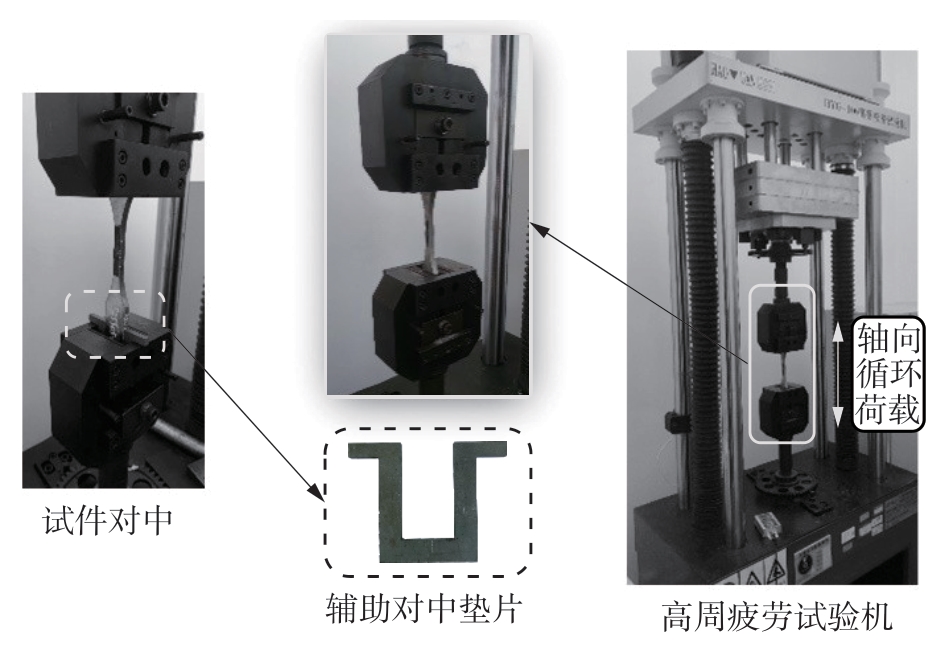
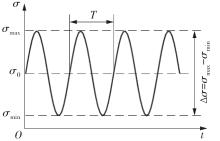
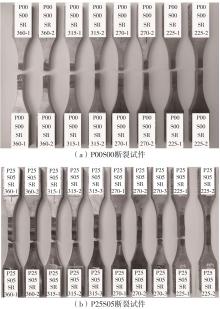
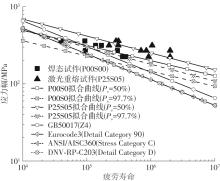
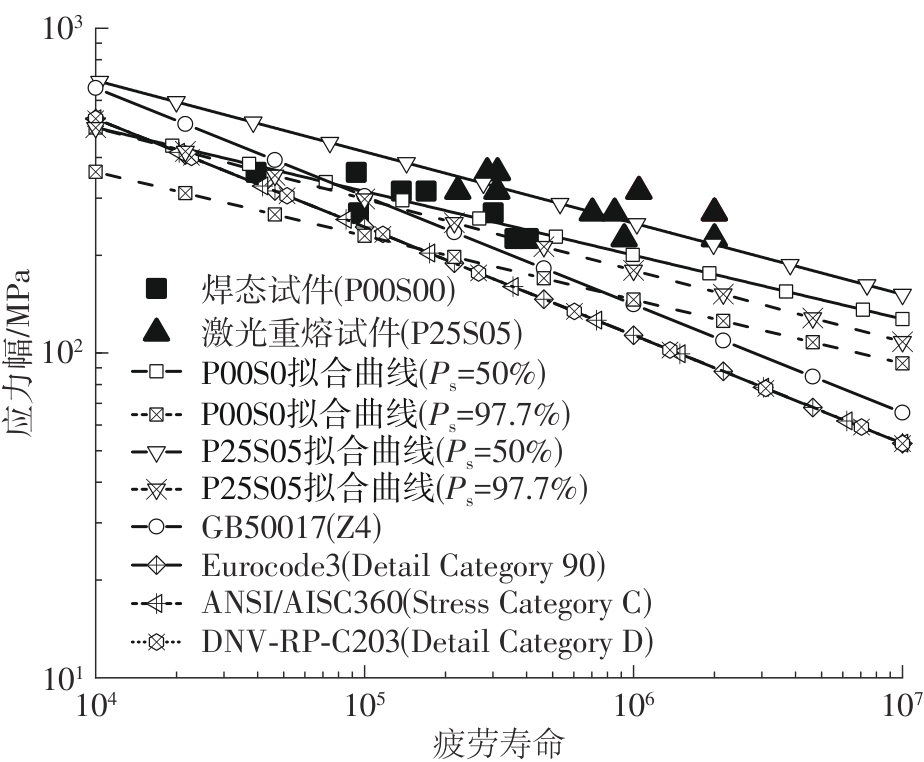
| 1 |
郭宏超,毛宽宏,万金怀,等 .高强度钢材疲劳性能研究进展[J].建筑结构学报,2019,40(4):17-28.
|
|
GUO Hongchao, MAO Kuanhong, WAN Jinhuai,et al .Research progress on fatigue properties of high strength steels[J].Journal of Building Structures,2019,40(4):17-28.
|
| 2 |
RADAJ D, SONSINO C M, FRICKE W .Recent deve-lopments in local concepts of fatigue assessment of welded joints[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2009,31(1):2-11.
|
| 3 |
WANG D Q Q, YAO D D, GAO Z B,et al .Fatigue mechanism of medium-carbon steel welded joint:competitive impacts of various defects[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2021,151:106363/1-11.
|
| 4 |
BRAUN M, WANG X .A review of fatigue test data on weld toe grinding and weld profiling[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2021,145:106073/1-16.
|
| 5 |
RAMALHO A L, FERREIRA J A M, BRANCO C A G M .Fatigue behaviour of T welded joints rehabilitated by tungsten inert gas and plasma dressing[J].Materials & Design,2011,32(10):4705-4713.
|
| 6 |
GAN J, SUN D, WANG Z,et al .The effect of shot peening on fatigue life of Q345D T-welded joint[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2016,126:74-82.
|
| 7 |
MALAKI M, DING H .A review of ultrasonic peening treatment[J].Materials & Design,2015,87:1072-1086.
|
| 8 |
DHAKAL B, SWAROOP S .Review:laser shock pee-ning as post welding treatment technique[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2018,32:721-733.
|
| 9 |
CHAN W L, CHENG H K F .Hammer peening techno-logy—the past,present,and future[J].International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2022,118(3/4):683-701.
|
| 10 |
CHAISE T, LI J, NELIAS D,et al .Modelling of multiple impacts for the prediction of distortions and residual stresses induced by ultrasonic shot peening (USP)[J].Journal of Materials Processing Techno-logy,2012,212(10):2080-2090.
|
| 11 |
CUNHA A, GIACOMELLI R O, KAUFMAN J,et al .An overview on laser shock peening process:from science to industrial applications[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 SBFoton International Optics and Photonics Conference (SBFoton IOPC).Sao Carlos,Brazil:IEEE,2021:1-6.
|
| 12 |
李坤,房嘉辉,廖若冰,等 .高性能金属激光能量场表面热处理技术研究现状及展望(特邀)[J].中国激光,2024,51(4):121-137.
|
|
LI Kun, FANG Jiahui, LIAO Ruobing,et al .Current research status and future prospects for high-performance metal laser-energy-field surface heat treatment technologies (invited)[J].China Journal of Laser,2024,51(4):121-137.
|
| 13 |
YU Y, ZHANG M, GUAN Y,et al .The effects of laser remelting on the microstructure and performance of bainitic steel[J].Metals,2019,9(8):912/1-12.
|
| 14 |
YAO Y, LI X, WANG Y Y,et al .Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Ti-Zr beta titanium alloy after laser surface remelting[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2014,583:43-47.
|
| 15 |
VIDYASAGAR K E C, RANA A, KALYANASUNDARAM D .Optimization of laser parameters for improved corrosion resistance of nitinol[J].Materials and Manufacturing Processes,2020,35(14):1661-1669.
|
| 16 |
李鸿鹏,盛金马,黎彬,等 .激光表面强化316L不锈钢的组织与性能研究[J].激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(19):199-204.
|
|
LI Hongpeng, SHENG Jinma, LI Bin,et al .Microstructures and properties of laser surface-reinforced 316L stainless steel[J].Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2020,57(19):199-204.
|
| 17 |
LAGO J, BOKŮVKA O, NOVÝ F .The weld toe improvement of advanced HSLA steel by laser remelting[J].Materials Today:Proceedings,2016,3(4):1037-1040.
|
| 18 |
STAMM H, HOLZWARTH U, BOERMAN D J,et al .Effect of laser surface treatment on high cycle fatigue of AISI 316L stainless steel[J].Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures,1996,19(8):985-995.
|
| 19 |
ZHAO X, ZHANG H, LIU Y .Effect of laser surface remelting on the fatigue crack propagation rate of 40Cr steel[J].Results in Physics,2019,12:424-431.
|
| 20 |
SARKAR S, KUMAR C S, NATH A K. Effects of different surface modifications on the fatigue life of selective laser melted 15-5 PH stainless steel[J].Mate-rials Science & Engineering A,2019,762:138109/1-14.
|
| 21 |
FROSTEVARG J, TORKAMANY M J, POWELL J,et al .Improving weld quality by laser re-melting[J].Journal of Laser Applications,2014,26(4):041502/1-4.
|
| 22 |
POWELL J, ILAR T, FROSTEVARG J,et al .Weld root instabilities in fiber laser welding[J].Journal of Laser Applications,2015,27:S29008/1-5.
|
| 23 |
邓德伟,马云波,马玉山,等 .重熔及退火对316L不锈钢激光熔覆层残余应力的影响[J].金属热处理,2020,45(8):113-118.
|
|
DENG Dewei, MA Yunbo, MA Yushan,et al .Influence of remelting and annealing on residual stress of 316L stainless steel laser clad layer[J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2020,45(8):113-118.
|
| 24 |
GUENNEC B, UENO A, SAKAI T,et al .Effect of the loading frequency on fatigue properties of JIS S15C low carbon steel and some discussions based on micro-plasticity behavior[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2014,66:29-38.
|
| 25 |
HONG Y, HU Y, ZHAO A .Effects of loading frequency on fatigue behavior of metallic materials:a li-terature review[J].Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures,2023,46(8):3077-3098.
|
| 26 |
LIAO X, WANG Y, WANG Z,et al .Effect of low temperatures on constant amplitude fatigue properties of Q345qD steel butt-welded joints[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2019,105:597-609.
|
| 27 |
TONG L W, NIU L C, REN Z Z,et al .Experimental investigation on fatigue behavior of butt-welded high-strength steel plates[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2021,165:107956/1-11.
|
| 28 |
Specification for structural steel buildings:ANSI/AI [S].
|
| 29 |
Eurocode 3:design of steel structure-Part 1-9:fatigue:EN 1993-1-9 [S].
|
| 30 |
Fatigue design of offshore steel structures:DNV-RP-C203 [S].
|
 ), LI Rongwen1, SU Jingyu1, FENG Lei2
), LI Rongwen1, SU Jingyu1, FENG Lei2