华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 71-83.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230385
EPB盾构刀盘泥饼成因分析及评价模型构建
- 1.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广东 广州 510640
2.华南岩土工程研究院,广东 广州 510640
-
收稿日期:2023-06-05出版日期:2024-05-25发布日期:2023-09-08 -
通信作者:杨辉泰(2000-),男,硕士,主要从事地下工程与结构研究。 E-mail:2641804764@qq.com -
作者简介:丁小彬(1984-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事岩土工程、地下工程等研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金资助项目(41827807);广东省现代土木工程技术重点实验室项目(2021B1212040003)
Formation Factor Analysis and Evaluation Model Construction of Mud Cake on EPB Cutterhead
DING Xiaobin1,2( ), YANG Huitai1(
), YANG Huitai1( ), SHI Yu1
), SHI Yu1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.South China Institute of Geotechnical Engineering,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-06-05Online:2024-05-25Published:2023-09-08 -
Contact:杨辉泰(2000-),男,硕士,主要从事地下工程与结构研究。 E-mail:2641804764@qq.com -
About author:丁小彬(1984-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事岩土工程、地下工程等研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(41827807)
摘要:
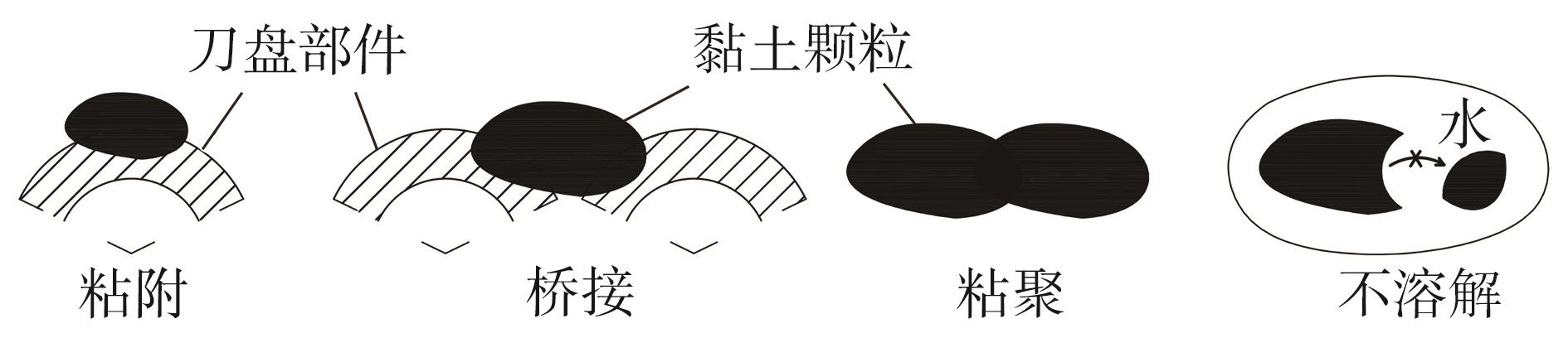
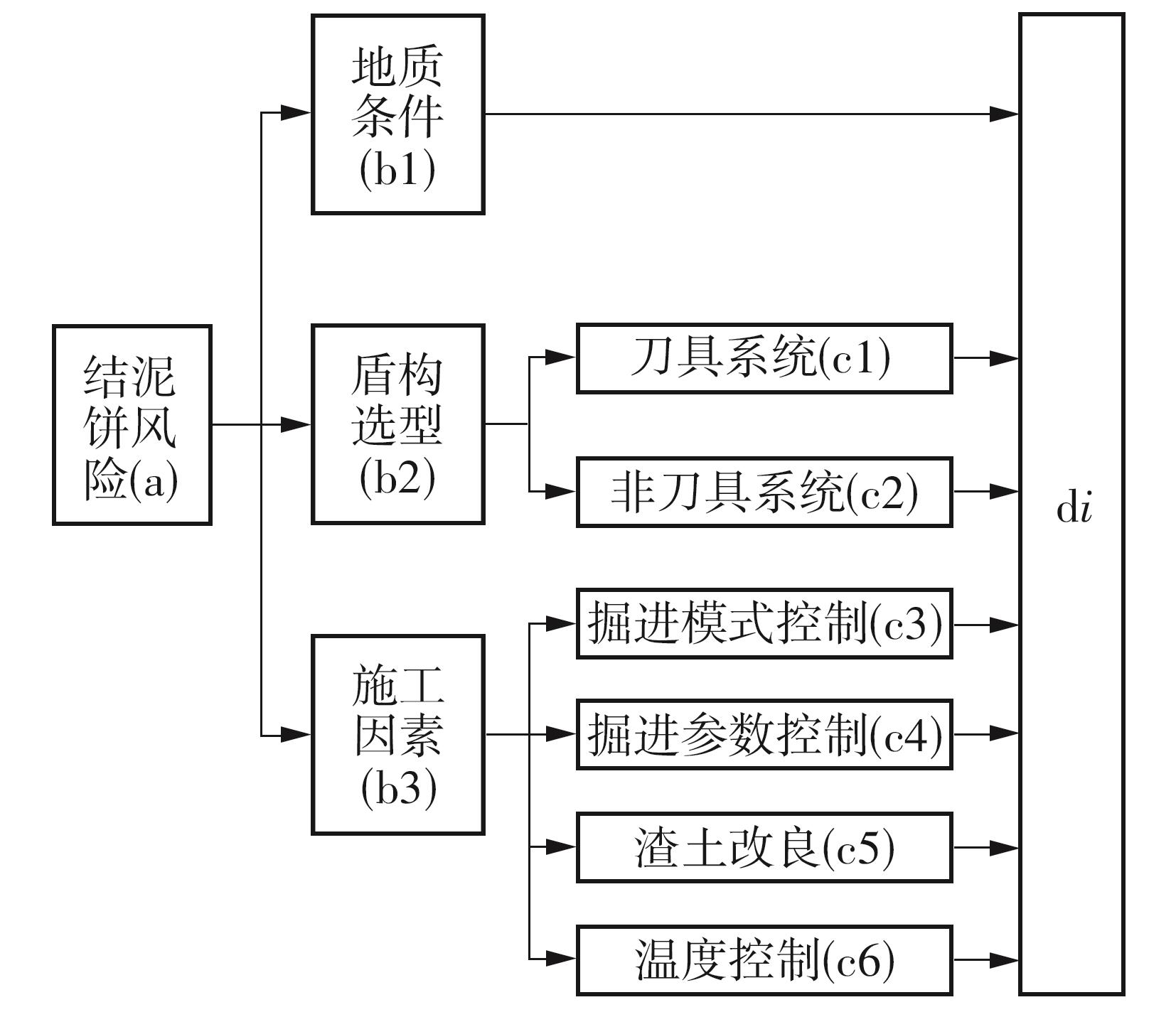
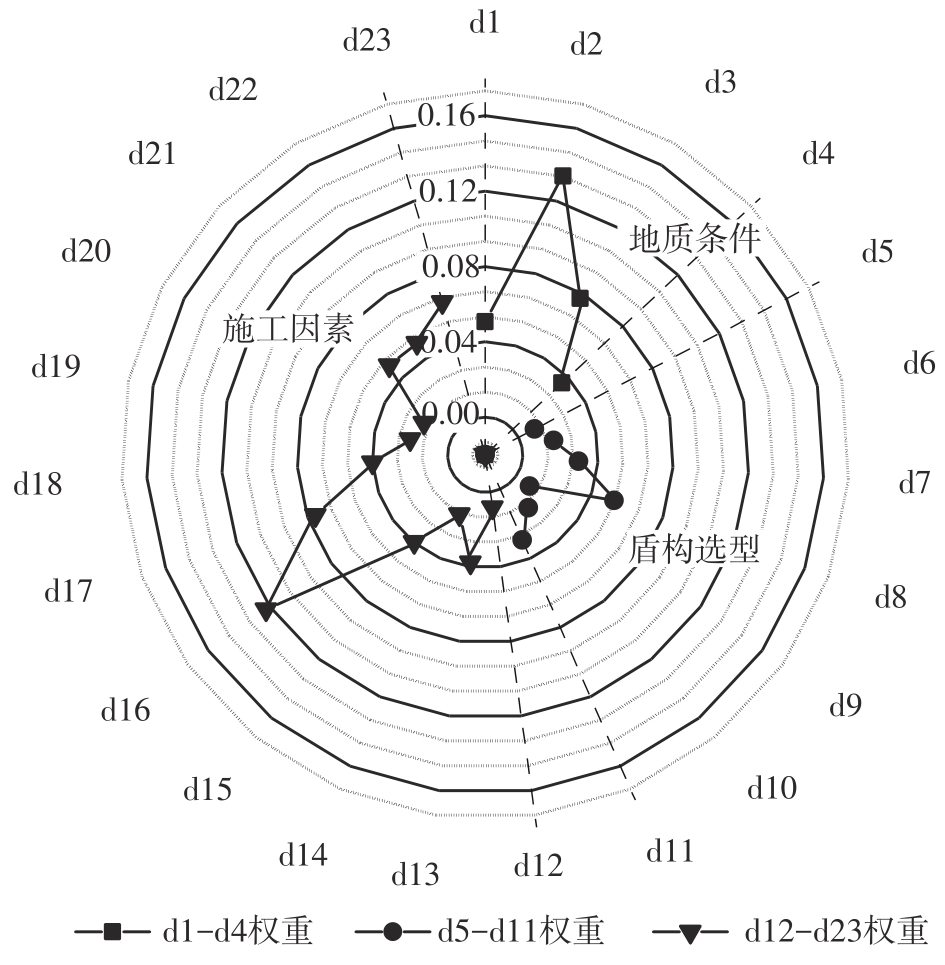
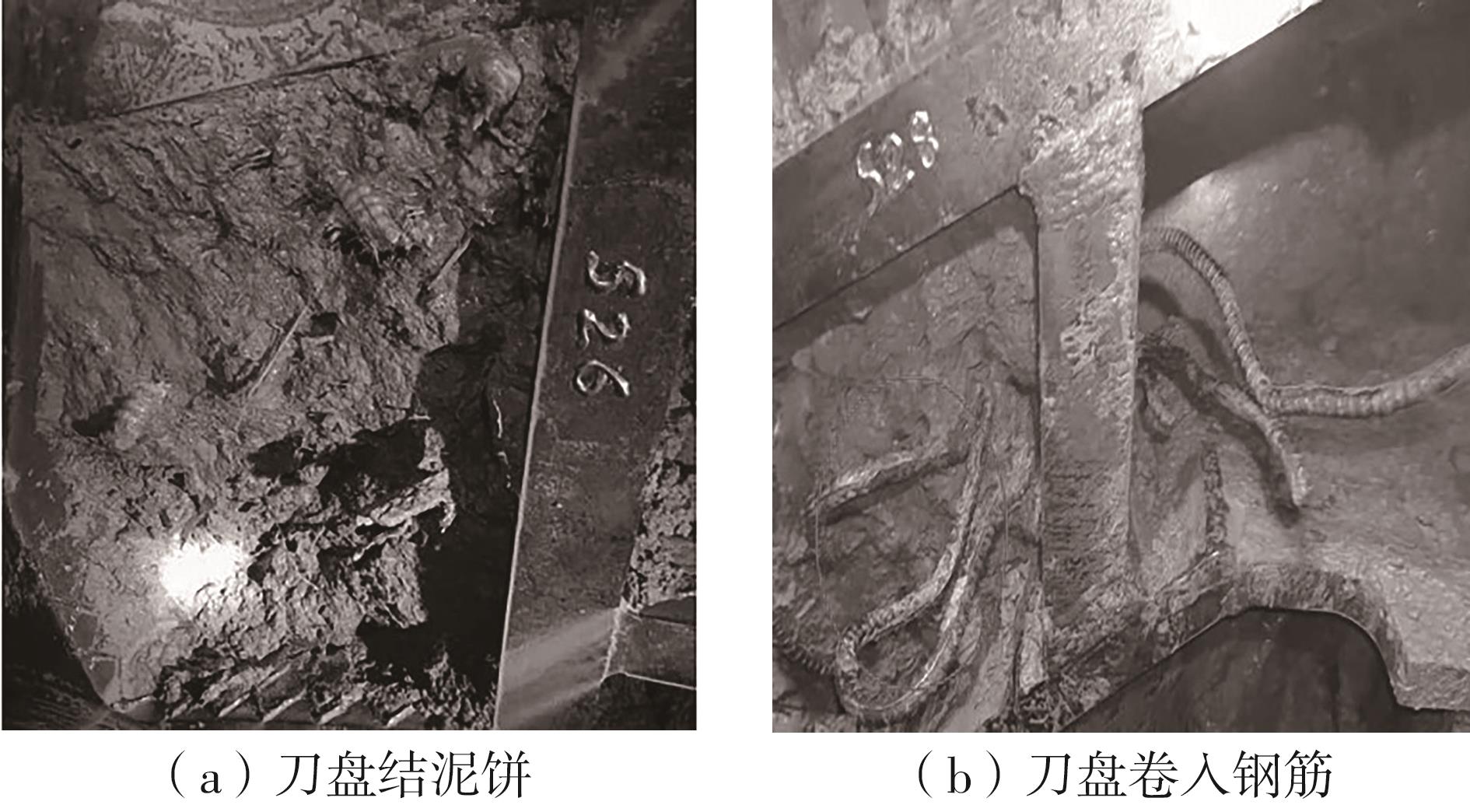
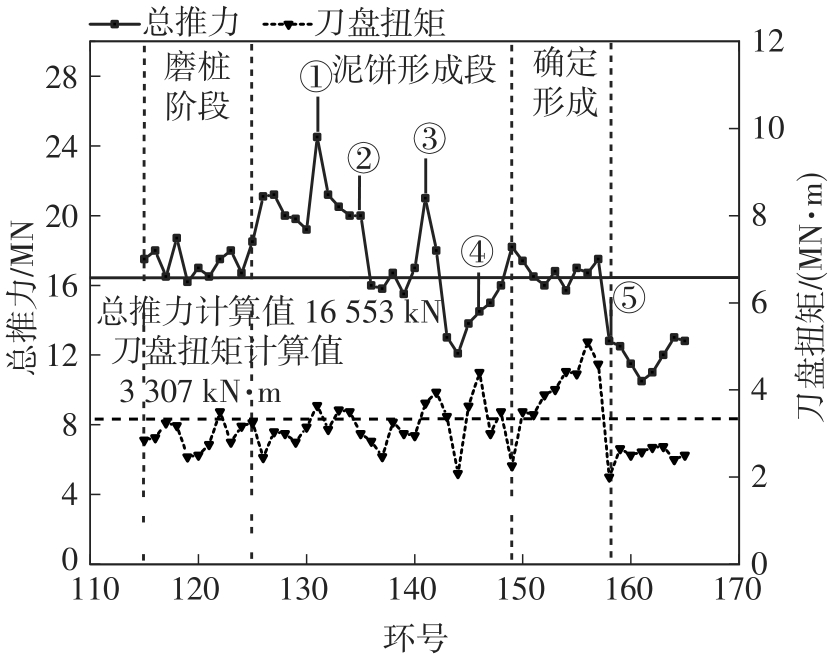
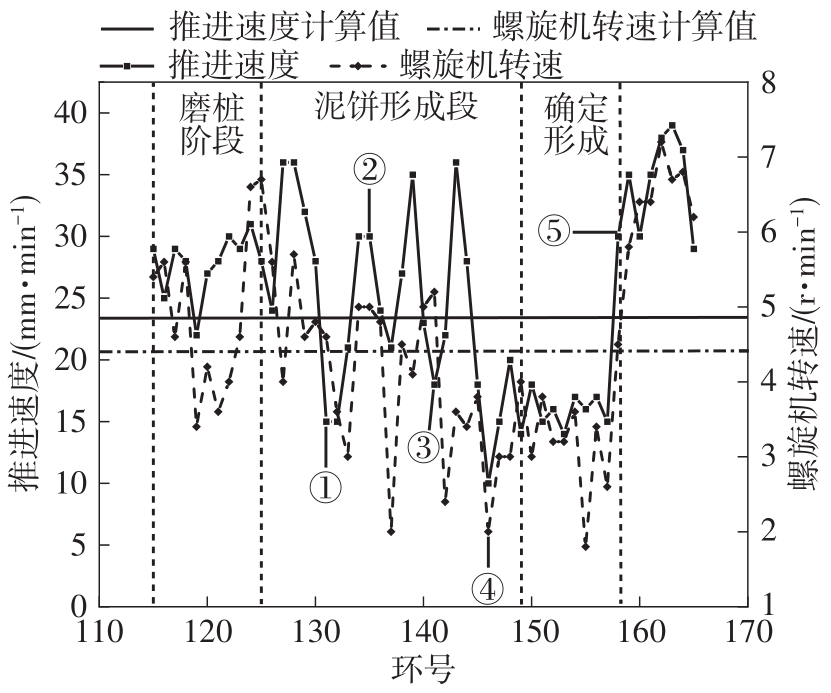
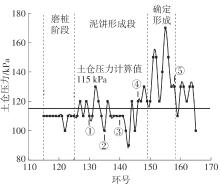
目前土压平衡(EPB)盾构机刀盘结泥饼的研究大都聚焦在单一因素上,缺少整体的、量化的评价标准,难以满足工程上对刀盘结泥饼的预测需求。针对以上问题,文中从地质条件、盾构选型、施工因素3个层面出发,系统总结了导致土压平衡盾构机刀盘泥饼形成的23个主要因素;将土压平衡盾构机在掘进过程中的刀盘结泥饼风险划分为4个等级:高风险、中风险、低风险和无风险。同时提出了结泥饼的风险因子量化标准,并结合层次分析法构建了土压平衡盾构的刀盘结泥饼风险评价模型;基于广州地铁14号线马创区间右线115-165环盾构隧道工程的掘进数据,计算出盾构机掘进过程中不同环的刀盘结泥饼风险程度,验证了刀盘结泥饼风险评价模型的预测性能。研究结果表明:结泥饼风险评价模型的23个影响因子中,以塑性指数、刀盘扭矩、液性指数、总推力的影响权重最大,启动扭矩的影响权重最小;结泥饼风险评价模型表现出了良好的预测性能,计算得到的结泥饼风险变化曲线与现场施工情况基本吻合;盾构掘进参数的变化能很好地反映掘进过程中泥饼的形成,其中总推力对泥饼产生最敏感,刀盘扭矩、土仓压力、推进速度和螺旋机转速的敏感度依次降低。研究成果可适用于类似工程中的土压平衡盾构机刀盘结泥饼的评价分析。
中图分类号:
引用本文
丁小彬, 杨辉泰, 施钰. EPB盾构刀盘泥饼成因分析及评价模型构建[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(5): 71-83.
DING Xiaobin, YANG Huitai, SHI Yu. Formation Factor Analysis and Evaluation Model Construction of Mud Cake on EPB Cutterhead[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 71-83.
表2
盾构选型影响因子量化表"
| 风险因子 | 高风险 | 中风险 | 低风险 | 无风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 刀具间距(d5) | 与理论值误差50%以上 | 与理论值误差25%~50% | 与理论值误差10%~25% | 与理论值误差10%以内 |
| 刀具高差(d6) | <20 mm | 20~35 mm | 35~50 mm | >50 mm |
| 刀具类型(d7) | 无针对性设计 | 少量针对性设计 | 部分针对性设计 | 针对性设计 |
| 刀具开口率(d8) | <33%或低于理论值25% | 33%~38%或低于理论值15% | 38%~45%或低于理论值5% | >45%或大于等于理论值 |
| 搅拌棒数量(d9) | <4 | 4~6 | 6~8 | >8 |
| 螺旋器相对伸入长度(d10) | <0.25 | 0.25~0.50 | 0.50~0.75 | >0.75 |
| 冲刷系统(d11) | 无冲刷系统 | 中心区域未设置冲刷孔 | 设置6路以上冲刷管道 | 设置10路以上冲刷管道且中心区域设置有冲刷孔 |
表3
施工因素影响因子量化表1)"
| 风险因子 | 高风险 | 中风险 | 低风险 | 无风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 启动扭矩(d12) | 大于地层土体摩擦力25%以上 | 大于地层土体 摩擦力10%~25% | 大于地层土体 摩擦力10%以内 | 等于地层土体摩擦力 |
| 渣土液面高度(d13) | 大于2/3土仓高度 | 1/2~2/3土仓高度 | 小于1/2土仓高度 | 空仓推进或气压辅助 |
| 停机时间(d14) | >12 h或6倍管片拼装时间 | 3~6倍管片拼装时间 | 2~3倍管片拼装时间 | 等于管片拼装时间 |
| 土仓压力(d15) | >1.60 max{T0,Te} | (1.40~1.60)max{T0,Te} | (1.10~1.40)max{T0,Te} | <1.10 max{T0,Te} |
| 刀盘扭矩(d16) | >1.50 max{T0,Te} | (1.30~1.50)max{T0,Te} | (1.10~1.30)max{T0,Te} | <1.10 max{T0,Te} |
| 总推力(d17) | >1.50 max{T0,Te} | (1.30~1.50)max{T0,Te} | (1.10~1.30)max{T0,Te} | <1.10 max{T0,Te} |
| 推进速度(d18) | <0.75 max{T0,Te} | (0.75~0.85)max{T0,Te} | (0.85~0.95)max{T0,Te} | >0.95 max{T0,Te} |
| 螺旋机转速(d19) | <0.75 max{T0,Te} | (0.75~0.85)max{T0,Te} | (0.85~0.95)max{T0,Te} | >0.95 max{T0,Te} |
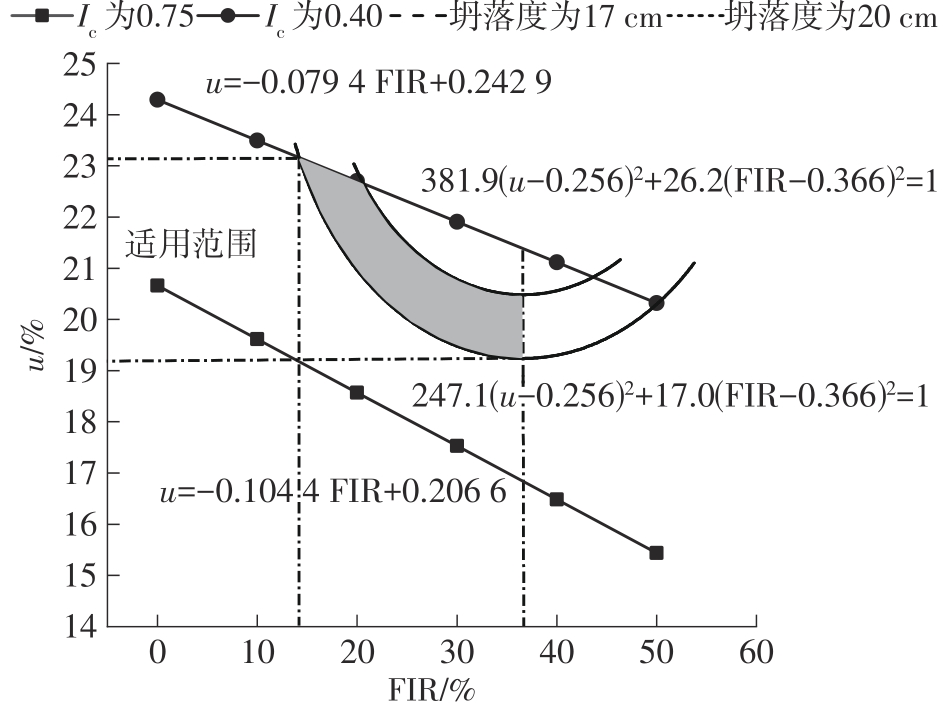
| 注入比FIR(d20) | 超出范围25% | 超出范围15% | 超出范围5% | 经验或理论公式结果范围内 |
| 发泡率FER(d21) | <15 | 15~20 | 20~30 | >30 |
| 泡沫半衰期(d22) | <4 min | 4~6 min | 6~8 min | >8 min |
| 渣土温度(d23) | >38 ℃ | 35~38 ℃ | 31~35 ℃ | 28~31 ℃ |
表5
结泥饼风险指标权重表"
| 二级指标 | 二级指标权重 | 三级指标 | 三级指标权重 | 风险因素(四级指标) | 同级权重 | 全局权重 wi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地质条件b1 | 0.297 3 | d1 | 黏粒含量 | 0.170 7 | 0.050 7 | ||
| d2 | 塑性指数 | 0.449 5 | 0.133 6 | ||||
| d3 | 液性指数 | 0.259 6 | 0.077 2 | ||||
| d4 | 抗崩解系数 | 0.120 2 | 0.035 7 | ||||
| 盾构选型b2 | 0.163 8 | 刀具系统c1 | 0.666 7 | d5 | 刀具间距 | 0.088 3 | 0.009 6 |
| d6 | 刀具高差 | 0.157 5 | 0.017 2 | ||||
| d7 | 刀具类型 | 0.271 8 | 0.029 7 | ||||
| d8 | 刀具开口率 | 0.482 4 | 0.052 7 | ||||
| 非刀具系统c2 | 0.333 3 | d9 | 搅拌棒数量 | 0.163 8 | 0.008 9 | ||
| d10 | 螺旋器深度 | 0.297 3 | 0.016 2 | ||||
| d11 | 冲刷系统 | 0.539 0 | 0.029 4 | ||||
| 施工因素b3 | 0.539 0 | 掘进模式控制c3 | 0.112 1 | d12 | 渣土液面高度 | 0.623 2 | 0.037 6 |
| d13 | 停机时间 | 0.239 5 | 0.014 5 | ||||
| d14 | 启动扭矩 | 0.137 3 | 0.008 3 | ||||
| 掘进参数控制c4 | 0.554 1 | d15 | 土仓压力 | 0.133 6 | 0.039 9 | ||
| d16 | 刀盘扭矩 | 0.410 1 | 0.122 5 | ||||
| d17 | 总推力 | 0.253 1 | 0.075 6 | ||||
| d18 | 推进速度 | 0.133 6 | 0.039 9 | ||||
| d19 | 螺旋机转速 | 0.069 6 | 0.020 8 | ||||
| 渣土改良效果c5 | 0.214 8 | d20 | 注入比FIR | 0.142 9 | 0.016 5 | ||
| d21 | 发泡率FER | 0.428 6 | 0.049 6 | ||||
| d22 | 泡沫半衰期 | 0.428 6 | 0.049 6 | ||||
| 温度控制c6 | 0.119 1 | d23 | 渣土温度控制 | 1.000 0 | 0.064 2 | ||
| 1 | 何川,封坤,方勇 .盾构法修建地铁隧道的技术现状与展望[J].西南交通大学学报,2015,50(1):97-109. |
| HE Chuan, FENG Kun, FANG Yong .Review and prospects on constructing technologies of metro tunnels using shield tunnelling method[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2015,50(1):97-109. | |
| 2 | 竺维彬,鞠世健 .盾构施工泥饼(次生岩块)的成因及对策[J].地下工程与隧道,2003,17(2):25-29,48. |
| ZHU Weibin, JU Shijian .Cause and countermeasure of mud cake(secondary rock)in shield machine driving[J].Underground Engineering and Tunnels,2003,17(2):25-29,48. | |
| 3 | 程池浩,赵国强,廖少明,等 .武汉老黏土地层土压盾构适应性研究[J].施工技术,2016,45(19):105-109,15. |
| CHENG Chihao, ZHAO Guoqiang, LIAO Shaoming,et al .Adaptability study of EPB shield machine in hard clay in Wuhan[J].Construction Technology,2016,45(19):105-109,15. | |
| 4 | FOUNTAINE E .Investigations into the mechanism of soil adhesion[J].Journal of Soil Science,1954,5(2):251-263. |
| 5 | STAFFORD J V, TANNER D W .The frictional characteristics of steel sliding on soil[J].Journal of Soil Science,1977,28(4):541-553. |
| 6 | BERGADO D T, CHAI J C, ABIERA H O,et al .Interaction between cohesive-frictional soil and various grid reinforcements[J].Geotextiles and Geomembranes,1993,12(4):327-349. |
| 7 | JIA X .Theoretical analysis of the adhesion force of soil to solid materials[J].Biosystems Engineering,2004,87(4):489-493. |
| 8 | BURBAUM U, SASS I .Physics of adhesion of soils to solid surfaces[J].Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2017,76(3):1097-1105. |
| 9 | KHABBAZI BASMENJ A, MIRJAVAN A, GHAFOORI M,et al .Assessment of the adhesion potential of kaolinite and montmorillonite using a pull-out test device[J].Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2017,76(4):1507-119. |
| 10 | 严辉 .盾构隧道施工中刀盘泥饼的形成机理和防治措施[J].现代隧道技术,2007,44(4):24-27,35. |
| YAN Hui .Mechanism of the formation and the prevention of clay cakes in shield tunneling[J].Modern Tunnelling Technology,2007,44(4):24-27,35. | |
| 11 | 傅鑫晖,莫涛,张晨,等 .复合地层盾构机刀盘结泥饼成因及预防措施[J].地下空间与工程学报,2020,16(S2):864-869. |
| FU Xinhui, MO Tao, ZHANG Chen,et al .Formation and precautions of mud cakes in mixed strata[J].Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering,2020,16(S2):864-869. | |
| 12 | THEWES M, BURGER W .Clogging risks for TBM drives in clay[J].Tunnels and Tunnelling International,2004,36(6):28-31. |
| 13 | THEWES M, HOLLMANN F .Assessment of clay soils and clay-rich rock for clogging of TBMs[J].Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2016,57:122-128. |
| 14 | REZAEI M, DAVOODI P K .Determining the relationship between shear wave velocity and physicomechanical properties of rocks[J].International Journal of Mining and Geo-Engineering,2021,55(1):65-72. |
| 15 | 蒲毅,刘建琴,郭伟,等 .土压平衡盾构机刀盘刀具布置方法研究[J].机械工程学报,2011,47(15):161-168. |
| PU Yi, LIU Jianqin, GUO Wei,et al .Research on cutting tool layout method of earth pressure balance shield[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2011,47(15):161-168. | |
| 16 | 赵雷刚,陈云节,刘发展 .复合盾构刀具布置分析与研究[J].现代隧道技术,2012,49(6):32-37. |
| ZHAO Leigang, CHEN Yunjie, LlU Fazhan .Analysis of and research on the cutter arrangement for a mix-shield[J].Modern Tunnelling Technology,2012,49(6):32-37. | |
| 17 | 何恩光,袁浩洋,周鹏,等 .砂卵石地层盾构刀具切削过程数值模拟分析[J].建筑机械,2023,43(4):51-60,4. |
| HE En-guang, YUAN Hao-yang, ZHOU Peng,et al .Numerical simulation analysis of cutting process of shield machine tool in sandy gravel stratum[J].Construction Machinery,2023,43(4):51-60,4. | |
| 18 | 王洪新 .土压平衡盾构刀盘开口率选型及其对地层适应性研究[J].土木工程学报,2010,43(3):88-92. |
| WANG Hongxin .Type selection of the head aperture ratio of EPB shield cutterheads and adaptability to stratum characteristics[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2010,43(3):88-92. | |
| 19 | 贾璐,温法庆,黄欣,等 .土压平衡盾构刀盘泥饼防治综合技术研究及应用[J].施工技术,2015,44(S1):243-246. |
| JIA Lu, WEN Faqing, HUANG Xin,et al .Study and application of cutter head-mudcake prevention comprehensive technology to EPB shield tunneling machine[J].Construction Technology,2015,44(S1):243-246. | |
| 20 | 邓如勇 .盾构刀盘结泥饼的机理及处置措施研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2018. |
| 21 | 姚印彬 .大直径泥水盾构常压可更换滚刀非正常磨损成因分析及应对措施[J].施工技术,2019,48(1):94-97. |
| YAO Yinbin .Causes analysis and corresponding solutions for abnormal wear of replaceable disc cutter under atmospheric of large dianmeter slurry shield[J].Construction Technology,2019,48(1):94-97. | |
| 22 | 陈玉亮,张若松,李明锷 .复合地层地质条件下复合式土压平衡盾构机刀盘泥饼防治[J].市政技术,2015,33(6):165-169. |
| CHEN Yuliang, ZHANG Ruosong, LI Ming’e .Prevention and cure of cutter-head mud-cake of composite EPBM in compound stratum[J].Journal of Municipal Technology,2015,33(6):165-169. | |
| 23 | 赵国栋,姚印彬 .刀盘中心体泥饼成因及其防治对策[J].铁道建筑技术,2017,55(3):69-72. |
| ZHAO Guodong, YAO Yinbin .Reason and solution for mud cake developing of cutting wheel center[J].Railway Construction Technology,2017,55(3):69-72. | |
| 24 | 王洪新,傅德明 .土压平衡盾构掘进的数学物理模型及各参数间关系研究[J].土木工程学报,2006,39(9):86-90. |
| WANG Hongxin, FU Deming .A mathematical model and the related parameters for EPB shield tunneling[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2006,39(9):86-90. | |
| 25 | 王洪新 .土压平衡盾构刀盘扭矩计算及其与盾构施工参数关系研究[J].土木工程学报,2009,42(9):109-113. |
| WANG Hongxin .Calculation of cutterhead torque for EPB shield and the relationship between cutterhead torque and shield driving parameters[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2009,42(9):109-113. | |
| 26 | 王洪新,傅德明 .土压平衡盾构平衡控制理论及试验研究[J].土木工程学报,2007,40(5):61-68,110. |
| WANG Hongxin, FU Deming .Theoretical and test studies on balance control of EPB shields[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2007,40(5):61-68,110. | |
| 27 | 魏康林 .土压平衡式盾构施工中“理想状态土体”的探讨[J].城市轨道交通研究,2007,10(1):67-70. |
| WEI Kanglin .On the "ldeal soil" in the earth pressure balanced shield tunnelling[J].Urban Mass Transit,2007,10(1):67-70. | |
| 28 | YE X, WANG S, YANG J,et al .Soil conditioning for EPB shield tunneling in argillaceous siltstone with high content of clay minerals:case study[J].International Journal of Geomechanics,2016,17(4):05016002/1-8. |
| 29 | 邓彬,顾小芳 .上软下硬地层盾构施工技术研究[J].现代隧道技术,2012,49(2):59-64. |
| DENG Bin, GU Xiaofang .Study of shield construction technology in soft upper stratum and hard under stratum[J].Modern Tunnelling Technology,2012,49(2):59-64. | |
| 30 | 李兴高,杨益 .考虑摩擦生热效应的泥水盾构刀盘热-结构耦合分析[J].土木工程学报,2020,53(S1):20-24. |
| LI Xinggao, YANG Yi .Thermal-mechanical coupling analysis of slurry shield cutterhead considering friction heat[J].Journal of Civil Engineering,2020,53(S1):20-24. | |
| 31 | 谭青,吕丹,夏毅敏,等 .泥饼工况下盾构刀盘热-力耦合分析[J].重庆大学学报,2013,36(10):61-66. |
| TAN Qing, Dan LÜ, XIA Yimin,et al .Thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of shield cutter head under mud cake condition[J].Journal of Chongqing University,2013,36(10):61-66. | |
| 32 | 方勇,王凯,陶力铭,等 .黏性地层面板式土压平衡盾构刀盘泥饼堵塞试验研究[J].岩土工程学报,2020,42(9):1651-1658. |
| FANG Yong, WANG Kai, TAO Li-ming,et al .Experimental study on clogging of cutterhead for panel earth-pressure-balance shield tunneling in cohesive strata[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(9):1651-1658. | |
| 33 | SAATY T L .The analytic hierarchy process[M].New York:McGraw Hill,1980. |
| 34 | 邓雪,李家铭,曾浩健,等 .层次分析法权重计算方法分析及其应用研究[J].数学的实践与认识,2012,42(7):93-100. |
| DENG Xue, LI Jiaming, ZENG Haojian,et al .Research on computation methods of AHP wight vector and its applications[J].Mathematics in Practice and Theory,2012,42(7):93-100. | |
| 35 | 王哲,吴淑伟,姚王晶,等 .盾构穿越既有桥梁桩基磨桩技术的研究[J].岩土工程学报,2020,42(1):117-125. |
| WANG Zhe, WU Shu-wei, YAO Wang-jing,et al .Grinding pile technology of shield tunnels crosssing pile foundation of existing bridges[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(1):117-125. |
| [1] | 彭波 何娟 蔡春丽 王汛杰 杨征文. 沥青面层施工碳排放量化评价方法及其应用[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(11): 102-109. |
| [2] | 丁万涛 刘克奇 王旭 朱建 李术才. 某土压平衡盾构始发地层的加固优化[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(5): 105-112. |
| [3] | 陈港 刘玉莎 文艾 何北海. 基于热重法的纸张热老化特性分析及其评价模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(1): 19-23,29. |
| [4] | 冯雨芹 冷军强 张亚平 李涵武 张春平. 城市道路路段燃油经济性评价模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(8): 104-108. |
| [5] | 卢凯 徐建闽 郑淑鉴. 相邻交叉口关联度分析及其应用[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 37(11): 37-42. |
| [6] | 陈国华 梁韬 张晖 颜伟文 陈清光. 用SAFETI定量评价液氯泄漏事故的风险[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(5): 103-108. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||