华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (12): 34-41.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220758
所属专题: 2023年机械工程
S变换子域适应的扶梯电机轴承迁移诊断
陈忠1 唐鑫1 张大明2 何东山3 张宪民1
- 1.华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院, 广东 广州 510640
2.日立电梯(广州)自动扶梯有限公司, 广东 广州 510660
3.广州地铁设计研究院股份有限公司, 广东 广州 510010
Stockwell Transform Combined with Subdomain Adaptation for Escalator Motor Bearing Transfer Diagnosis
CHEN Zhong1 TANG Xin1 ZHANG Daming2 HE Dongshan3 ZHANG Xianmin1
- 1.School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Hitachi Elevator (Guangzhou) Escalator Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510660,Guangdong,China
3.Guangzhou Metro Design and Research Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510010,Guangdong,China
摘要:
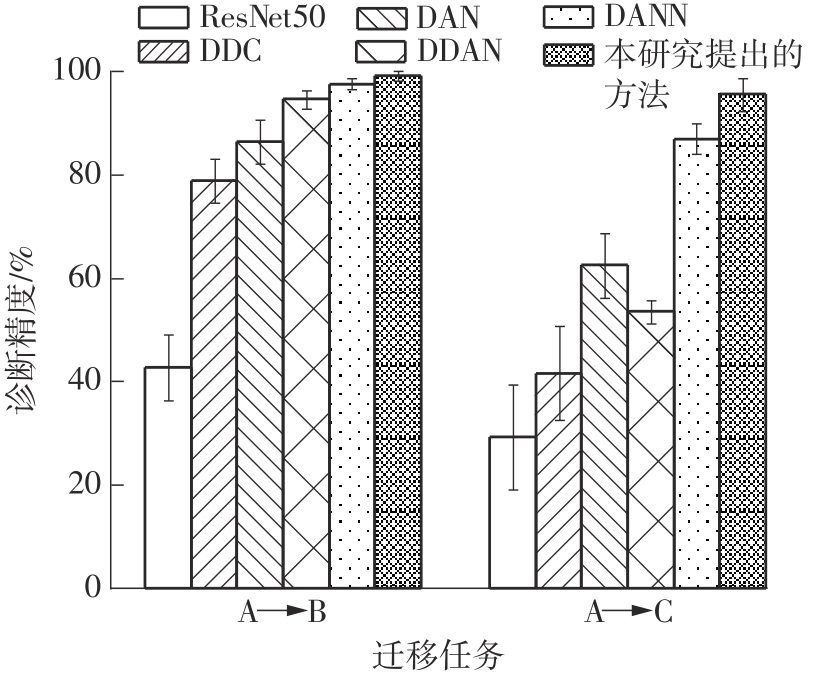
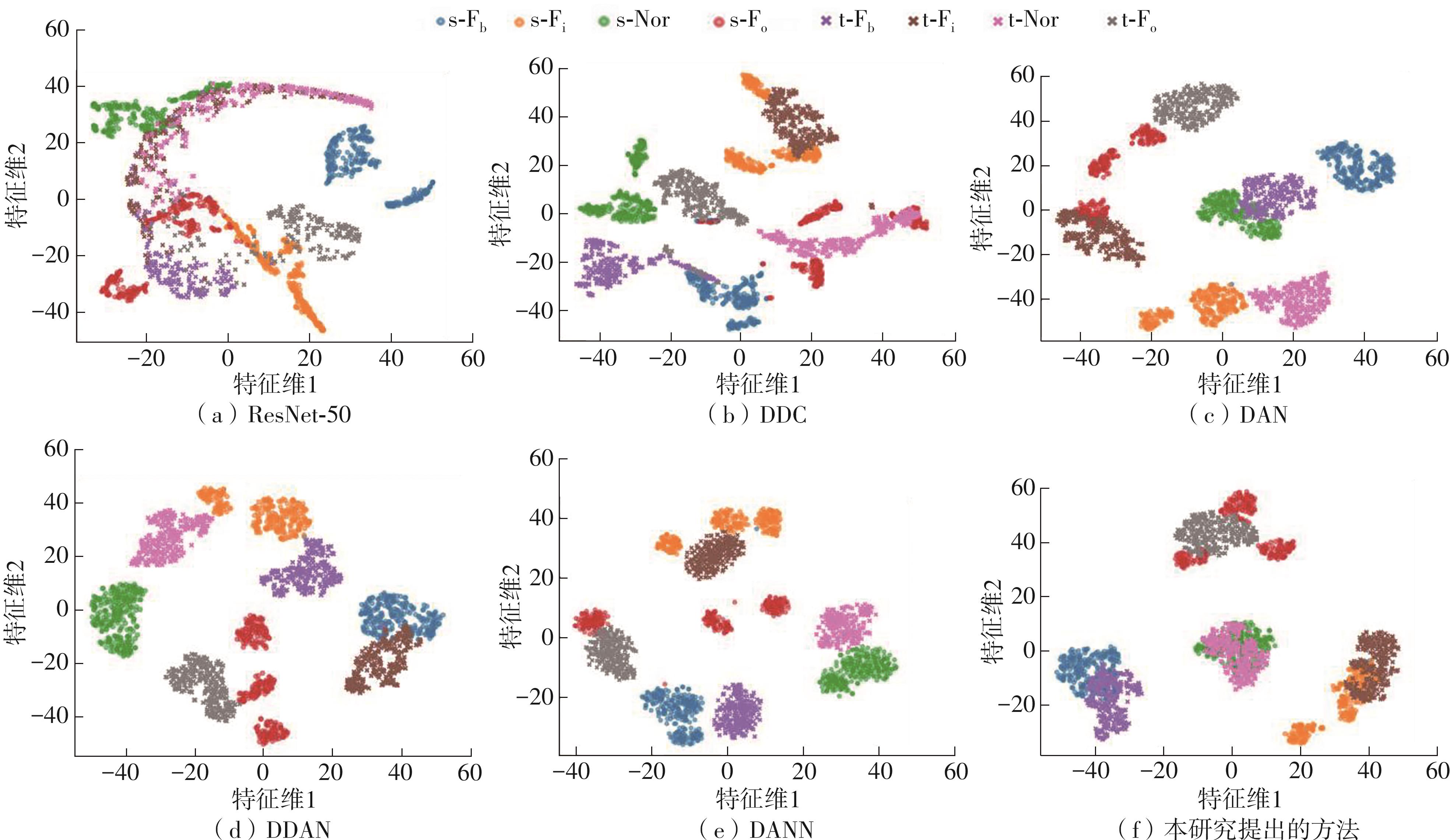
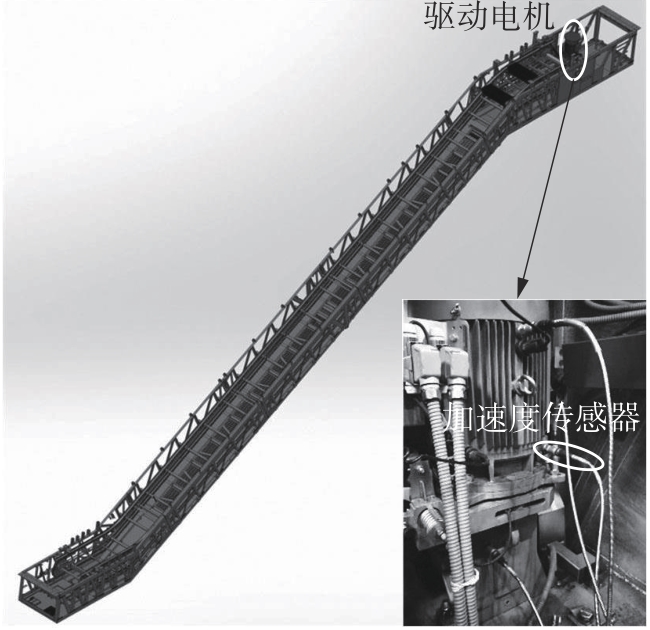
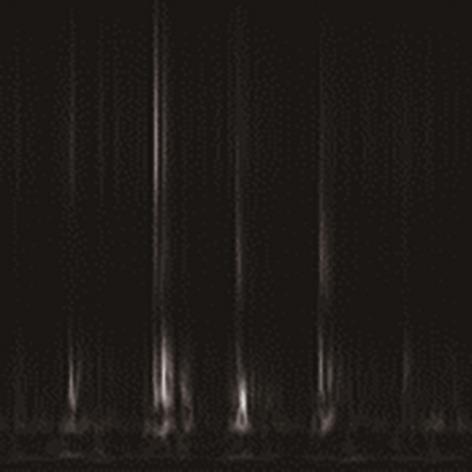
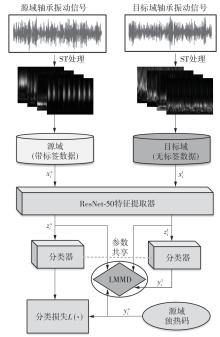
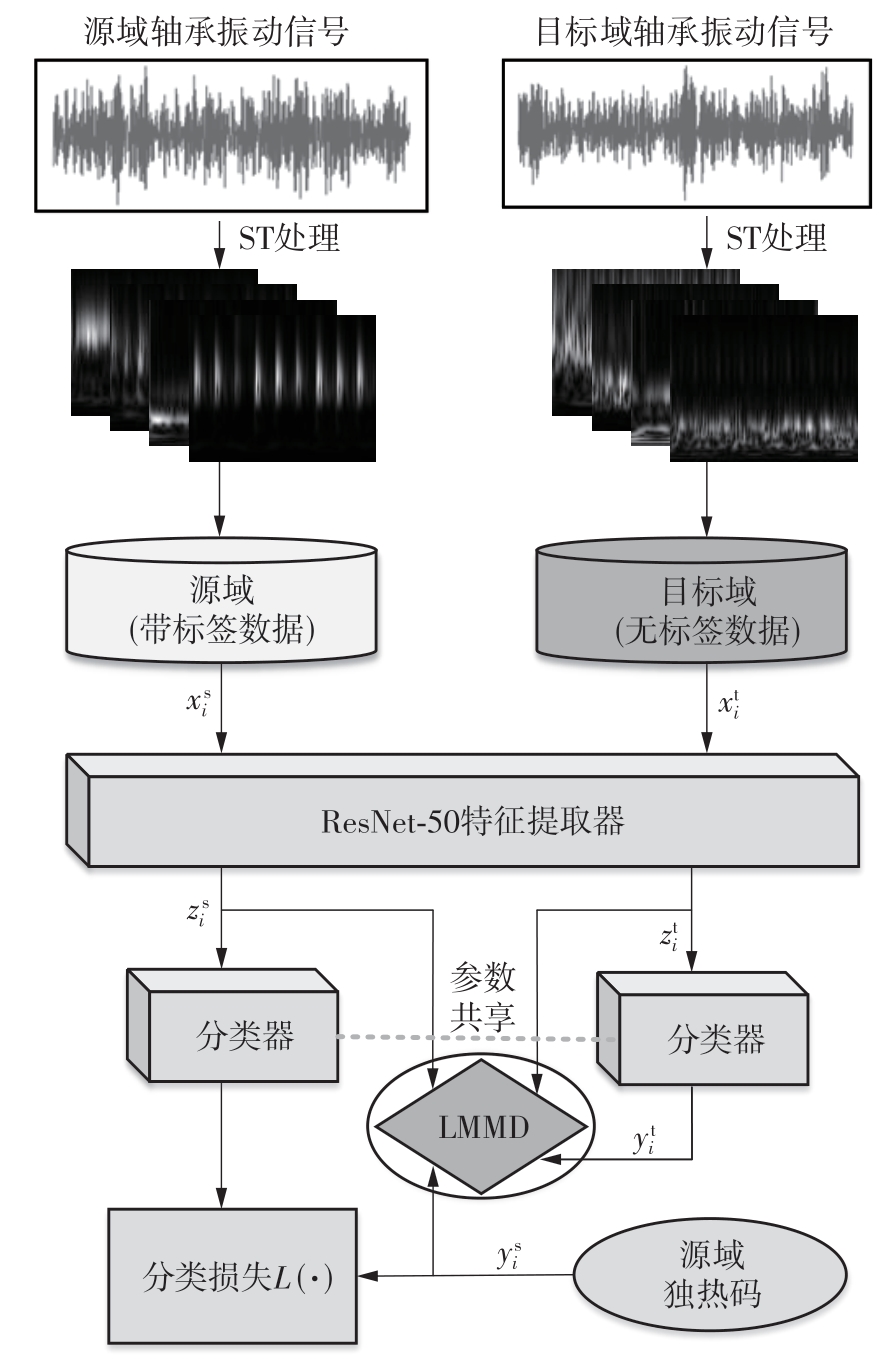
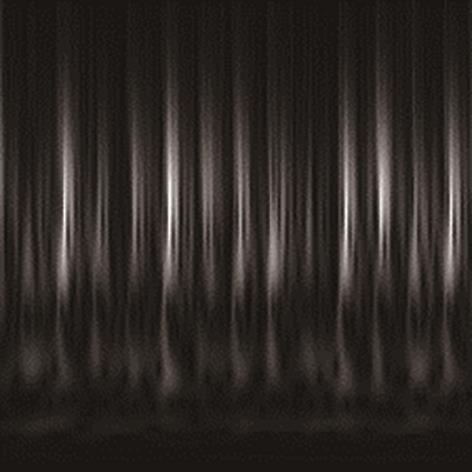
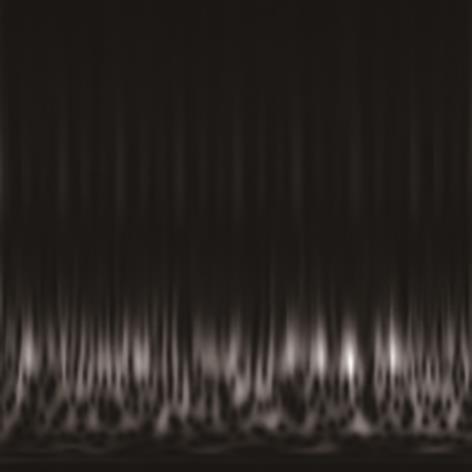
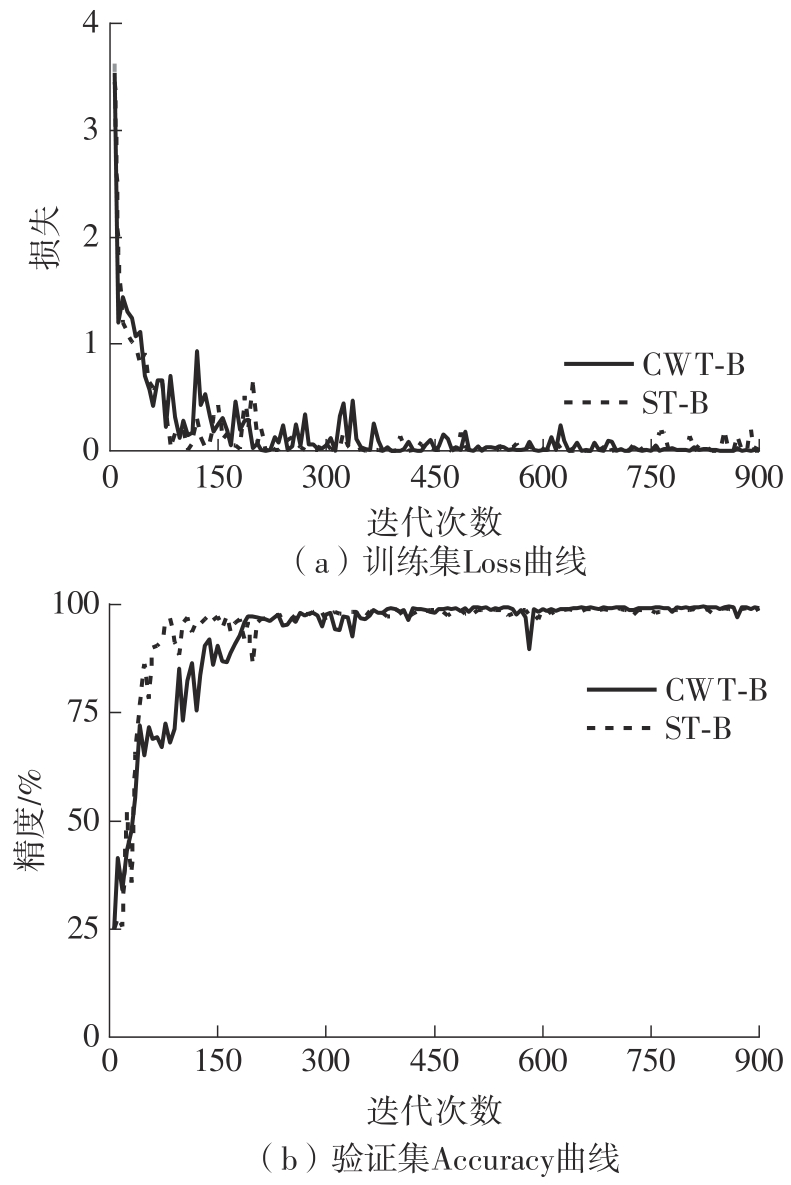
在缺乏足够的扶梯电机轴承故障数据的情况下,针对扶梯在频繁变载变速的运行状态中轴承故障特征不稳定的问题,提出了Stockwell(S)变换结合子域适应的扶梯电机轴承迁移诊断方法。首先,针对扶梯电机轴承的故障特点,采用S变换结合双线性插值算法生成振动信号时频图。该时频图能有效反映轴承故障特征,并与后续的生成/与特征提取网络输入要求相适应。其次,在基于深度残差神经网络ResNet-50的特征提取网络层的输出端引入局部最大均值差异(LMMD),将故障样本的类别置信度作为映射后的权重引入最大均值差异(MMD),在对齐源域和目标域全局分布的同时,对齐同类别样本所属的子域的分布,同时拓展可迁移学习的范围。然后,构建网络的最小化LMMD和交叉熵损失函数,采用小批量梯度下降法训练网络。从而可通过细化不同故障类别间特征差异实现故障子域自适应,并克服迁移诊断精度低的问题。最后,基于两个公开的轴承故障数据集和少量扶梯电机轴承故障数据构建S变换后的时频数据集,并进行迁移诊断实验验证。结果表明,本方法对扶梯轴承的两种源域到目标域的迁移诊断平均准确率分别达到99.1%和95.49%,识别精度和鲁棒性明显优于5种常用的诊断方法。
中图分类号:






 B
B C
C