华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 112-118.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230016
密集城市群中基于智能反射面的传输方案
庄陵 刘宇航
- 重庆邮电大学 通信与信息工程学院/移动通信技术信产部重点实验室,重庆 400065
Research on Transmission Scheme Based on Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface in Dense Urban Agglomeration
ZHUANG Ling LIU Yuhang
- School of Communication and Information Engineering /Key Laboratory of Mobile Communication Technology,Ministry of Industry and Information,Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Chongqing 400065,China
摘要:
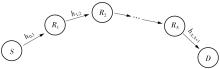
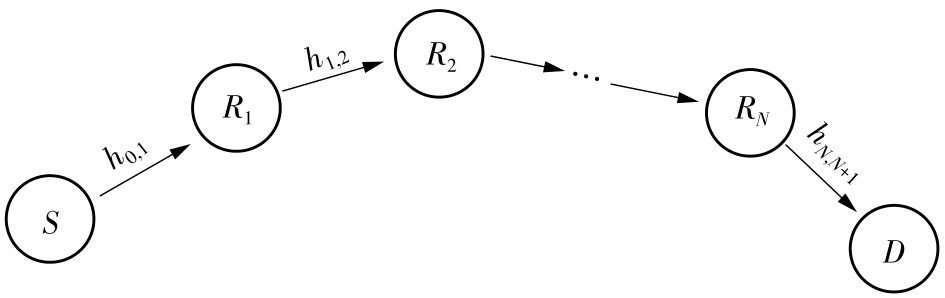
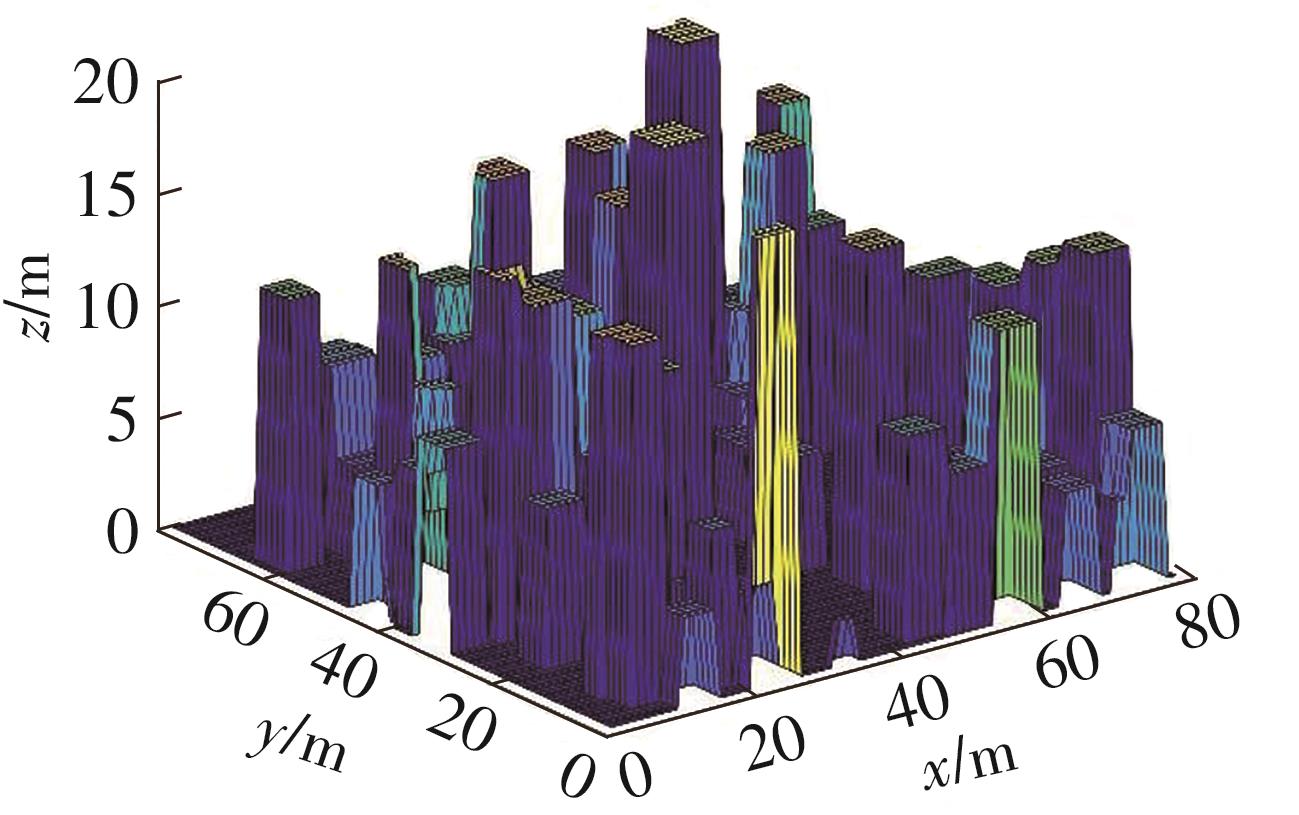
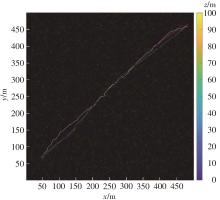
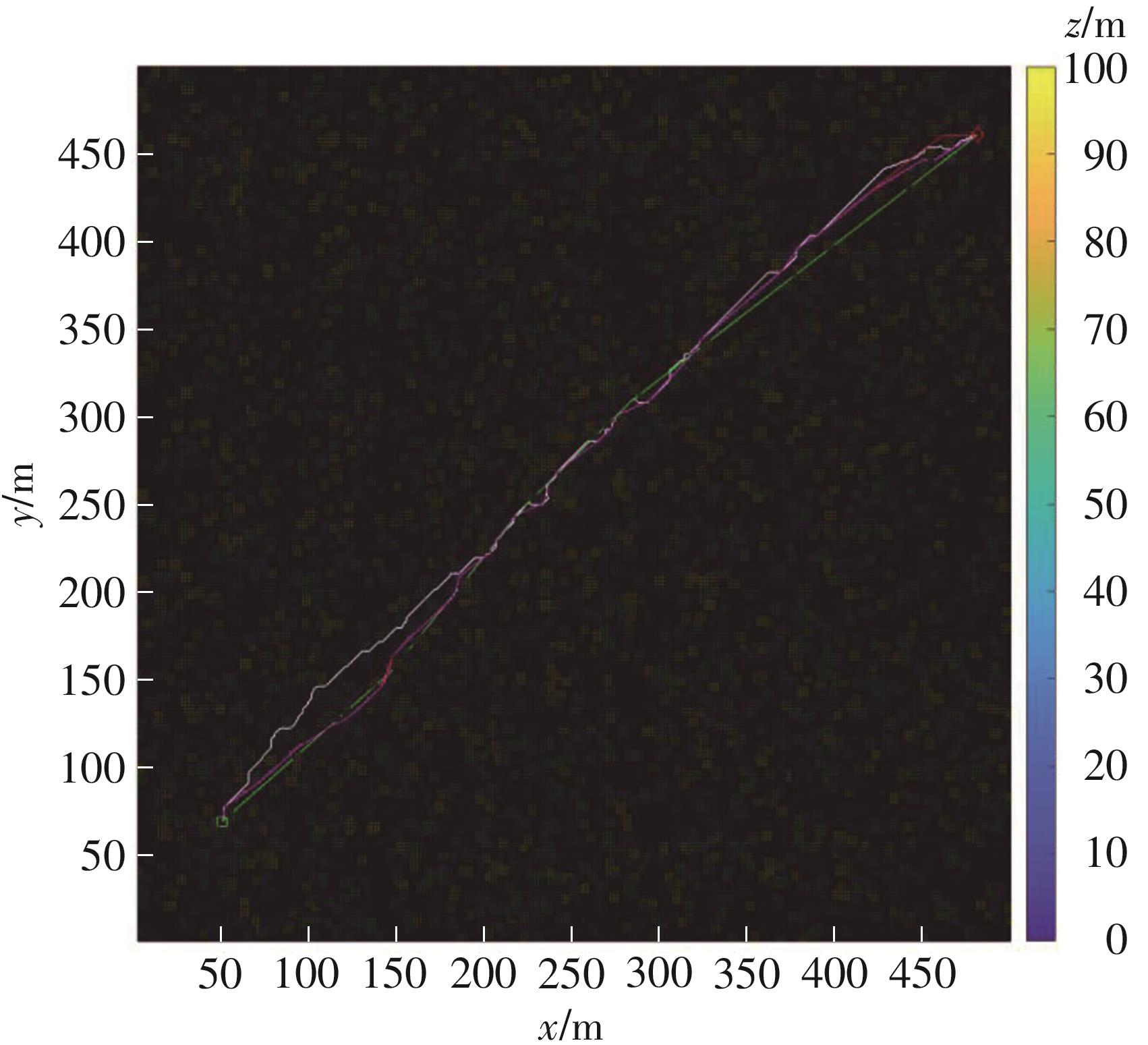
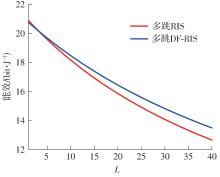
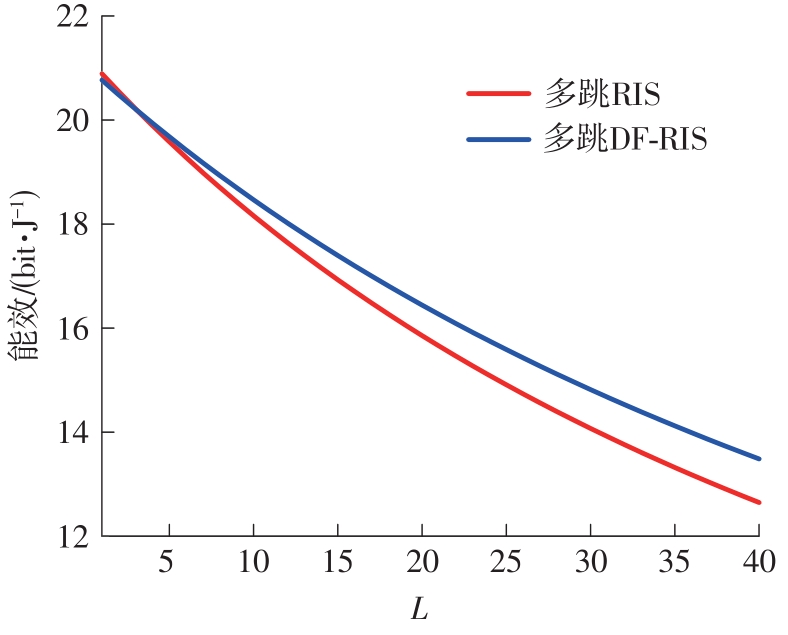
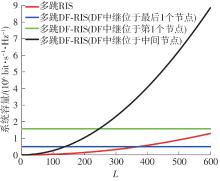
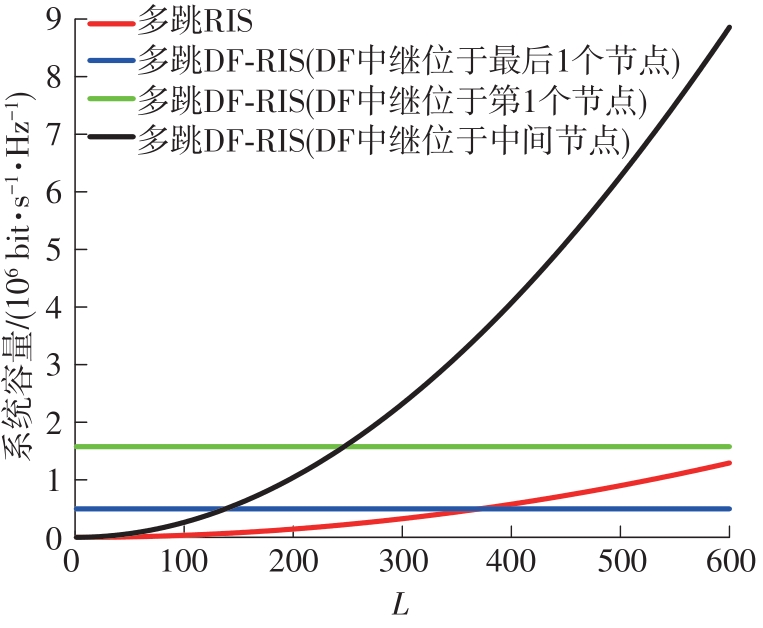
由于低频段资源紧缺,未来移动通信网络将逐渐转移至更高频段,电磁波的自由空间传播损耗、绕射损耗以及穿透损耗较大,容易产生覆盖盲区以及弱覆盖区域。智能反射面(RIS)通过重新配置信号的传播环境以提高网络性能并扩大网络覆盖范围,成为解决密集城市群覆盖问题的新热点。基于有RIS参与的下一代移动通信网络密集城市群布网时的多跳通信模式,对多跳RIS传输方案与提出的一种解码转发(DF)中继辅助多跳RIS传输方案(DF-RIS)进行全面比对。首先,对两种传输方案的传输损耗、能效以及系统容量进行了理论推导及分析。其次,在密集城市群三维环境模型中进行仿真,为改善复杂环境搜索效率降低以及计算量增大的问题提出了一种改进Lazy Theta*算法,并对改进算法与常见路径搜索算法的搜索时间以及搜索路径长度进行仿真对比。使用改进算法选取相同仿真环境下两种传输方案分别所需节点,节点选取中考虑了DF中继位于多跳DF-RIS传输方案中的不同位置。最后在确定节点后对两种传输方案的传输损耗、能效以及系统容量进行仿真分析比较。仿真结果不但验证了改进Lazy Theta*算法的有效性,也说明了RIS反射元件数与两种传输方案性能之间的关系。表明两种传输方案各有其适用性,可根据对性能的实际需求选择合适的传输方案。
中图分类号: