华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 134-144.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210778
所属专题: 2023年交通运输工程
• 交通运输工程 • 上一篇
基于语义分割模型的三维沥青路面车辙异常分析方法
王艾迪1 郎洪1 丁朔1 陆键1 洪小刚2 温添1
- 1.同济大学 道路与交通工程教育部重点实验室, 上海 201804
2.山西高速公路工程检测有限公司, 山西 太原 030008
Rutting Abnormality Analysis Method for 3D Asphalt Pavement Surfaces Based on Semantic Segmentation Model
WANG Aidi1 LANG Hong1 DING Shuo1 LU Jian1 HONG Xiaogang2 WEN Tian1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering of the Ministry of Education, Tongji University, Shanghai 201804, China
2.Shanxi Expressway Engineering Inspection Co. , Ltd. , Taiyuan 030008, Shanxi, China
摘要:
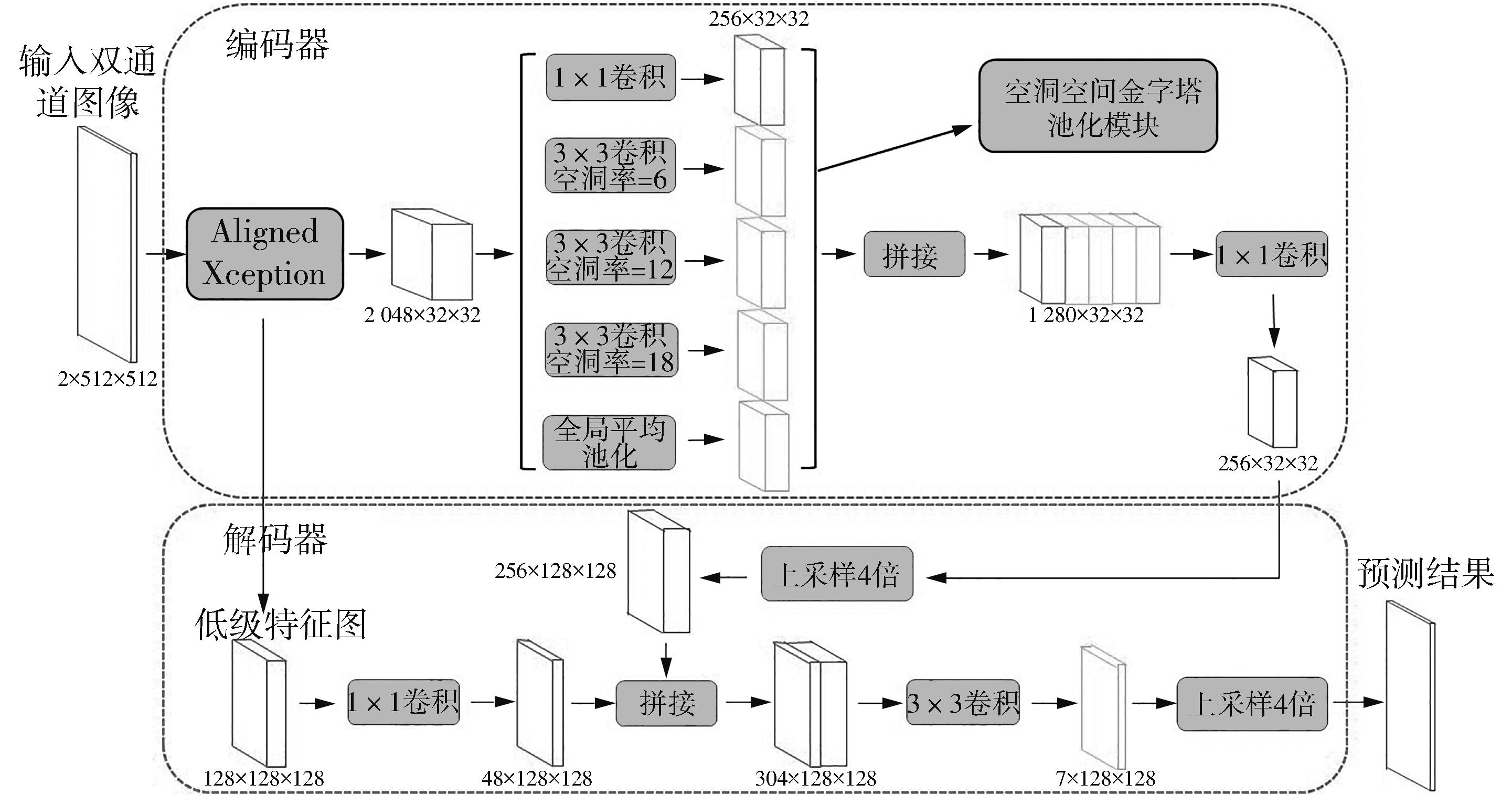
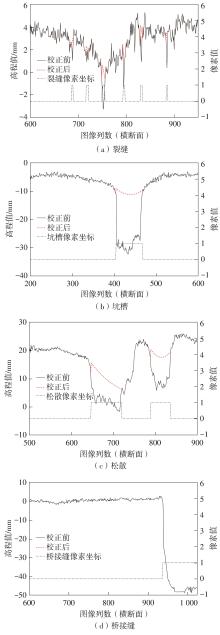
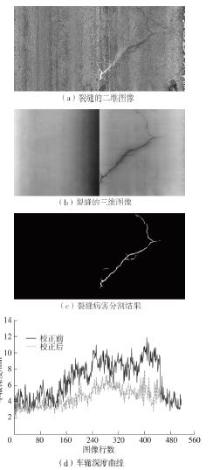
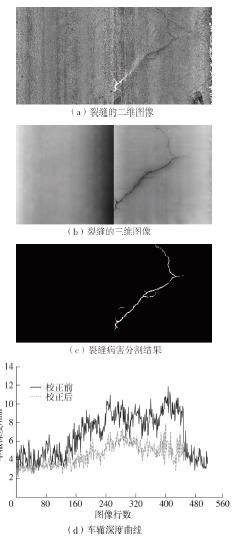
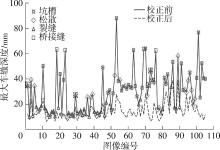
车辙深度是路面状况评价和道路养护的一个重要指标。现有车辙深度测量方法未考虑复杂路况下坑槽、松散、裂缝和桥梁接缝等对车辙计算的影响,其有效性和适用性受到了限制,测量结果的真实性也有待进一步验证。有鉴于此,文中提出了一种基于语义分割模型的沥青路面车辙异常检测与校正方法。采用三维线激光技术采集道路横断面高程数据,利用包络线算法提取车辙深度。对于最大车辙深度超过10 mm的横断面,搭建基于深度学习的语义分割框架,提出改进的DeepLabV3+网络对病害类型进行自动辨识和像素定位,并结合最大车辙深度高程点,设计基于拉格朗日插值的校正规则来对异常车辙进行校正。研究结果表明,改进的DeepLabV3+模型能较为准确地识别和定位造成车辙检测异常的路面病害,其对5种路面特征和病害的综合检测准确率达81.63%,在均交并比(MIoU)和大部分交并比(IoU)上的表现均优于U-Net、PSPNet、DeepLabV3+模型。现场验证结果表明,文中方法不仅能够自动分析车辙异常的原因,还能通过对异常车辙的校正排除其他病害的影响,从而较大程度地还原实际车辙深度水平。文中研究成果可为路面预防性养护提供科学数据支撑。
中图分类号: