华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (10): 1-10.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210783
所属专题: 2022年交通运输工程
不同行为模型框架下的数据驱动类人驾驶模型比较
黄玲1,2,3 黄子虚1 吴泽荣1 游峰1 崔躜1 曾译萱1 钟浩川1
- 1.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广东 广州 510640
2.东南大学 现代城市交通技术江苏高校协同创新中心,江苏 南京 210096
3.华南理工大学 亚热带建筑科学国家重点实验室,广东 广州 510640
Comparison of Data-Driven Human-Like Driving Models Under Different Behavior Model Frameworks
HUANG Ling1,2,3 HUANG Zixu1 WU Zerong1 YOU Feng1 CUI Zhuan1 ZENG Yixuan1 ZHONG Haochuan1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Urban ITS,Southeast University,Nanjing 210096,Jiangsu,China
3.State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
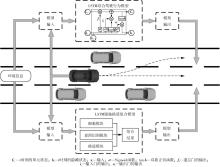
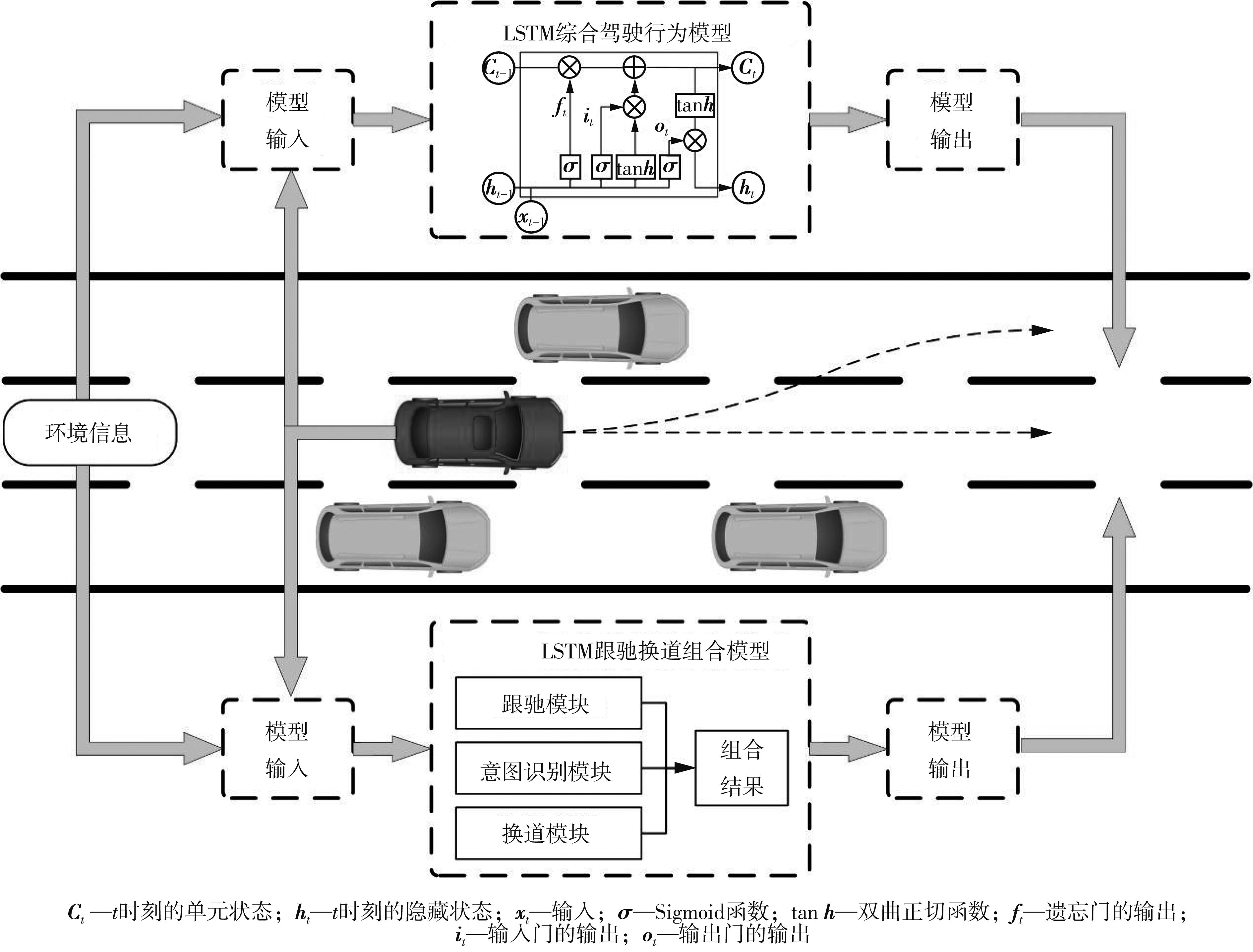
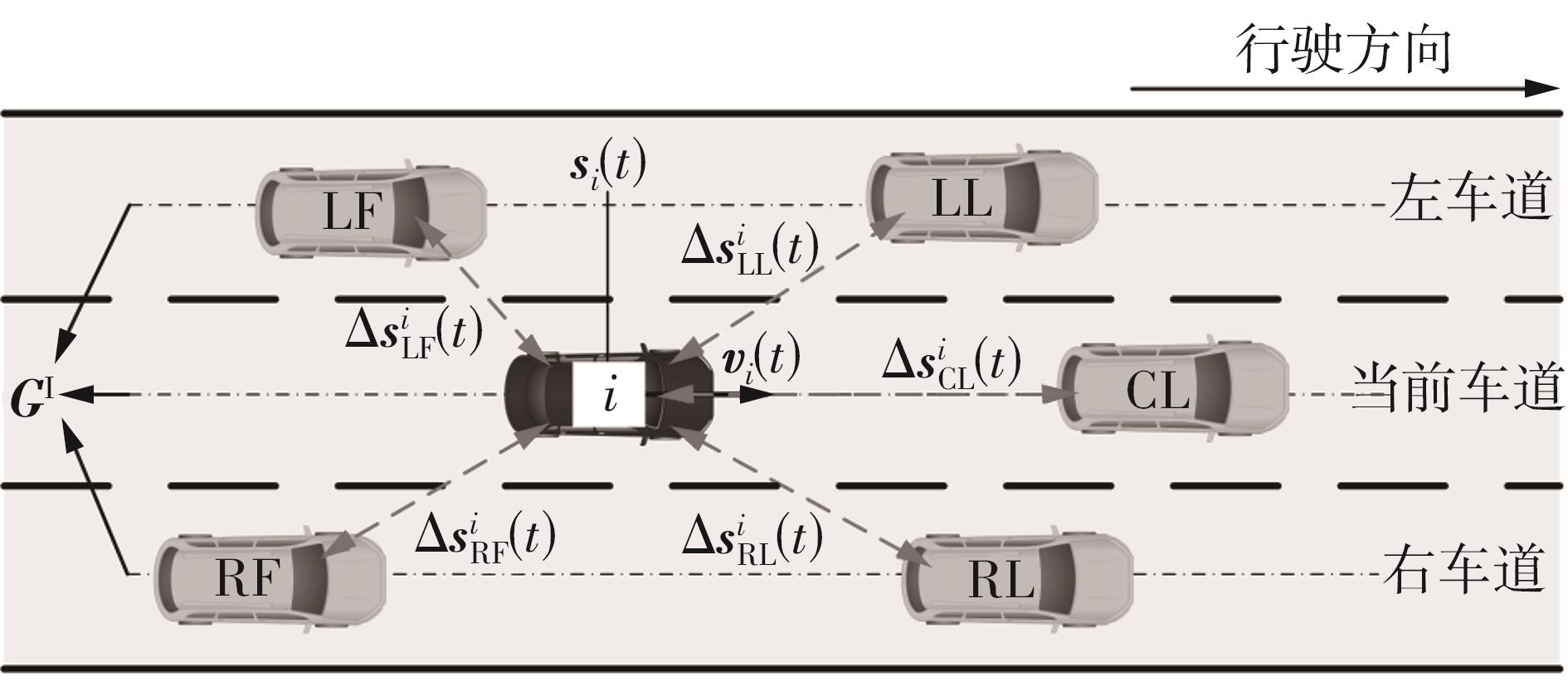
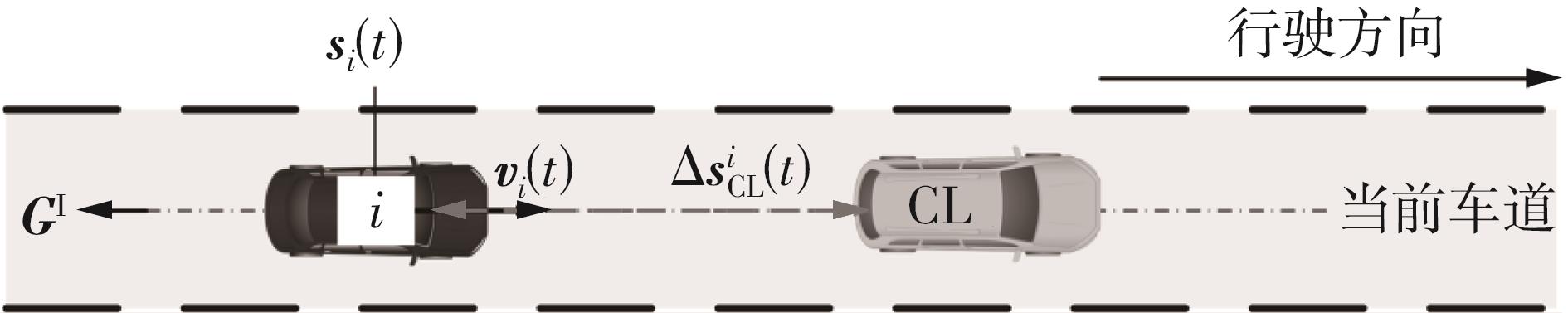
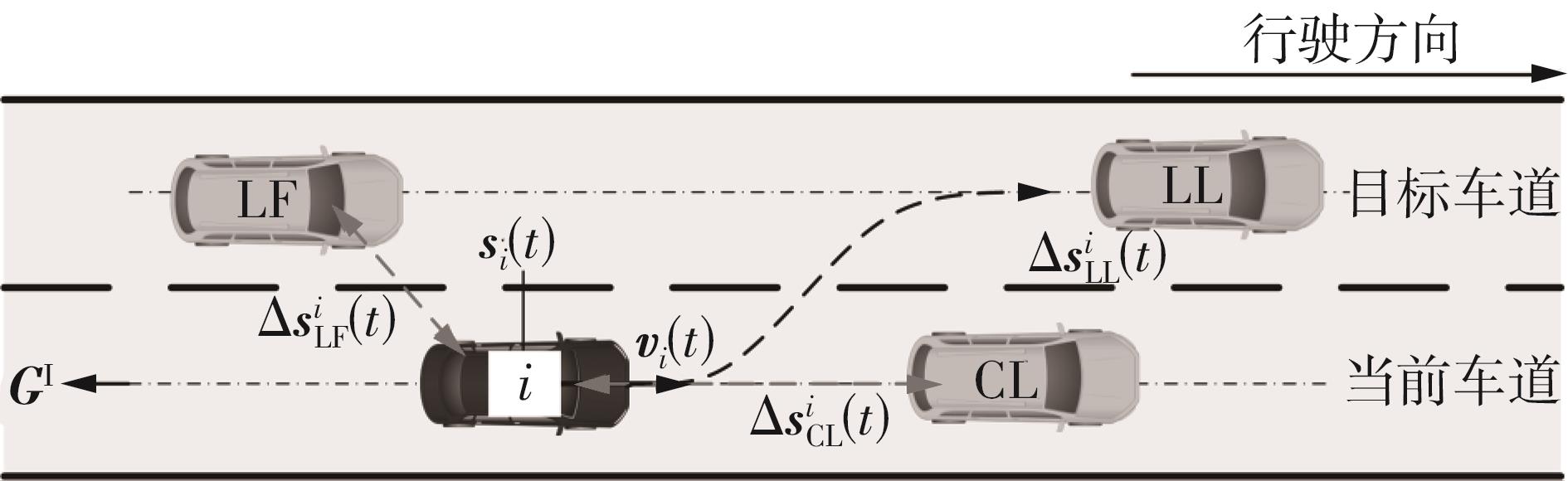
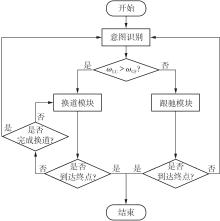
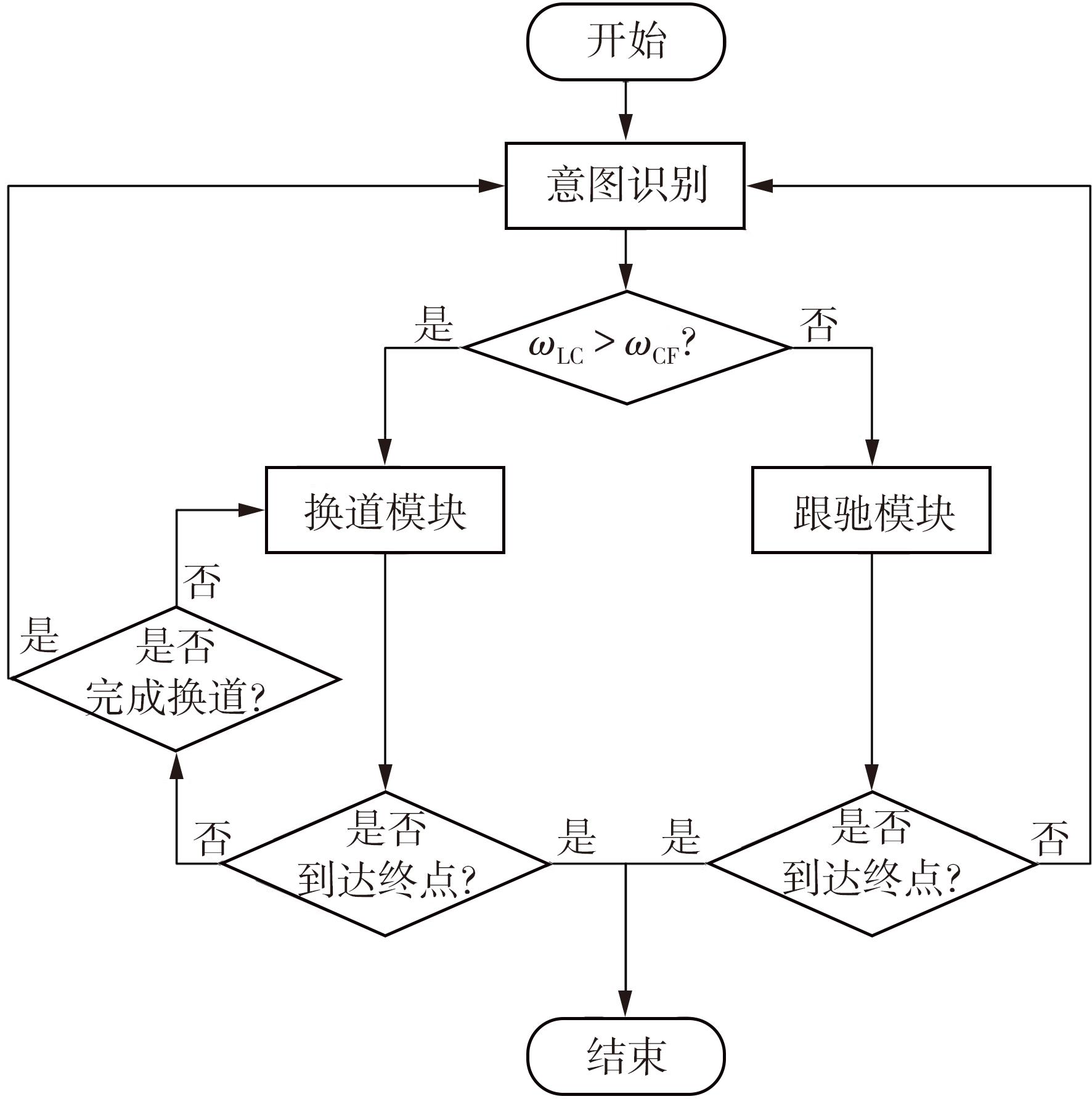
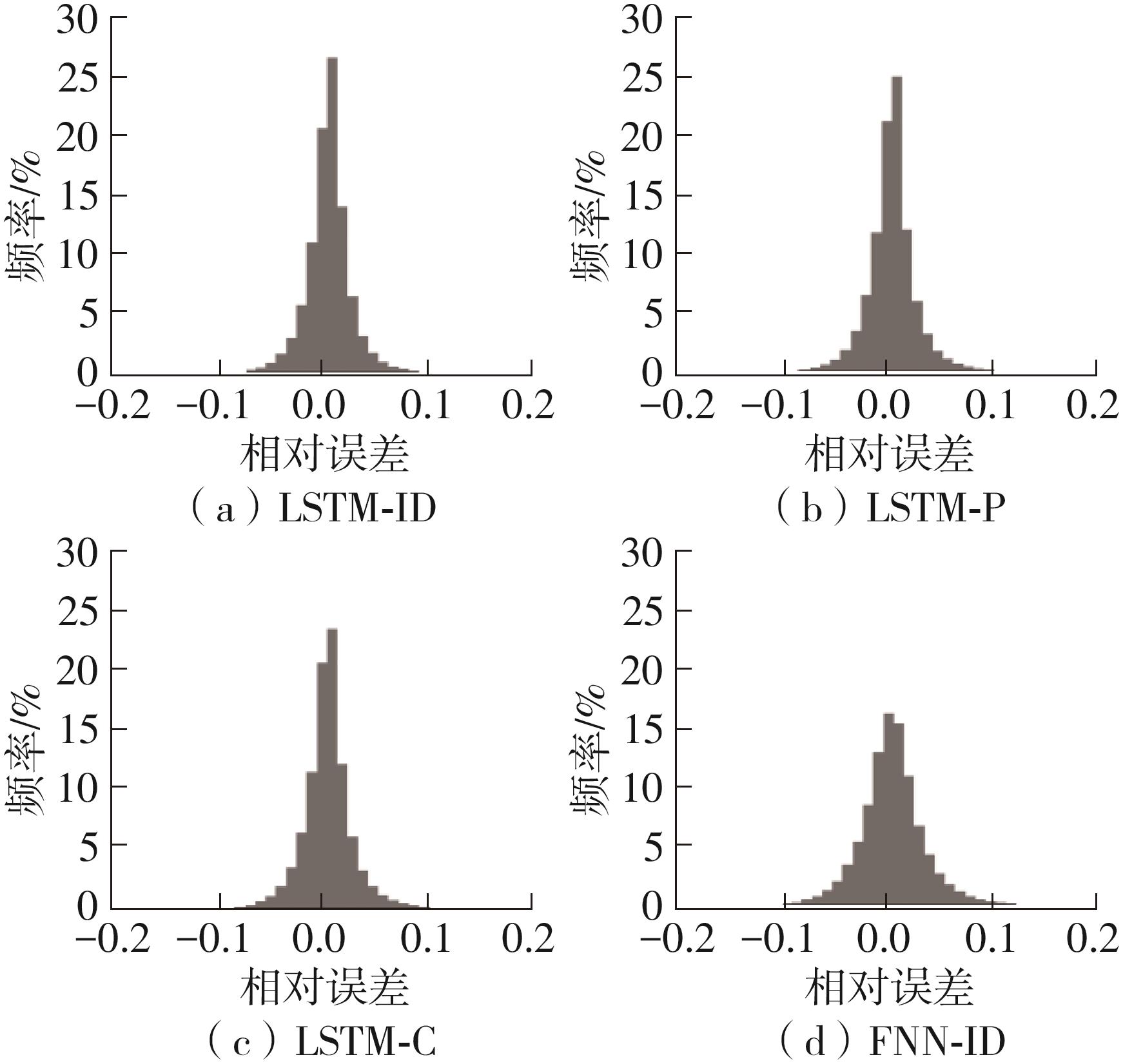
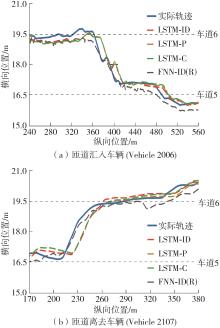
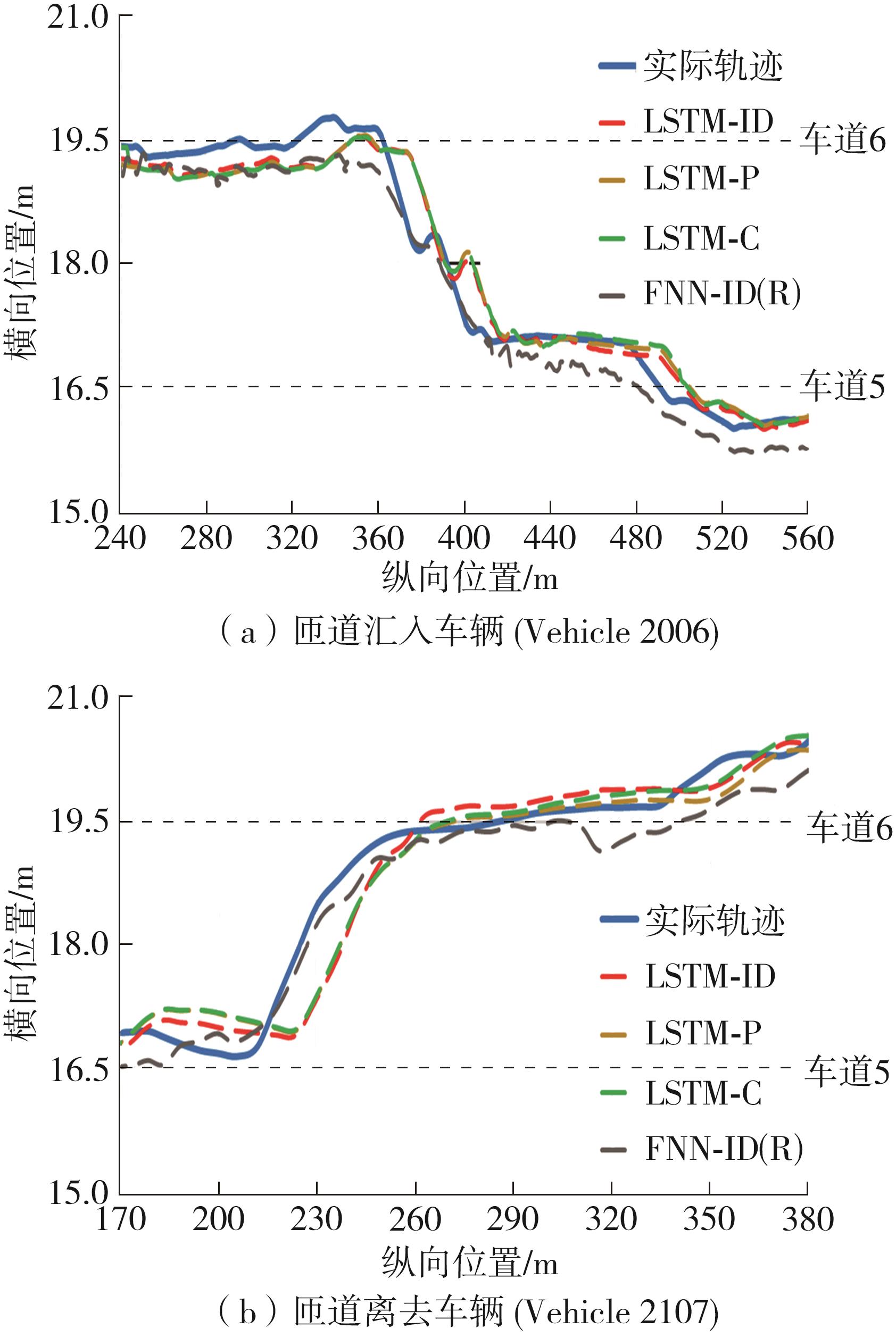
传统的驾驶行为模型框架把驾驶行为划分为跟驰行为和换道行为两大类,并分别进行模型构建;而综合驾驶行为模型框架则认为跟驰行为和换道行为密不可分,因此将所有驾驶行为看作一个整体来进行建模。文中基于这两种行为模型框架,对数据驱动类人驾驶模型的性能进行分析。首先,建立综合驾驶行为模型框架和跟驰换道组合模型框架,并根据驾驶过程中的影响因素,确定模型的输入和输出。其次,提出了基于跟驰、换道和意图识别模块的两种跟驰换道组合方式:判别组合和概率组合。随后,对原始数据集进行处理筛选,构建综合驾驶行为、跟驰行为、换道行为和意图识别4个样本库,分别用于对相应行为模块进行训练和标定。最后,将两种跟驰换道组合模型与综合驾驶行为模型进行模型精度、安全性、鲁棒性和迁移性比较。结果表明:在模型输入输出、参数标定流程和样本数据库一样的情况下,基于长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)的类人驾驶模型精度优于基于FNN的模型,其中基于LSTM的模型均方误差可达到0.227 m2,基于FNN的模型均方误差为0.470 m2。而在基于LSTM的模型中,采用跟驰换道组合模型框架的模型比采用综合驾驶行为模型框架的模型具有更好的鲁棒性和迁移性,其中跟驰换道组合模型在±10%噪声下的鲁棒性均方误差可达到1.383 m2,迁移性均方误差可达到0.462 m2;综合驾驶行为模型在±10%噪声下的鲁棒性均方误差为2.314 m2,迁移性均方误差为0.484 m2。
中图分类号: