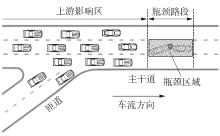
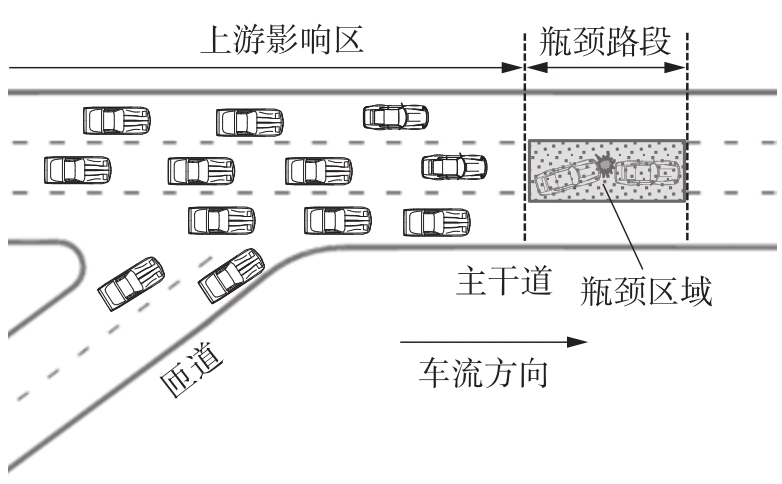
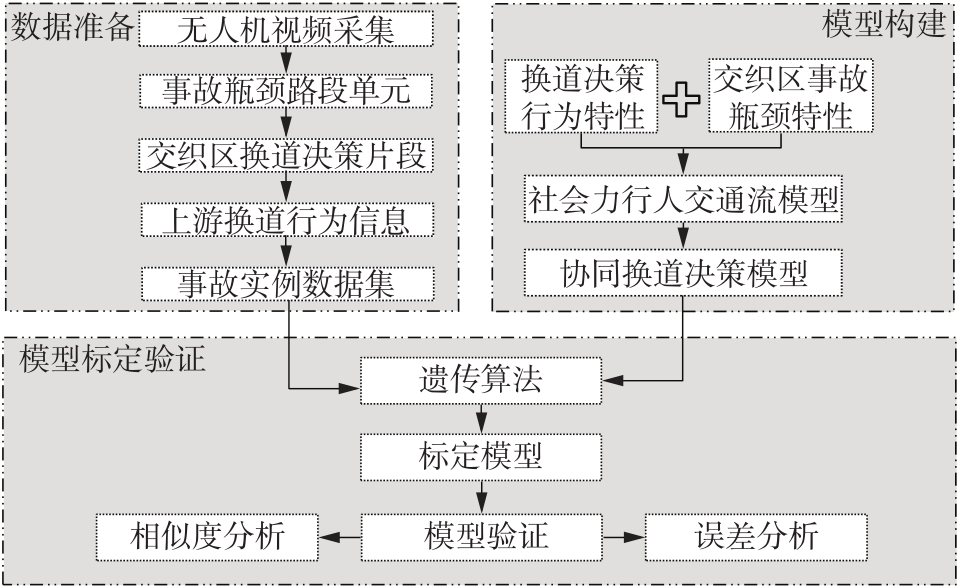
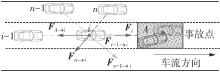
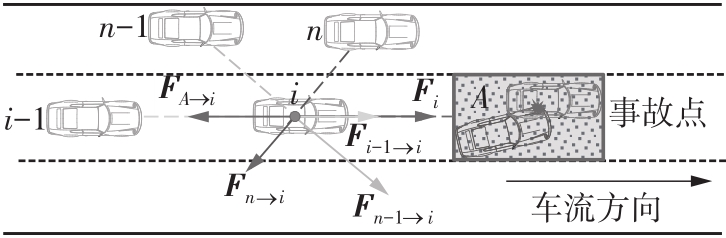
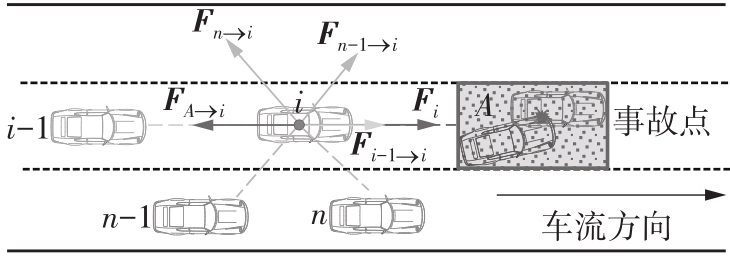
| 1 | ZHAO J, LIU P, XU C,et al .Understand the impact of traffic states on crash risk in the vicinities of type A weaving segments:a deep learning approach[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2021,159:106293. |
| 2 | REN J, CHEN Y, XIN L,et al .Detecting and locating of traffic incidents in a road segment based on lane-changing characteristics[J].Transportmetrica A:Transport Science,2017,13(10):853–873. |
| 3 | YANG D, WU Y, SUN F,et al .Freeway accident detection and classification based on the multi-vehicle trajectory data and deep learning model[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2021,130:103303. |
| 4 | SUN C, PEI X, HAO J,et al .Role of road network features in the evaluation of incident impacts on urban traffic mobility[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2018,117:101-116. |
| 5 | CAO D, WU J, DONG X,et al .Quantification of the impact of traffic incidents on speed reduction:a causal inference based approach[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2021,157:106163/1-14. |
| 6 | DAS A, KHAN M N, AHMED M M .Detecting lane change maneuvers using SHRP2 naturalistic driving data:a comparative study machine learning techniques[J/OL].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2020,142:105578. |
| 7 | WANG Z, SHI X, ZHAO X,et al .Modeling decentralized mandatory lane change for connected and autonomous vehicles:an analytical method[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2021,133:103441. |
| 8 | 王殿海,陶鹏飞,金盛,等 .跟驰模型参数标定及验证方法[J].吉林大学学报(工学版),2011,41(S1):59-65. |
| 8 | WANG Dian-hai, TAO Peng-fei, JIN Sheng,et al .Method of calibrating and validating car-following model[J].Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2011,41(S1):59-65. |
| 9 | UO D, MA J, CHANG R .Lane-changing-decision characteristics and the allocation of visual attention of drivers with an angry driving style[J].Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2020,71:62-75. |
| 10 | 陈慧,王洁新 .基于驾驶人不满度的高速公路自动驾驶换道决策[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(12):1-9,45. |
| 10 | CHEN Hui, WANG Jie-xin .A decision-making method for lane changes of automated vehicles on freeways based on drivers' dissatisfaction[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2019,32(12):1-9,45. |
| 11 | 彭博,王玉婷,谢济铭,等 .城市干线短交织区元胞自动机多级换道决策模型[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(4):41-48,70. |
| 11 | PENG Bo, WENG Yu-ting, XIE Ji-ming,et al .Multi-stage lane changing decision model of urban trunk road’s short weaving area based on cellular automata[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2020,20(4):41-48,70. |
| 12 | 张兰芳,陈程,张佳妍,等 .基于自然驾驶数据的高速公路出口换道决策模型[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(3):318-325,333. |
| 12 | ZHANG Lan-fang, CHEN Cheng, ZHANG Jia-yan,et al .Modeling lane-changing behavior in freeway off-ramp areas using naturalistic driving data[J].Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science),2018,46(3):318-325,333. |
| 13 | 张青周,李振龙,曹政,等 .高速公路浓雾环境下换道决策规则提取及决策算法[J].科学技术与工程,2019,19(21):303-308. |
| 13 | ZHANG Qing-zhou, LI Zhen-long, CAO Zheng,et al .Decision-making rule extraction and decision-making algorithm for lane change in dense fog environment[J].Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(21):303-308. |
| 14 | 李立,徐志刚,赵祥模,等 .智能网联汽车运动规划方法研究综述[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(6):20-33. |
| 14 | LI Li, XU Zhi-gang, ZHAO Xiang-mo,et al .Review of motion planning methods of intelligent connected vehicles[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2019,32(6):20-33. |
| 15 | WANG H, HUANG Y, KHAJEPOUR A,et al .Local path planning for autonomous vehicles: crash mitigation[C]∥ Proceeding of 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV).Changshu:IEEE,1602-1606. |
| 16 | FENG Z, FU M, SONG W,et al .Decision making and local trajectory planning for autonomous driving in off-road environment[C]∥ Proceeding of 2020 3rd International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS).Harbin:IEEE,1180-1186. |
| 17 | FENG Z, SONG W, FU M,et al .Decision-making and path planning for highway autonomous driving based on spatio-temporal lane-change gaps[J].IEEE Systems Journal,2021:1-11. |
| 18 | KUEFLER A, MORTON J, WHEELER T,et al .Imitating driver behavior with generative adversarial networks[C/OL]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV).Redondo Beach:IEEE,2017:204-211. |
| 19 | 陈大飞 .基于社会力的城市道路混合交通流建模与分析[D].长沙:中南大学,2011. |
| 20 | DENG J-H, FENG H-H .A multilane cellular automaton multi-attribute lane-changing decision model[J].Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,2019,529:121545. |
| 21 | 杨达,苏刚,吴丹红 .基于社会力模型的无车道划分异质交通流研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2018,18(3):94-100. |
| 21 | YANG Da, SU Gang, WU Dan-hong .Non-lane-based heterogeneous traffic flow research based on social force model[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2018,18(3):94-100. |
| 22 | 邱小平,孙若晓,马丽娜,等 .基于社会力的信号交叉口施工区交通流建模[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2016,16(1):99-104. |
| 22 | QIU Xiao-ping, SUN Ruo-xiao, MA Li-na,et al .Modeling and analyzing of traffic flow on the work zone of urban signalized intersection based on social force[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2016,16(1):99-104. |
| 23 | YANG X, YANG X, LI Y,et al .Obstacle avoidance in the improved social force model based on ant colony optimization during pedestrian evacuation[J].Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications,2021,583:126256/1-15. |
| 24 | LI G, MA J, YANG Z .Characteristics of heavy vehicle discretionary lane changing based on trajectory Data[J]?.Transportation Research Record,2022,2676(3),258-275. |
| 25 | ZHU M, WANG X, TARKO A,et al .Modeling car-following behavior on urban expressways in Shanghai:a naturalistic driving study[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2018,93:425-445. |
| 26 | YANG D, ZHOU X, SU G,et al .Model and simulation of the heterogeneous traffic flow of the urban signalized intersection with an island work zone[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2019,20(5):1719-1727. |
| 27 | LIU S, WANG X, HASSANIN O,et al .Calibration and evaluation of responsibility-sensitive safety (RSS) in automated vehicle performance during cut-in scenarios[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2021,125:103037. |
| 28 | 余朝军,江驹,徐海燕,等 .基于改进遗传算法的航班-登机口分配多目标优化[J].交通运输工程学报,2020,20(2):121-130. |
| 28 | YU Chao-jun, JIANG Ju, XU Hai-yan,et al .Multi-objective optimization of flight-gate assignment based on improved genetic algorithm [J].Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2020,20(2):121-130. |
| 29 | 禚保玲 .基于社会力的同伴群走行模型研究[D].北京:北京交通大学. 2014. |
| 30 | 王建强,吴剑,李洋 .基于人-车-路协同的行车风险场概念、原理及建模[J].中国公路学报,2016,29(1):105-114. |
| 30 | WANG Jian-qiang, WU Jian, LI Yang .Concept,principle and modeling of driving risk field based on driver-vehicle-road interaction[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2016,29(1):105-114. |
| 31 | SAIFUZZAMAN M, ZHENG Z, MAZHARUL HAQUE M,et al .Revisiting the task-capability interface model for incorporating human factors into car-following models[J/OL].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2015,82:1-19. |
| 32 | LI L X, WANG F Y .The automated lane-changing model of intelligent vehicle highway systems[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems.Singapore:IEEE,2002. |
| 33 | LI A, JIANG H, LI Z,et al .Human-like trajectory planning on curved road:learning from human drivers[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2020,21(8):3388-3397. |
| 34 | 孙秦豫,付锐,王畅,等 .人机协作系统中车辆轨迹规划与轨迹跟踪控制研究[J].中国公路学报,2021,34(9):146-160. |
| 34 | SUN Qin-yu, FU Rui, WANG Chang,et al .Vehicle trajectory-planning and trajectory-tracking control in human-autonomous collaboration system [J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2021,34(9):146-160. |