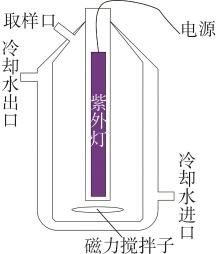
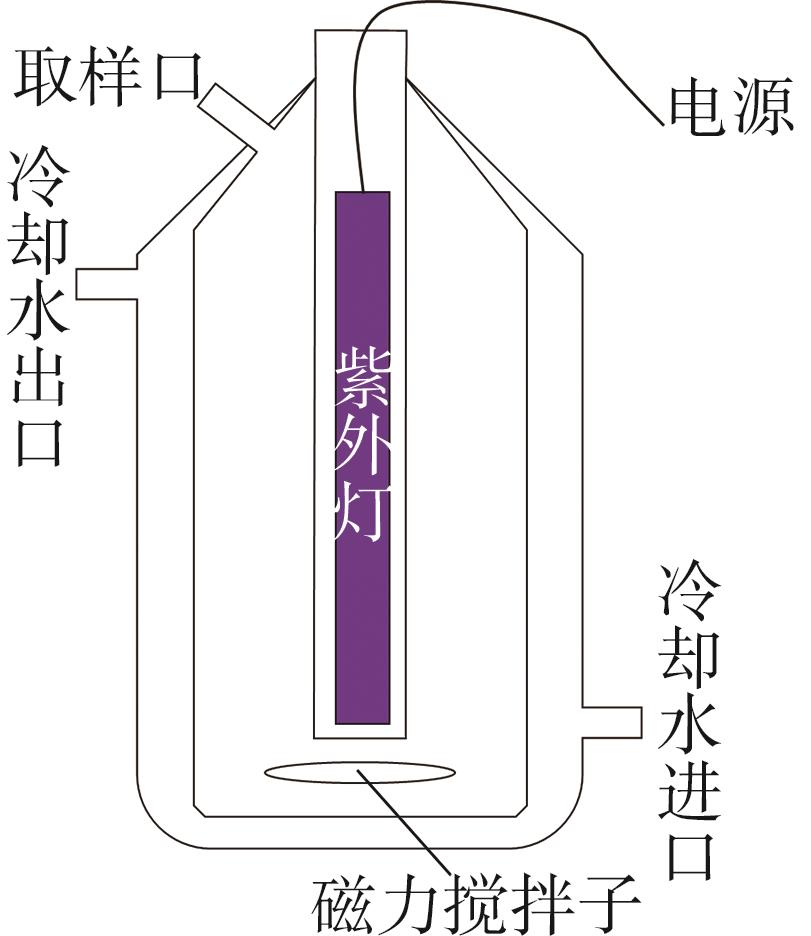
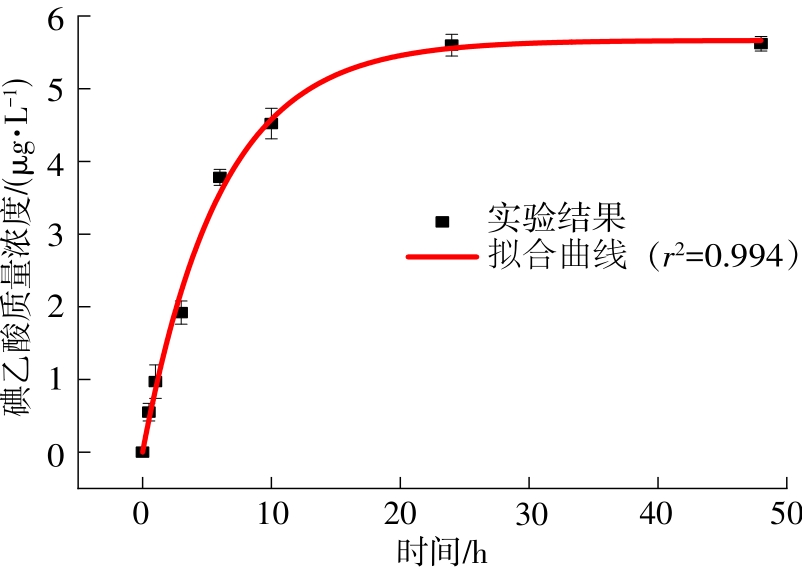
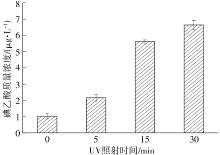
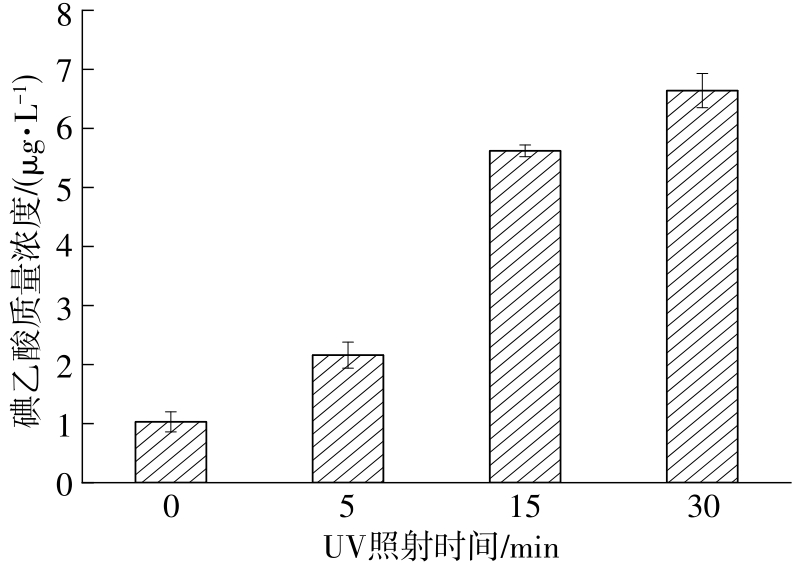
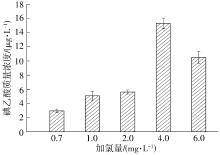
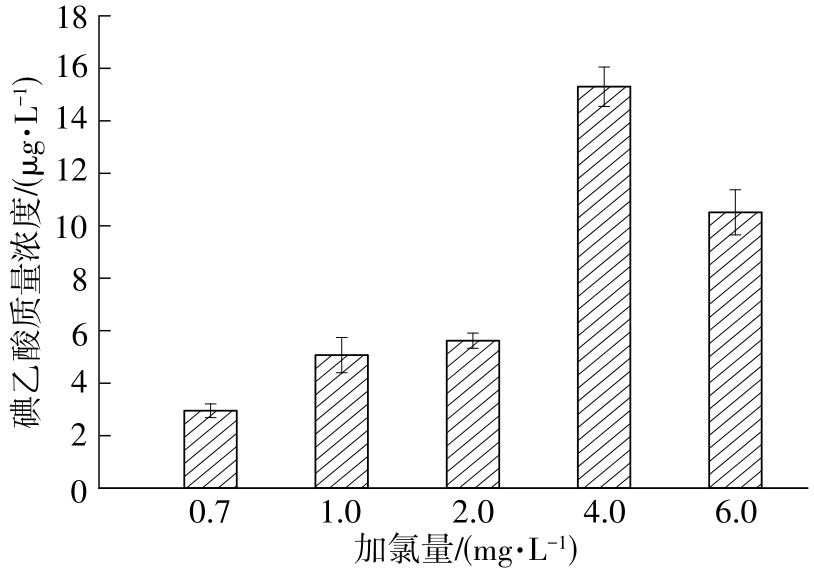
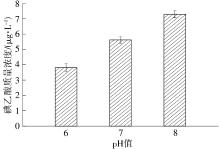
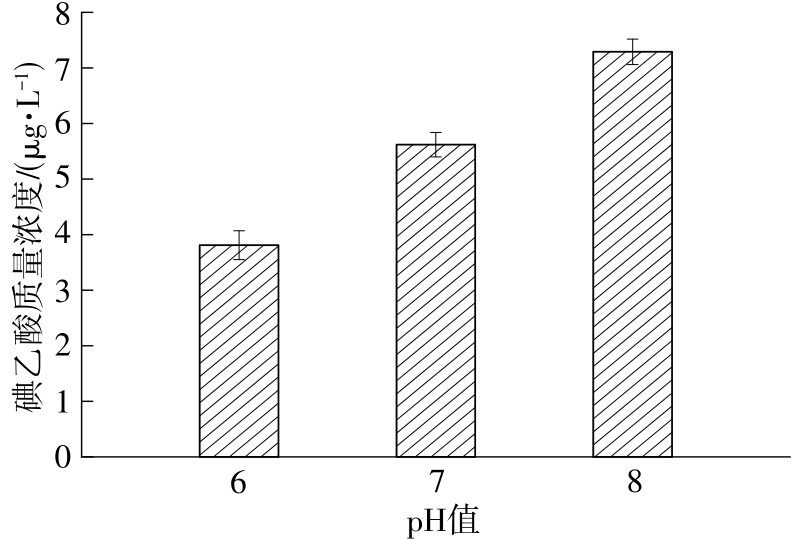
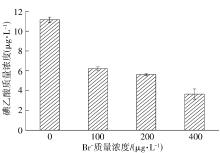
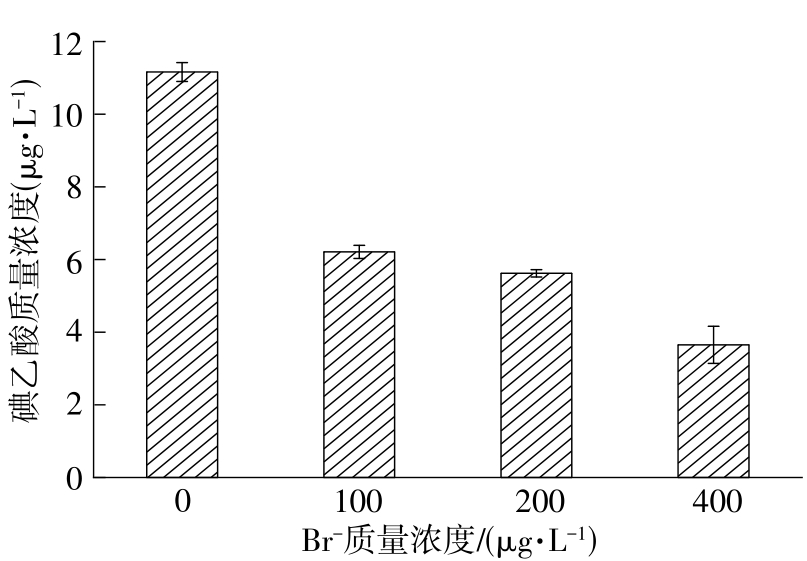
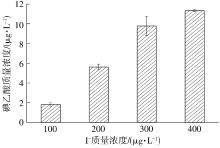
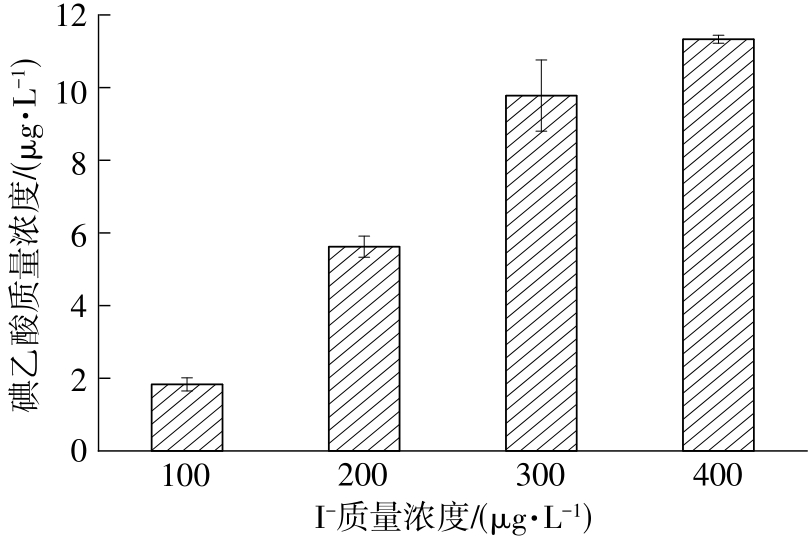
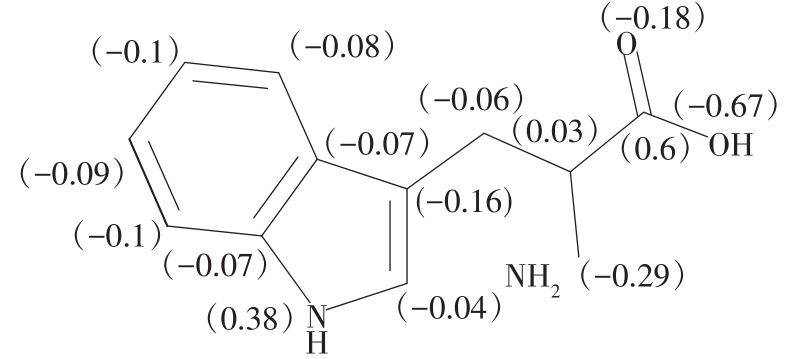
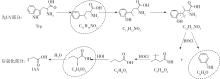
| 1 |
TREHY M L, YOST R A, MILES C J .Chlorination by-products of amino-acids in natural-waters[J].Environmental Science & Technology,1986,20(11):1117-1122.
|
| 2 |
DU P, ZHAO H, CAO H,et al .Transformation of halobenzoquinones with the presence of amino acids in water:products,pathways and toxicity[J].Water Research,2017,122:299-307.
|
| 3 |
WANG X, WANG J, ZHANG Y H,et al .Characterization of unknown iodinated disinfection byproducts during chlorination/chloramination using ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry[J].Science of the Total Environment,2016,554/555:83-88.
|
| 4 |
WANG L S, HU H Y, WANG C .Effect of ammonia nitrogen and dissolved organic matter fractions on the genotoxicity of wastewater effluent during chlorine disinfection[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(1):160-165.
|
| 5 |
TIAN F X, XU B, LIN Y L,et al .Photodegradation kinetics of iopamidol by UV irradiation and enhanced formation of iodinated disinfection by-products in sequential oxidation processes[J].Water Research,2014,58:198-208.
|
| 6 |
LIU J Q, ZHANG X R .Comparative toxicity of new halophenolic DBPs in chlorinated saline wastewater effluents against a marine alga:halophenolic DBPs are generally more toxic than haloaliphatic ones[J].Water Research,2014,65:64-72.
|
| 7 |
CHU W H, GAO N Y, YIN D Q,et al .Trace determination of 13 haloacetamides in drinking water using liquid chromatography triple quadrupole mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2012,1235:178-181.
|
| 8 |
RICHARDSON S D, FASANO F, ELLINGTON J J,et al .Occurrence and mammalian cell toxicity of iodinated disinfection byproducts in drinking water[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2008,42(22):8330-8338.
|
| 9 |
LIU L Z, XING X C, HU C,et al .Effect of sequential UV/free chlorine disinfection on opportunistic pathogens and microbial community structure in simulated drinking water distribution systems[J].Chemosphere,2019,219:971-980.
|
| 10 |
ZHOU X H, ZHU L J, WANG L,et al .Protective effect of Edaravone in primary cerebellar granule neurons against iodoacetic acid-induced cell injury[J].Oxidative Medicine & Cellular Longevity,2015,2015:606987/1-8.
|
| 11 |
PROCHAZKA E, ESCHER B I, PLEWA M J,et al .In vitro cytotoxicity and adaptive stress responses to selected haloacetic acid and halobenzoquinone water disinfection byproducts[J].Chemical Research in Toxicology,2015,28(10):2059-2068.
|
| 12 |
ESCOBAR L F, HOYOS L S, LONDONO E,et al .Genotoxic and clastogenic effects of monohaloacetic acid drinking water disinfection by-products in primary human lymphocytes[J].Water Research,2013,47(10):3282-3290.
|
| 13 |
RICHARDSON S D, PLEWA M J, WAGNER E D,et al .Occurrence,genotoxicity,and carcinogenicity of regulated and emerging disinfection by-products in drinking water:a review and roadmap for research[J].Mutation Research-Reviews in Mutation Research,2007,636(1/2/3):178-242.
|
| 14 |
PLEWA M J, WAGNER E D, RICHSRDSON S D,et al .Chemical and biological characterization of newly discovered iodoacid drinking water disinfection byproducts[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2004,38(18):4713-4722.
|
| 15 |
SAYESS R, KHALIL A, SHAH M,et al .Comparative cytotoxicity of six iodinated disinfection byproducts on nontransformed epithelial human colon cells[J].Environmental Science & Technology Letters,2017,4(4):143-148.
|
| 16 |
WEI X, XIN C, WANG X,et al .Occurrence of regulated and emerging iodinated DBPs in the Shanghai drinking water[J].PLoS One,2013,8(3):e59677/1-7.
|
| 17 |
LIU S G, LI Z L, DONG H Y,et al .Formation of iodo-trihalomethanes,iodo-acetic acids,and iodo-acetamides during chloramination of iodide-containing waters:factors influencing formation and reaction pathways[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2017,321:28-36.
|
| 18 |
COTTON C A, OWEN D M, CLINE G C,et al .UV disinfection costs for inactivating cryptosporidium[J].Journal American Water Works Association,2001,93(6):82-94.
|
| 19 |
RAND J L, HOFMANN R, ALAM M Z B,et al .A field study evaluation for mitigating biofouling with chlorine dioxide or chlorine integrated with UV disinfection[J].Water Research,2007,41(9):1939-1948.
|
| 20 |
赵敬国 .紫外线/高铁酸钾与氯联合消毒工艺特性研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2016.
|
| 21 |
HU J, SONG H, KARANFIL T .Comparative analysis of halonitromethane and trihalomethane formation and speciation in drinking water:the effects of disinfectants,pH,bromide,and nitrite[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2010,44(2):794-799.
|
| 22 |
陈新波 .水体中氨基酸氯化生成常规及碘代三卤甲烷的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学 2017.
|
| 23 |
YE T, XU B, LIN Y L,et al .Formation of iodinated disinfection by-products during oxidation of iodide-containing waters with chlorine dioxide[J].Water Research,2013,47(9):3006-3014.
|
| 24 |
LI C, LIN Q, DONG F,et al .Formation of iodinated trihalomethanes during chlorination of amino acid in waters[J].Chemosphere,2019,217:355-363.
|
| 25 |
HUA G H, RECKHOW D A, KIM J .Effect of bromide and iodide ions on the formation and speciation of disinfection byproducts during chlorination[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2006,40(9):3050-3056.
|
| 26 |
ZHANG T Y, XU B, HU C Y,et al .A comparison of iodinated trihalomethane formation from chlorine,chlorine dioxide and potassium permanganate oxidation processes[J].Water Research,2015,68:394-403,479.
|
| 27 |
LIU Z, LIN Y L, XU B,et al .Formation of iodinated trihalomethanes during breakpoint chlorination of iodide-containing water[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,353:505-513.
|
| 28 |
GAO Z C, LIN Y L, XU B,et al .Effect of bromide and iodide on halogenated by-product formation from different organic precursors during UV/chlorine processes[J].Water Research,2020,182:116035.
|
| 29 |
BOND T, HUANG J, GRAHAM N J D,et al .Examining the interrelationship between DOC,bromide and chlorine dose on DBP formation in drinking water - a case study[J].Science of the Total Environment,2014,470:469-479.
|
| 30 |
ZHANG K, PARKER K M .Halogen radical oxidants in natural and engineered aquatic systems[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(17):9579-9594.
|
| 31 |
ZHU X H, ZHANG X R .Modeling the formation of TOCl,TOBr and TOI during chlor(am)ination of drinking water[J].Water Research,2016,96:166-176.
|
| 32 |
TREHY M L, YOST R A, MILES C J .Chlorination byproducts of amino acids in natural waters[J].Environmental Science & Technology,1986,20(11):1117-1122.
|